Improvement of management tactics for pregnant women with cervical dysplasia, by correcting innate immunity indicators
Objective. To elaborate new approaches to therapy for cervical dysplasia in pregnant women, by correcting the expression of innate immunity factors.Dobrohotova Yu.E., Gankovskaya L.V., Borovkova E.I., Zalesskaya S.A., Svitich O.A., Filina A.B., Bistritskaya E.P., Zaidieva Z.S., Harutyunyan A.M., Stepanyants I.V.
Subjects and methods. A study group included 30 patients with cervical dysplasia [low-grade squamous epithelial lesion (LSIL) (43.33%) and high-grade squamous epithelial lesion HSIL (56.67%)]; a comparison group consisted of 11 patients without cervical disease. The patients’ age was 31.6 ± 1.7 years in the study group and 31.9 ± 2.2 years in the comparison group. Real-time PCR was used to investigate the expression of innate immunity factors (TNF-α, TLR9, TLR2, and HBD-1) in the cervical canal epithelium and in the vagina. The HPV titer was determined using the digene HPV test.
Results. During cytokine therapy, there were 1.2- and 1.8-fold reductions in the viral loads of HPV of Groups A9 and A7, respectively. There was a 2-fold increase in the expression of TNF-α and a 10-fold rise in that of NBD-1 and TLR9 and TLR2 in the cervical canal. In the vaginal epithelium, the level of TLR9 increased 5.3-fold.
Conclusion. The Syperlymph-induced change in the viral load correlates with innate immunity activation in both the cervical canal mucosa and the vagina due to the activation of the expression of the TLR2 and TLR9 genes and the effector molecules TNF-α and HBD-1.
Keywords
Malignant neoplasms are the second most common cause of death in women of reproductive age. During pregnancy, oncological diseases are diagnosed in 1 case per 1,000 patients and are most often represented by cervical, breast and thyroid cancer [1].
Incidence of cervical cancer amounts to 1.8-10.9 cases per 100,000 births and has no tendency to decrease. The cervical dysplasia prevalence increases annually both in the young patients’ population (up to 34 years) and among older women [2].
According to the conclusion of the international consensus, pregnancy is not a significant factor contributing to the disease progression and deterioration in the prognosis for a patient. A number of retrospective studies did not identify any difference in longevity of women with cervical cancer associated with pregnancy and with a disease identified outside gestation [3]. It was assumed that pregnancy-induced physiological cervix elongation helps to reduce the stromal invasion depth and slows down lymph nodes metastasis [4].
Dysplasia and cervical cancer are virus-associated diseases. Among etiopathogenetic factors involved in the given disease development, there are not only oncogenic human papilloma viruses (HPV), but also immunological factors [3].
It is known that skin and mucous membranes are the “entrance gate” for the infection caused by HPV. Primarily, virions contact the innate immunity receptors which are localized on epithelial cells and keratinocytes. In recent years, the role of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) has been actively studied [5]. TLR2 and TLR9 are distinguished among them; TLR2 identifies the virions surface structures, and the TLR9 endosomal receptors are capable of identifying HPV DNA. TLRs interaction with viral ligands leads to the activation of the whole cascade of signaling molecules; it results in the activation of a number of transcription factors and production of proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α). It is the activation of TLR-mediated reactions that appears to be one of the key moments in launching the innate immunity in response to a viral infection [6, 7, 8].
Another factor of innate immunity which provides antiviral protection of the mucous membranes is the antimicrobial peptides. HBD-1 (human beta defensin-1) is of particular interest, as it is expressed at a permanent level by keratinocytes and epithelial cells. A deficiency in this peptide production is directly related to the infectious processes development. In case of balanced operation of the innate immunity (recognizing receptors, proinflammatory link, direct antimicrobial protection), adaptive immunity activation occurs that results in the virus elimination from the body. In case of innate immunity factors insufficiency, infection chronicity and persistence occur [9, 10, 11].
The objective of the study was to develop new approaches to the treatment of cervical dysplasia in pregnant women by correcting the innate immunity factors expression.
Materials and methods
Prospective study included 41 patients: main group consisting of 30 pregnant women with cervical dysplasia and comparison group composed of 11 patients without cytological changes and HPV.
The patients were included according to the following criteria: 1) cervical dysplasia diagnosed on the basis of oncology and cytology smear results; 2) absence of sexually transmitted infections and inflammatory processes in the vagina; 3) women’s informed consent; 4) lack of hypersensitivity to proteins of porcine origin.
Conducted study design is presented in Figure 1.
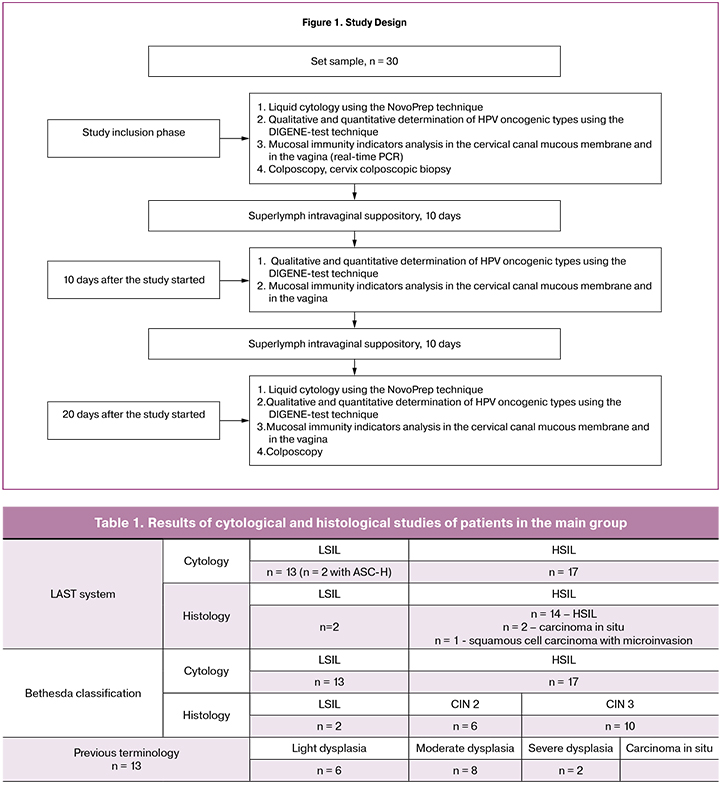
After the patients were included in the study, they were prescribed one Superlymph suppository (25 U) intravaginally for 20 days. The drug is a complex of natural antimicrobial peptides and cytokines which are universal stimulators of the immune system with an activity factor. This factor inhibits migration of macrophages, interleukin-1 and interleukin-6, as well as tumor necrosis factor which transforms the growth factor secreted by leukocytes of porcine peripheral blood (the preparation was developed at the Department of Immunology, N.I. Pirogov Russian National Research Medical University, Moscow).
Superlymph is an immunomodulator that has an antiviral and antimicrobial effect and stimulates functional activities of the phagocytic line of cells (monocytes and neutrophils): it activates phagocytosis and cytokine (IL-1 and TNF-α) production, induces antitumor cytotoxicity of macrophages, contributes to the elimination of intracellular parasites, regulates cells migration into the inflammation area and increases the natural killers’ activity. It also has antioxidant effect, reduces the inflammatory reactions development, and stimulates regeneration and epithelization of wound defects. According to the manufacturer’s instruction, Superlymph has no contraindications for use during pregnancy.
Cytological study was carried out twice: at the time a patient was included and after 20 days; it was performed using the NovoPrep liquid cytology technique. Totally, 60 studies were completed.
Qualitative and quantitative determination of the HPV oncogenic type was carried out using the DIGENE-test technique. Material sampling was performed by a cytologic brush from the cervical canal, at the stage when patients were included in the study, 10 and 20 days after the beginning of the treatment. A total of 90 samples were taken.
Study of innate immunity indicators included the determination of TLR9, TLR2 and HBD-1 gene expression and tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) determination in the cervical canal epithelial cells and in the posterior vaginal fornix. Real-time PCR technique was used. Material sampling was performed from the cervical canal by a cytologic brush (D1 type), and from the posterior vaginal fornix by a sterile gynecological tube (A type). Study of the innate immunity expression factors was carried out at the Department of Immunology, N.I. Pirogov Russian National Research Medical University, Moscow (Prof. L.V. Gankovskaya, Head of the Department). A total of 180 studies were performed. The systems for the immunity factors determination were carried out according to a standard approved technique [12].
In order to process the results, a non-parametric method of evaluation according to the Mann-Whitney criterion was used. All graphs and calculations were performed using the GraphPad Prism 6 and Microsoft Office Excel software programs. Results were considered reliable, when P ≤ 0.05.
Results
The patients’ age in the main group ranged from 20 to 41 years (31.6 ± 1.7) and in the comparison group (n = 11) it ranged from 18 to 45 years (31.9 ± 2.2). In the main group, most patients were multiparas (n = 20, 66.67%), 75% of them had 2-3 pregnancies in anamnesis, 25% of them had 4 or more pregnancies. Ten patients (50%) stated that they had artificial abortions in the past. In the comparison group, primigravidas composed 63.64% of the patients, and multiparas were 36.36% of the patients. Two women had artificial abortions in their case histories.
At the stage when patients were included into the study, in the main group five women had the first-trimester pregnancy (9-12 weeks, 16.67%), eleven patients were in the second-trimester (20-28 weeks, 36.67%) and fourteen patients were in the third trimester (29-38 weeks, 46.67%) of pregnancy. In the comparison group, the gestation period from 19 to 28 weeks was in six women (54.55%) and the gestation period from 28 to 35 weeks was in five patients (44.45%). Among pregnant women of the main group, thirteen patients (43.33%) were diagnosed with light cervical dysplasia (low-grade squamous epithelial lesion, LSIL), biopsy was not performed; in two of them (15.38%) there were atypical squamous cells (ASC-H) that could not exclude high grade lesion. In this regard, targeted biopsy of the cervix was performed, and the histological diagnosis coincided with the cytological one, CIN1 (LSIL).
Severe dysplasia (high grade squamous intraepithelial lesions, HSIL) was detected in seventeen patients (56.67%); and targeted colposcopic cervical biopsy was performed. Histological diagnosis corresponded to severe cervical dysplasia (CIN 2-3 or HSIL) in fourteen pregnant women. In three cases (17.65%) cervical cancer was diagnosed: two pregnant women had carcinoma in situ (after the course of therapy, cervix cone biopsy was performed); one patient had non-keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma with a 0.08 cm microinvasion (T1A1aN0M0 stage). After the conclusion of the interdisciplinary oncology council, it was decided to conduct a preplanned cesarean section at 38-39 weeks gestation followed by cervix amputation 3 weeks after delivery.
Table 1 presents the data on cytological and histological studies of the patients from the main group at the stage when they were included into the study.
In 100% of cases, HPV oncogenic type was detected in pregnant women with cervical dysplasia. Most frequently HPV from group A9 was detected (16, 31, 33, 35, 52 and 58 types): it was in twenty patients (66.67%). HPV from groups A5/A6 (51 and 56 types) was found in eleven women (36.67%) and A7 group (18, 39, 45, 59 and 68 types) in four pregnant women (13.33%). In most cases, the women were infected with HPV of one group; only in four cases (13.33%) combination of the virus from different groups was detected.
Quantitative evaluation of the viral load showed that prior to the treatment the viral titer from group A9 was 5.2±1.2 DNA Lg per 105 cells. After 10 days of therapy using Superlymph, the indicators decreased to 4.5±0.8 DNA Lg per 105 cells, and after 20 days of therapy it was 4.3±0.2 DNA Lg per 105 cells.
No alterations in the viral load were found in A5/A9 viral group: before the start of the treatment average values were 3.3±1.1 DNA Lg per 105 cells, after 10 days they were 3.4±0.9 DNA Lg per 105 cells and after 20 days they became 3.3±0.4 DNA Lg per 105 cells.
For A7 viral group, positive dynamics was noted with a significant decrease in the number of viral particles: before the start of the treatment it was 4.9±1.9 DNA Lg per 105 cells, after 10 days it became 4.4±1.3 DNA Lg per 105 cells and after 20 days it was 2.7±0.9 DNA Lg per 105 cells.
Thus, quantitative analysis of the viral load dynamics during the Superlymph therapy revealed its positive effect in decreasing the number of HPV of A9 group (16, 31, 33, 35, 52 and 58 types) by 1.2 times and viruses of A7 group (18, 39, 45, 59 and 68 types) by 1.8 times. No changes were observed in the 51 and 56 types viral titer. In the course of the treatment three patients had an increase in viral load in A5/A6 group from 4.7 to 6.4 DNA Lg per 105 cells.
After completing the course of the treatment, material sampling for cytological study was repeated; none of the thirty samples showed any progression of dysplasia. In eight cases (29.63%) positive changes in the results were registered: regression from HSIL to ASCUS was noted in one case, from HSIL to LSIL in two cases, from ASC-H to LSIL in one case, from ASC-H to ASCUS in one case, from LSIL to NILM in two cases and regression from HSIL to LSIL in one case. Cytological diagnosis of cervical dysplasia was abolished in two patients.
Since the HPV strains spectrum and viral load in patients with cervical dysplasia were different, it became necessary to study the immune factors that could affect the infectious process. In the present study, attention was focused on innate immunity whose mechanisms develop in response to a viral infection at the mucous membranes level. Four factors were identified that could provide information on the state of protective mechanisms: TLR2 (can identify HPV surface structures), TLR9 (identifies HPV), TNF-α (one of the key proinflammatory cytokines) and HBD-1 (defensin providing virus protection at the mucous membranes level). Epithelial cells were used as material for the study; they were taken from the mucous membranes of various localizations: the cervical canal and vagina.
Our research found that normal TLR2 expression was significantly higher (6 times) in the cervical canal epithelial cells than in the vaginal cells. At the same time, the TLR9 gene expression was different in the opposite direction. In the vagina, the expression level of the researched gene exceeded similar indicator in the cervical canal cells by 2.9 times. This could be explained by the fact that the cervical canal cells constantly contact pathogen (both bacterial and viral); there is a need in control by innate immunity which is carried out indirectly through TLR2. TLR9 is a more significant factor in defining a viral infection; therefore, its presence and quantity are extremely necessary in the vagina. TNF-α gene expression is also activated on pathogens that are localized in the vaginal cells. Production of beta defensin-1 is genetically mediated and constitutive; therefore, the expression indicator is not significantly different in epithelial cells of different localization.
When studying factors of innate immunity, the following patterns were identified. Tumor necrosis factor in patients with LSIL before the start of the therapy was 3 times higher than normal in the cervical canal and by 1.4 times in the vagina. In the course of the treatment, an increase in the TNF-α gene expression in the cervical canal was detected by 1.6 and 27 times from the initial level, after 10 and 20 days, respectively. In the vaginal epithelial cells, a slight decrease in gene expression was observed after 10 days of the treatment followed by an increase by almost 3 times on day 20 (Figure 1).
In pregnant women with HSIL, the gene expression of tumor necrosis factor in the cervical canal epithelium before treatment was 2.9 times higher than the normal indicators and continued to grow due to therapy by 1.7 and 1.9 times from the initial level. Prior to treatment, the gene level in the vagina was reduced by 1.4 times compared to the normal value, but in the course of the treatment with Superlymph preparation, the level increased by 6.7 times by the 20th day.
Before the treatment started, the patients with LSIL in the cervical canal had TLR9 gene expression exceeding the normal indicators by 3.8 times, and in the vagina, it corresponded to the comparison group indicators. Pregnant women with HSIL were characterized by the initial level of the cervical canal gene expression corresponding to normal; and in the vagina it was 3 times lower. TLR9 gene expression induction in the cervical canal was noted only in the patients with HSIL and was manifested by its 3-fold increase on the 10th day of the treatment accompanied by the same level to the 20th day of the therapy (Figure 2).

TLR9 expression increased by 3 times in the vagina fornix cells in patients with LSIL during the course of treatment with the Superlymph preparation. Prior to the treatment pregnant women with HSIL experienced the TLR9 gene expression reduction by 2 times compared to the normal indications; after taking the preparation a dramatic increase was noted by the 10th day which was accompanied by stabilization at the level of patients with LSIL by the 20th day.
Pregnant women with LSIL demonstrated that before starting the treatment TLR2 in the cervical canal and vagina exceeded normal indicators by 2 and 8 times, respectively, and after 20 days of the treatment it almost corresponded to the normal indicators. Patients with HSIL had the initial gene level below normal in the cervical canal, but it increased twice to the 20th day of treatment. TLR2 gene expression in the vagina increased by 3.8 times to the 10th day, and by 41 times from the initial level to the 20th day, i.e. 152 times higher than the normal indicators (Figure 3).
Before the treatment, the level of HBD-1 gene expression in patients of the main group was 3 or more times lower than normal indicators both in the cervical canal cells and in the vagina (regardless of the dysplasia severity). After the treatment in the cervical canal production of defensin gradually increased and reached the normal values to the 20th day (Figure 4).
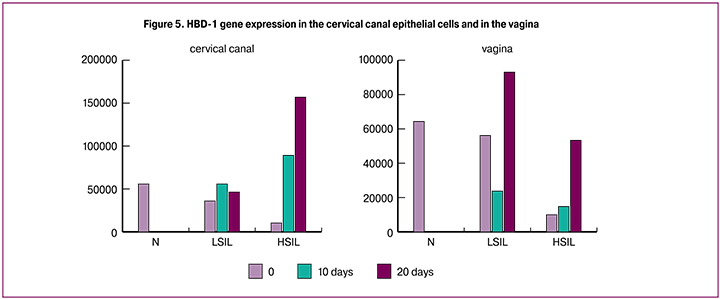
Prior to the treatment, defensin expression in the vaginal fornix cells was significantly reduced, normalization to the comparison group indicators was registered in pregnant women with LSIL by the 20th day. Patients with HSIL experienced slight increase in the expression level by the 10th day of the treatment, but by the 20th day the level almost reached the normal value.
When comparing viral load level and innate immunity indicators, we found out that patients with HPV (A9 group), whose viral load did not change during the whole course of the treatment, experienced a 2-fold increase in the cervical canal TNF-α expression (in regard to the comparison group) and remained stable. In women, whose viral load (A9 group HPV) was decreasing, the TNF-α level increased twice.
Correlation was established between the expression level of TLR9 receptor recognizing viral DNA and viral load level.
The TLR2 function is to identify the viral envelope proteins. Its expression increased by 5.5 times in pregnant women with cervical dysplasia and A9 group HPV leading to a significant reduction in viral load. In the vagina, similar dependence was found in most patients; it was manifested by a decrease in viral load accompanied by the TLR2 gene expression increase. Several pregnant women with A9 group HPV had the stable viral load titer which was accompanied by the sharp increase in the TLR2 receptors expression. Perhaps, the 20-day course of the treatment in their case was not enough to ensure decrease in the viral load.
HBD-1 is an antimicrobial peptide that is secreted by the epithelial cells of the mucous membrane and has direct antiviral, antibacterial and antifungal effect. It was found out that in patients with HBD-1 gene stable expression in the cervical canal there were no alterations and viral load. Using Superlymph in the vagina fornix cells led to the HBD-1 gene activation, while its expression increase by 2 times was not accompanied by decrease in the viral load, and an increase by 7 or more times led to significant decrease in A9 group HPV titer.
Conclusion
We confirmed the presence of oncogenic HPV types mainly of the A9 group (16, 31, 33, 35, 52 and 58 types) and in titer exceeding 3.5 DNA Lg per 105 cells in 100% of cases of cervical dysplasia. Innate immunity factors expression in pregnant women with cervical dysplasia differs from normal indicators and reflects intensity of antiviral protection factors both in the cervical canal epithelium and in the vagina. For most of the studied indicators, significant excess in the initial level of the gene expression was revealed. In the course of the treatment with Superlymph, in all samples (the cervical canal and vagina) regardless of dysplasia severity, we noted an increase in the expression of the genes that were responsible for viral DNA identification and cytokine production. During the treatment and increase in the genes expression regarding local immunity factors, there was a decrease in viral load and improvement in the results of cytological studies.
Gradual decrease in viral load was revealed in 90% of patients: decrease by 1.2 times for A9 group HPV (16, 31, 33, 35, 52 and 58 types) and by1.8 times for A7 group HPV (18, 39, 45, 59 and 68 types). After completing the course of the treatment, 29.63% of cases showed positive dynamics in the fluid cytology results followed by entire normalization in 7.4% of pregnant women. In the course of the treatment regarding cervical canal epithelium, a 2-fold increase in the tumor necrosis factor gene expression was observed in women with cervical dysplasia; the amount of antimicrobial HBD-1 gene and gene expression of identifying receptor of TLR9 and TLR2 increased by 10 or more times, which led to the decrease in the HPV titer. During the treatment in the vagina epithelium the HBD-1 gene expression increased regardless of the viral titer. Evident increase in the TNF-α gene expression was observed in comparison with that in the cervical canal, it did not depend on the viral load dynamics.
Thus, in most cases alteration in viral load was observed when using Superlymph; it correlated with the activation of the innate immunity indicators both in the cervical canal mucous membrane and in the vagina. Perhaps the Superlymph components activate expression of genes identifying innate immunity receptors (TLR2 and TLR9) and antiviral effector molecules (TNF-α and HBD-1 antimicrobial peptide). The consequence of the activation mechanisms of innate immunity is reduction in the viral load especially expressed in A9 group HPV.
References
1. Hatem A. Azim Jr., ed. Managing cancer during pregnancy. Springer; 2016. 191p.
2. Amant F., Halaska M.J., Fumagalli M., Dahl Steffensen K., Lok C., Van Calsteren K. et al. Gynecologic cancers in pregnancy: guideline of a second international consensus meeting. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer. 2014; 24(3): 394-403.
3. Tainio K., Athanasiou A., Tikkinen K.A.O., Aaltonen R., Hernándes J.C., Glazer-Livson S. et al. Clinical course of untreated cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2 under active surveillance: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2018; 360: k499.
4. Lee J.M., Lee K.B., Kim Y.T., Ryu H.S., Kim Y.T., Cho C.H. et al. Cervical cancer associated with pregnancy: results of a multicenter retrospective Korean study (KGOG-1006). Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2008; 198(1): 92. e1-6.
5. Wilt T.J., Harris R.P., Qaseem A.; High Value Care Task Force of the American College of Physicians. Screening for cancer: advice for high-value care from the American College of Physicians. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015; 162(10): 718-25.
6. Mishra B.B., Gundra U.M., Teale J.M. Expression and distribution of Toll-like receptors 11–13 in the brain during murine neurocysticercosis. J. Neuroinflammation. 2008; 5: 53.
7. McAllum B., Sykes P.H., Sadler L., Macnab H., Simcock B.J., Mekhail A.K. Is the treatment of CIN 2 always necessary in women under 25 years old? Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2011; 205(5): 478. e1-7.
8. Kawai T., Akira S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 2010; 11(5): 373-84.
9. Свитич О.А., Краснопрошина Л.И., Ганковская Л.В., Шибина Л.В., Зайцева И.А. Исследование изменения уровней экспрессии генов TLRs в эпителиальных клетках цервикального канала женщин с воспалительными заболеваниями органов малого таза. Медицинская иммунология. 2015; 17(3): 269-74. [Svitich O.A., Krasnoproshina L.I., Gankovskaya L.V., Shibina L.V., Zaitseva I.A. Investigation of changes in TLR gene expression levels in cervical canal epithelial cells in women with pelvic inflammatory diseases. Medical immunology. Medical immunology. 2015; 17(3): 269-74. (in Russian)]
Received 16.11.2018
Accepted 07.12.2018
About the Authors
Dobrohotova, Yulia E., MD, professor, head of the Department of obstetrics and gynecology of medical faculty Russian National Research Medical University namedafter N.I. Pirogov. 117997, Russia, Moscow, Ostrovitianov str. 1/9. Tel.: +74957226399. E-mail: pr.dobrohotova@mail.ru
Gankovskaya, Lyudmila V., MD, professor, Leader of Department of Immunology Russian National Research Medical University named after N.I. Pirogov.
117997, Russia, Moscow, Ostrovitianov str. 1/9. Tel.: +74854343165. E-mail: lvgan@yandex.ru
Borovkova, Ekaterina I., MD, professor, Department of obstetrics and gynecology of medical faculty Russian National Research Medical University named after N.I. Pirogov.
117997, Russia, Moscow, Ostrovitianov str. 1/9.Tel.: +79037855793. E-mail: katyanikitina@mail.ru
Zalesskaya, Sofia A., assistant Department of obstetrics and gynecology of medical faculty Russian National Research Medical University named after N.I. Pirogov.
117997, Russia, Moscow, Ostrovitianov str. 1/9. Tel.: +79670621312. E-mail: sofa.zalesskaya@mail.ru
Svitich, Оksana A., MD, corresponding member of Russian Academy of Sciences, Head of the Laboratory of Molecular Immunology Mechnikov Research Institute
of Vaccines and Sera, professor Department of Immunology Russian National Research Medical University named after N.I. Pirogov.
117997, Russia, Moscow, Ostrovitianov str. 1/9. Tel.: +79261488322. E-mail: svitichoa@yandex.ru
Filina, Аleksandra B., junior researcher of Laboratory of Molecular Immunology Mechnikov Research Institute of Vaccines and Sera.
105064, Russia, Moscow, Malyy Kazennyy per. 5A. Tel.: +79096915157. E-mail: byzonka@yandex.ru
Bistritskaya, Еlizaveta P., laboratory assistant researcher of Laboratory of Molecular Immunology Mechnikov Research Institute of Vaccines and Sera.
105064, Russia, Moscow, Malyy Kazennyy per. 5A. Tel.: +79151558618
Zaidieva, Zulya S., PhD, head of clinical diagnostic laboratory of the maternity hospital of city hospital №40.
129301, Russia, Moscow, Taymyrskaya str. 6. Tel.: +79037883995. E-mail: dr.zaydieva@mail.ru
Harutyunyan, Anna M., post-graduate student Department of obstetrics and gynecology of medical faculty Russian National Research Medical University named
after N.I. Pirogov. 117997, Russia, Moscow, Ostrovitianov str. 1/9. Tel.: +79166970554. E-mail: annochka21.90@mail.ru
Stepanyants, Irina V., obstetrician-gynecologist is a maternity city hospital №40.
129301, Russia, Moscow, Taymyrskaya str. 6. Tel.: +7 4956831570. E-mail: apoplexia@rambler.ru.
For citations Dobrohotova Yu.E., Gankovskaya L.V., Borovkova E.I., Zalesskaya S.A., Svitich O.A., Filina A.B., Bistritskaya E.P., Zaidieva Z.S.,. Harutyunyan A.M, Stepanyants I.V. Improvement of management tactics for pregnant women with cervical dysplasia, by correcting innate immunity indicators. Akusherstvo i Ginekologiya/Obstetrics and Gynecology. 2018; (12): 42-9. (in Russian)
http://dx.doi.org/10.18565/aig.2018.12.42-49



