Метод экстракорпорального оплодотворения (ЭКО) является наиболее распространенным в лечении бесплодия различного генеза. Последние десятилетия демонстрируют значительный прогресс развития метода ЭКО, а также увеличение доли успешных исходов. Качество эмбрионов является ключевым фактором, определяющим исход проведения программы ЭКО. При этом показатель частоты имплантации среди перенесенных эмбрионов часто не превышает 40% суммарно по всем возрастным группам пациентов [1]. До настоящего времени нерешенным остается вопрос стандартизации и унификации оценки эмбрионов человека, культивируемых in vitro. Существующие классификации, в частности Стамбульский консенсус 2011 г., упрощенно оценивают эмбрионы только морфологически без учета генетического, протеомного, метаболомного и других статусов. Именно разработка объективного метода оценки морфологии эмбрионов является задачей особой важности. В некоторых современных публикациях эмбриолога, проводящего визуальный анализ эмбриона, предлагается заменить на искусственный интеллект (ИИ), которому для оценки будут передаваться, например, изображения эмбрионов [2]. Совместно с молекулярными биологами разрабатываются неинвазивные тесты, которые могут дать информацию о метаболических или других параметрах жизнеспособности эмбриона [3, 4]. Именно такой совместный подход фундаментальной науки и клинической практики может дать самую оптимальную систему оценки эмбриона в программах лечения бесплодия методами вспомогательных репродуктивных технологий (ВРТ).
В настоящем обзоре проанализированы современные подходы к прогнозированию исходов программ ВРТ с применением различных неинвазивных молекулярно-биологических, физических и математических методов.
Оценка генетического статуса эмбриона по свободной ДНК в культуральной среде
С появлением преимплантационного генетического тестирования (ПГТ) как дополнительного метода диагностики качества эмбрионов показатели успешных исходов программ ВРТ увеличились. Однако наличие инвазивности метода, клеточного мозаицизма, случаев рождения генетически нормального ребенка после переноса анеуплоидного эмбриона [5] и, вероятно, выраженная способность эмбрионов к самокоррекции генетических ошибок на ранних стадиях развития требуют переоценки значимости ПГТ [6].
Обнаружение свободной внеклеточной ДНК (cfDNA) в среде культивирования эмбрионов стало значимым моментом для неинвазивной диагностики генетического статуса эмбрионов. Как ранее указывалось, ПГТ эмбрионов имеет ряд недостатков, что делает генетический анализ свободной эмбриональной ДНК потенциально полезным для оценки генетической конституции эмбрионов и предлагает альтернативу традиционному ПГТ.
В исследовании Rubio C. et al. на основании изучения 115 образцов культуральной среды эмбрионов и биопсии трофэктодермы приводятся выводы о потенциале cfDNA в отношении характеристики хромосомного статуса эмбриона [7]. В целом общий коэффициент соответствия плоидности и пола между результатами биопсии трофэктодермы и данными cfDNA среды культивирования составил 78,7%, а чувствительность и специфичность – 94,5% и 71,7% соответственно. Значительное увеличение всех данных показателей наблюдалось для образцов 6-го и 7-го дня по сравнению с образцами 5-го дня (общий коэффициент соответствия плоидности и пола составил 84%, а чувствительность и специфичность – 95,2% и 82,1% соответственно). Показатель имплантации эуплоидных эмбрионов по данным биопсии трофэктодермы и cfDNA среды культивирования был в 3 раза выше, чем у эмбрионов, эуплоидных по биопсии, но анеуплоидных по данным анализа cfDNA (52,9% против 16,7% соответственно).
В проспективном исследовании Yeung Q.S.Y. et al., где приводятся самые масштабные сведения по данной теме на сегодняшний день, на основании 48 циклов ПГТ на анеуплоидии (ПГТ-А) и 168 образцов культуральной среды эмбрионов продемонстрирована эффективность применения неинвазивного ПГТ-А (NiPGT-A) в оценке плоидности и пола эмбриона, а также в прогнозировании исхода переноса [8]. По данным ПГТ-А, 49 эмбрионов 5-х суток культивирования были эуплоидными (29,2%) и 119 – анеуплоидными (70,8%). Забор культуральной среды эмбрионов осуществлялся в день биопсии трофэктодермы. После процесса амплификации и фильтрации от образцов с недостаточным содержанием ДНК процессу секвенирования нового поколения подлежали только 116 проб. Показатели соответствия двух сравниваемых методов были рассчитаны с применением критерия χ2. Коэффициент полной конкордантности по аутосомам между результатами ПГТ-А и NiPGT-A составил 62,1% (72/116): 27 образцов среды культивирования (23,3%) показали абсолютно идентичные данным ПГТ-А результаты и 45 образцов (38,8%) демонстрировали частичное соответствие, то есть случаи, когда NiPGT-A определяло увеличение/уменьшение экспрессии какой-либо хромосомы или сегмента хромосомы, в то время как ПГТ-А идентифицировало потерю аналогичных хромосомы или сегмента (33 образца (73,3%)) или комплементарных хромосомы или сегмента (12 образцов (26,7%)). Показатель несоответствия между результатами ПГТ-А и NiPGT-A составил 37,9% (44 случая), из них ложноотрицательных (NiPGT-A определяет эмбрион как эуплоидный, в то время как ПГТ-А идентифицирует его анеуплоидный статус) – 16 случаев, ложноположительных (по данным NiPGT-A – анеуплоидия, по данным ПГТ-А – эуплоидия) – 15 случаев и 13 случаев диагностирования анеуплоидии эмбриона по данным ПГТ-А и NiPGT-A, но по совершенно разным хромосомам. Показатель соответствия данных ПГТ-А и NiPGT-A по половой принадлежности составил 82,4% (89/108): мужской генотип (XY) идентифицирован у 43 эмбрионов, женский (XX) – у 42, генотип Х0 определен у 4 эмбрионов. Морфологическая оценка эмбрионов также соотносилась с данными NiPGT-A и ПГТ-А. Из 116 образцов среды культивирования 63 (54,3%) соответствовали средам эмбрионов морфологически отличного и хорошего качества, 53 (45,7%) – эмбрионов плохого качества. Показатель соответствия плоидности и морфологии для эмбрионов отличного/хорошего и плохого качества составил 58,7% против 66,0%. Перенос 14 эуплоидных эмбрионов, по данным ПГТ-А, привел к 3 случаям живорождения, 3 случаям продолжающейся беременности и 5 случаям выкидыша. Очевидно, что к интерпретации результатов NiPGT-A стоит подходить осторожно, т.к. только в 1 из 5 случаев выкидыша было получено генетическое заключение о плоидности эмбриона, частично подтверждающее данные NiPGT-A, а перенос 2 из 7 анеуплоидных эмбрионов, по данным анализа свободной ДНК среды культивирования, привел к рождению здоровых детей. Однако, принимая во внимание феномен клеточного мозаицизма при проведении ПГТ-А, метод вполне претендует на существование, так как потенциально может более полно отразить генетическую конституцию эмбриона, о чем свидетельствуют его чувствительность и специфичность в оценке плоидности и половой принадлежности эмбриона: 81,6% и 48,3% соответственно. Прогностическая ценность положительного результата составила 82,6%, прогностическая ценность отрицательного результата – 46,7%.
В исследовании Jiao J. et al. результат генетического статуса эмбриона, по данным NiPGT, соотносится с результатами образцов биопсии его тканей и трофэктодермы [9]. Для 21 эмбриона от пар с нормальным кариотипом данные ПГТ-А образцов культуральной среды и биопсии трофэктодермы совпадали с результатами ПГТ-А образцов тканей эмбриона в 90% и 86% случаев соответственно, а в 76% случаев наблюдалось полное соответствие кариотипов. Для 41 эмбриона от пар с хромосомными перестройками в кариотипе показатели соответствия данных ПГТ-СП (структурные перестройки) образцов культуральной среды, биопсии трофэктодермы и результатов ПГТ-СП образцов тканей эмбриона составили 90% и 100% соответственно. Исследование выполнено при помощи гибридного линейного метода полногеномной гибридизации, что значительно ускорило процесс создания библиотеки данных и теоретически позволяет осуществлять перенос эмбрионов в стимулированном цикле без криоконсервации эмбрионов.
Проспективное многоцентровое исследование [10], проведенное десятью центрами ВРТ после того, как их эмбриологи прошли обучение и подтвердили свои результаты с использованием NiPGT-A, показало возможность обнаружения мозаицизма в эмбрионе по внеклеточной ДНК в культуральной среде. Согласно данным исследования, эуплоидные бластоцисты были диагностированы в 36,4% (80/220) случаев, анеуплоидия – в 31,3% (69/220) и мозаицизм – в 32,3% (71/220; анеуплоидия ≥60%). Значения мозаичности варьировались от 29,8% до 33,8% в разных возрастных группах. По отдельности наиболее частой хромосомной аномалией была XXY (синдром Клайнфельтера), встречающаяся в 18 случаях, за которой следовала аномалия хромосомы 21 (трисомия/моносомия) в 8 случаях. Данные NiPGT-A показали, что частота анеуплоидных клеток составляет ≥60% во всех случаях хромосомного мозаицизма. Это первое сообщение в научной литературе, которое связывает хромосомную плоидность в бластоцистах, проанализированную с помощью NiPGT-A, c увеличением возраста пациентов.
Суммарно на сегодняшний день можно говорить об эффективности применения метода NiPGT-A, который демонстрирует высокие показатели соответствия с результатами традиционного ПГТ-А. Однако остается до конца не решенной проблема ложноположительных результатов при контаминации среды культивирования материнской ДНК, а также вызывает опасения недостаточная численность выборки многих исследований.
Необходимо отметить, что даже при использовании NiPGT-A с ПГТ-А нет гарантий, что произойдет имплантация и наступит беременность, которая приведет к рождению здорового ребенка. Именно поэтому сохраняется необходимость в дополнительных подходах, прежде всего неинвазивных, способных рационально оценить не только генетический статус эмбриона, но и его метаболическую активность.
Данные приведенных выше исследований представлены в таблице 1.

Омиксные технологии при исследовании культуральных сред для прогнозирования исходов ЭКО
В связи с достаточно высокой информативностью изучения культуральных сред эмбрионов одним из перспективных направлений в поиске маркеров оценки качества эмбрионов с максимальной имплантационной способностью служит изучение молекулярных компонентов культуральных сред. Среда культивирования эмбрионов различных стадий развития – уникальный объект исследования, содержащий информацию об энергетической, метаболической активности и состоянии сигнальных систем конкретного эмбриона [11].
Множество работ было посвящено изучению взаимосвязи уровня митохондриальной ДНК эмбрионов с их качеством и имплантационным прогнозом. Оптимистичные предположения относительно эффективности метода постепенно приняли скептический характер, так как ранее большинство предпринятых попыток оценить потенциал эмбриона к развитию при количественном анализе митохондриальной ДНК эмбриона показали противоречивые результаты [12]. Однако, как показали модели исследования на животных, функционирование эмбриональной митохондрии, главной органеллы энергетического обмена, возможно оценить неинвазивно путем идентификации флавинадениндинуклеотида (FAD) и никотинамидаденинуклеотида (NADH) – коферментов, которые участвуют в многочисленных биохимических реакциях и играют центральную роль в окислительном фосфорилировании [13].
Большого внимания заслуживает изучение обнаруженных в культуральной среде эмбрионов некодирующих белок РНК (ncRNA) и их роли в процессах имплантации эмбриона и его нормального развития в связи с доказанным ранее их многофункциональным действием на транскрипционном и посттранскрипционном уровнях регуляции экспрессии генов [14]. В исследовании Ni M. et al. приведены данные о корреляции экспрессии определенных ncRNA с хромосомным статусом эмбриона, ранее установленным при помощи метода NGS. Было показано, что содержание miR-145 и miR-886-3p в средах культивирования эмбрионов с нормальным хромосомным набором было значительно ниже, чем в средах эмбрионов с хромосомными нарушениями [15]. Однако в другом исследовании, также посвященном поиску предиктора плоидности эмбрионов, значимых различий в структуре и количестве ncRNA, обнаруженных методом NGS и подтвержденных полимеразной цепной реакцией (ПЦР), в средах культивирования эуплоидных и анеуплоидных эмбрионов обнаружено не было. Предполагается, что идентифицированные ncRNA имеют неэмбриональное происхождение [16]. Исследование Abu-Halima M. et al. демонстрирует ассоциацию уровня экспрессии определенных ncRNA в средах культивирования эмбрионов и образцах спермы с морфологической оценкой эмбриона и положительным исходом беременности. Идентификация всей совокупности ncRNA в названных средах осуществлялась при помощи количественного профилирования и валидации ПЦР с обратной транскрипцией. Было установлено, что в средах культивирования морул класса G1 содержание miR-320a и miR-15a-5p было значительно выше по сравнению с образцами G2, а miR-21-5p экспрессировалась интенсивнее, чем в средах G3. В средах морул G2 уровень miR-20a-5p был выше, чем в средах G3. Низкое содержание miR-19b-3p как в средах культивирования, так и в образцах спермы коррелировало с успешным исходом беременности [17]. На основании результатов вышеперечисленных и многих других современных исследований вполне смело можно утверждать, что поиск биомаркера качества эмбриона и его имплантационного потенциала на основе транскриптомного анализа сред культивирования является многообещающим для репродуктивной медицины. Однако отсутствие понимания регуляции секреции ncRNA, а также стандартизированной оценки содержания данных молекул в различных средах исследования затрудняет внедрение метода в рутинную практику и требует проведения более масштабных исследований [18].
В настоящий момент активно набирает популярность анализ метаболизма эмбрионов, культивированных в условиях лаборатории, с использованием высокочувствительных методов для установления связи с морфологией, успешной имплантацией, развитием клинической беременности и рождением ребенка [19].
Метаболомика – относительно новая область науки, сочетающая в себе научные основы медицины, биохимии и молекулярной биологии. Данная технология не просто предоставляет качественную и количественную оценку метаболома единичной клетки или целого организма, но и отражает его функционирование и физиологию как результат динамического взаимодействия генома и окружающей среды в данный момент времени [20].
Множество исследований посвящено изучению метаболизма главных субстратов: аминокислот, глюкозы и пирувата при помощи точного обнаружения специфических молекул.
В исследовании Зориной И.М. и соавт. [3] был продемонстрирован профиль аминокислот, глюкозы и глутамата в средах культивирования в зависимости от качества эмбриона, его плоидности и показателей имплантации. Анализ питательных сред эмбрионов 5-х суток культивирования был проведен методом флуоресцентной фотометрии и высокоэффективной жидкостной хроматографии/масс-спектрометрии (ВЭЖХ/МС). Часть эмбрионов прошла ПГТ-А. Образцы были разделены на группы в соответствии с морфологической классификацией эмбрионов (по Гарднеру), данными ПГТ-А и результатами имплантации. Сравнительный анализ профилей сред в разных группах не выявил значимых различий между эуплоидными и анеуплоидными эмбрионами. В средах имплантировавшихся эмбрионов было отмечено понижение концентрации L-валина, L-пролина, аланил-глутамила, фенилпирувата и β-L-фукоза-1-фосфата и повышение содержания L-фенилаланина. Потребление глюкозы эмбрионами морфологически отличного качества на 5-е сутки было в 1,75 раза больше, чем у эмбрионов хорошего качества. Показатель потребления глюкозы эуплоидными эмбрионами 2,5 (2,0–3,4) нмоль был определен как предиктор успешной имплантации. В ранее опубликованной работе этих же авторов показано, что качественная оценка профилей отработанных сред культивирования эмбрионов 5-х суток развития свидетельствует о специфических для каждого морфологического класса профилях метаболитов (аминокислоты, пируват, глюкоза) [21].
Благодаря исследованию Ding J., Xu T. также удалось обнаружить, что эмбрионы морфологически высокого качества поглощают из культуральной среды большее количество триптофана, чем эмбрионы визуально плохого качества, что также может служить дополнительным маркером качества эмбриона на этапе селекции для переноса [22].
В 2008 г. в работе Seli E. et al. при анализе 34 образцов культуральных сред эмбрионов 3-х суток культивирования методом спектроскопии ядерного магнитного резонанса (ЯМР) была показана корреляция между содержанием глутамата, коэффициентом соотношения аланина к лактату, пирувата, глюкозы и наступлением беременности [23]. Было обнаружено, что в средах эмбрионов, перенос которых привел к развитию беременности (n=17), содержание глутамата было значительно выше, чем в средах эмбрионов, беременность в результате переноса которых не наступила (n=17). Использование метода обратной регрессии наименьших квадратов определило коэффициенты содержания глутамата и соотношения аланин/лактат в средах культивирования эмбрионов, успешно имплантировавшихся после переноса. На основании данных коэффициентов (глутамат, аланин/лактат) был рассчитан индекс жизнеспособности для каждого образца среды, который для успешно имплантировавшихся эмбрионов был достоверно выше (0,6201 и 0,1619 соответственно) по сравнению с теми, которые не смогли имплантироваться (0,3799 и 0,2660 соответственно) (Р<0,002). Исследование также сообщает об обнаруженной тенденции к снижению концентрации глюкозы и пирувата к 3-му дню культивирования в средах эмбрионов, перенос которых привел к развитию беременности. Эти данные не имели статистической значимости (ДИ=90%), но согласовывались с результатами предыдущих исследований. В целом, по данным исследования, метаболомное профилирование культуральных сред эмбрионов методом ЯМР имело чувствительность 88,2% и специфичность 88,2% в прогнозировании репродуктивного потенциала эмбриона.
Данные исследования Katz-Jaffe M.G. et al. указывают на существование различий в белковой экспрессии эмбрионов, культивированных до стадии бластоцисты [24]. Морфологически данные эмбрионы характеризовались как прогрессирующие (n=16, из которых ранних бластоцист – 6, поздних – 10) и дегенеративные (n=5). Анализ культуральной среды эмбрионов методом поверхностно-усиленной лазерной десорбционно-ионизационной времяпролетной масс-спектрометрии (SELDI TOF-MS) и обработка полученных кластеров при помощи непараметрического критерия Манна–Уитни выявили повышенную экспрессию 6 белков (P<0,01) и снижение синтеза еще нескольких (P≈0,05) в культуральной среде дегенеративных эмбрионов в сравнении с данными протеомного профиля среды культивирования прогрессирующих эмбрионов. При использовании инструментов TagIdent в базе данных Swiss-prot удалось предварительно идентифицировать данные белки и предположить, что в средах эмбрионов, остановившихся в развитии, повышена экспрессия белков-предшественников: гепаринсвязывающего эпидермального фактора роста (HB-EGF), цистатина-9 (CTS-9), каспазы-1 (CASP-1), ферментов – НАДН-дегидрогеназы (NDU), цитохром-С-оксидазы (CСО), белка – β-катенина (CTNNbIP1) и нейропептида – кокаин-и амфетамин-регулируемого транскрипта (CART). Примечательно, что развивающиеся бластоцисты, несмотря на идентичный морфологический статус, экспрессировали различный уровень аналогичных белков. Так, предполагается, что в поздних бластоцистах повышен синтез паратгормоноподобного пептида (PTHrP) и белка-ингибитора роста-1(ING1) в сравнении с белковым профилем ранних бластоцист (P<0,05). Исследование, несомненно, предлагает новый горизонт знаний о раннем развитии эмбриона и его репродуктивном потенциале, но все же требует подтверждения в виде проведения дополнительных, более масштабных, исследований с бо́льшим числом выборки.
В исследовании молекулярного состава культуральной среды эмбрионов человека 5-х суток культивирования Ambrou C.M. et al. показали значимость содержания в среде культивирования эмбрионов β-хорионического гонадотропина человека (hCGβ), интерлейкина-8 (IL-8) и фактора некроза опухоли-α (TNF-α) в прогнозировании наступления беременности [25]. Полученные сведения о концентрациях данных веществ сопоставлялись с морфологической оценкой эмбрионов. При помощи спектрометрии электрохимического импеданса удалось установить, что высокое содержание IL-8 и TNF-α в культуральной среде ассоциировалось с аномальным клеточным делением и гибелью клеток, соответственно. hCGβ определялся только в средах эмбрионов высокого качества, но интересным оказалось то, что не все культуральные среды эмбрионов с наилучшей морфологической оценкой содержали hCGβ. В дальнейшем у данных эмбрионов (в средах которых не определялся hCGβ) было отмечено развитие дефекта трофобласта, что влекло за собой нарушение в синтезе hCGβ. В исследовании Huang G. et al. подтверждается важность содержания IL-8 в культуральной среде эмбрионов как предиктора инвазии трофобласта [26].
Большой интерес для репродуктивной медицины представляет изучение растворимого человеческого лейкоцитарного антигена-G (sHLA-G). sHLA-G, продуцируемый клетками трофобласта, играет ключевую роль в формировании иммунологической толерантности на границе мать-плод, контролируя инвазию трофобласта и способствуя сосудистому ремоделированию спиральных артерий путем изменения цитокиновой секреции и супрессии Т-клеточного иммунитета [27]. В недавнем исследовании Díaz R.R. et al. [28] продемонстрирована положительная корреляция между содержанием sHLA-G в среде культивирования и показателем наступления беременности. Данные об уровне sHLA-G в образцах культуральных сред 86 эмбрионов 3-х суток культивирования были получены при помощи иммуноферментного анализа и проанализированы методом регрессионного анализа для группы женщин, у которых в результате переноса эмбрионов наступила беременность, и для женщин с отрицательным результатом переноса. Была обнаружена статистическая значимость между более высокими уровнями секреции sHLA-G и частотой наступления беременности для групп с положительным и отрицательным результатом переноса (28,0±18,8 ЕД/мл против 19,0±17,6 ЕД/мл, Р<0,005). Применение логистической модели частичного регрессионного анализа позволило определить отношение шансов для общего числа ооцитов – 1,074 (95% ДИ 1,017–1,11; Р=0,015) и для числа зрелых ооцитов (MII) – 1,65 (95% ДИ 1,015–1,106; Р=0,014). При сравнении полученных данных для группы с положительным и отрицательным результатами переноса отмечалось значительное различие по количеству полученных ооцитов (11±5 против 7±3 соответственно, Р=0,001), по числу зрелых ооцитов (MII) (10±4 против 7±3 соответственно, Р≤0,001). При сравнении данных о качестве перенесенных эмбрионов в группе с положительным и отрицательным результатами переноса не было выявлено значимых различий (1,7±0,47 против 1,5±0,48 соответственно; P=0,70). Тем не менее в группе с положительным результатом переноса отмечалось более высокое качество когорты эмбрионов по сравнению с отрицательной группой (3,8±5 против 2,4±1,3 соответственно; P=0,016).
Данные метаанализа, представленного Niu Z. et al., также демонстрируют корреляцию между содержанием sHLA-G в культуральной среде эмбрионов и показателями имплантации, клинической беременности, многоплодной беременности и невынашивания беременности [29]. При анализе данных в общей сложности 6170 случаев программ ЭКО/ИКСИ было показано, что перенос эмбрионов, в культуральной среде которых содержался sHLA-G, ассоциировался со значительно более высокими показателями имплантации и клинической беременности по сравнению с теми, в средах культивирования которых sHLA-G не был определен; отношения шансов (ORs) составили 2,66 (95% ДИ 1,75–4,06; P<0,00001), 3,79 (95% ДИ 2,69–5,33; P<0,00001) соответственно. Достоверного различия в частоте многоплодной беременности (ОRs 1,87; 95% ДИ 0,55–6,31) и выкидыша (ОРs 0,77; 95% ДИ 0,52–1,16) выявлено не было.
Важность исследования протеома культуральных сред эмбрионов человека находит подтверждение в исследовании Lindgren K.E. et al. [30], которые на основании молекулярного анализа образцов сред эмбрионов человека идентифицировали корреляцию между уровнем секретируемых эмбрионом специфических белков и его способностью к дальнейшему развитию. В исследовании при помощи мультиплексного анализа были оценены и сравнены между собой образцы культуральных сред эмбрионов, остановившихся в развитии, и тех, что благополучно были культивированы до 6-х суток. Данные молекулярного профиля были соотнесены с морфологической оценкой. В культуральной среде на 6-й день развития было обнаружено 9 белков, которые находились в более высокой концентрации, чем фоновые уровни в кондиционированной среде (т.е. в культуральной среде без эмбриона): сосудистый эндотелиальный фактор роста А (VEGF-A), интерлейкин-6 (IL-6), индуктор внеклеточной матриксной металлопротеиназы (EMMPRIN), плацентарный фактор роста (PlGF), цистатин B (CSTB), молекула клеточной адгезии эпителия (EpCAM), каспаза-3 (CASP3), эпидидимальный секреторный белок (HE-4) и интерлейкин-8 (IL-8). Ранее уже сообщалось о возможности использования CASP3 в качестве маркера в прогнозировании качества эмбриона и его имплантационного потенциала [31]. В данном исследовании уровни EMMPRIN и IL-6 были достоверно выше, а содержание CASP3 – ниже у развившихся в бластоцисты эмбрионов по сравнению с остановившимися в развитии (Р=0,003, 0,059, 0,076 соответственно). В культуральных средах эмбрионов морфологически высокого качества уровень CASP3 был достоверно ниже, а уровень VEGF-A – выше (P=0,052) по сравнению с таковым в средах эмбрионов с низкой оценкой морфологии (P=0,043). Это может свидетельствовать о том, что данные белки можно рассматривать как потенциальные маркеры успешного развития эмбриона. Уровни экспрессии PlGF, CSTВ, EpCAM, HE-4 и IL-8 не отличались существенно в средах эмбрионов как с низкой, так и с высокой морфологической оценкой. Тем не менее значимость их в развитии эмбриона человека известна [32]. Предполагают, что выявленный в данном исследовании PlGF играет аутокринную роль в функции трофобласта на ранних стадиях развития эмбриона, а также паракринную роль в последующем ангиогенезе в ходе имплантации и плацентации.
В настоящее время метаболомика располагает достаточным количеством технологических платформ для разделения и идентификации биомаркеров, но основными являются: газовая хроматография (ГХ-МС), капиллярный электрофорез (КЭ-МС), ВЭЖХ/МС, ЯМР, масс-анализатор ионно-циклотронного резонанса с преобразованием Фурье (МА-ИЦР-МС) [33]. Одним из перспективных методов изучения молекулярного профиля среды является метод фотонно-кристаллических волноводов (ФКВ). Метод уже успешно зарекомендовал себя в определении протеомного состава сложных сред, а полученные результаты продемонстрировали функциональность предложенного подхода [34].
Возможности спектроскопии для оценки метаболического статуса эмбриона человека in vitro
Несмотря на использование Рамановской спектрометрии в науке уже более двух десятков лет и значительные возможности в диагностике многих заболеваний, дороговизна метода и низкая чувствительность к малым концентрациям метаболитов долгое время оставались препятствием к широкому внедрению в практику репродуктивной медицины [35].
Недавнее исследование Liang B. et al. [36] продемонстрировало практическую ценность применения Рамановской спектрометрии в определении плоидности эмбрионов. При помощи метода были проанализированы 87 образцов культуральных сред от эмбрионов, которые также прошли ПГТ-А. Полученные данные выявили характерные различия в метаболомном профиле сред эуплоидных и анеуплоидных эмбрионов, спектральные кривые которых отличались по уровню содержания малых РНК и липидов. Показатель соответствия плоидности эмбрионов по данным спектрометрии и данным ПТГ-А составил 95,9%.
В исследовании Baştu E. et al. продемонстрирована возможность применения метода Рамановской спектрометрии в определении имплантационного потенциала эмбриона в дополнение к традиционной морфологической характеристике. При исследовании 31 образца отработанных культуральных сред эмбрионов 3-х суток развития были получены спектральные данные для группы эмбрионов, перенос которых привел к клинической беременности, и группы с отрицательным результатом переноса. В ходе проведения частотного анализа с применением U-критерия Манна–Уитни выяснилось, что диапазон спектральных кривых 890–950 см-1 содержит статистически значимые данные (P<0,5). Данный диапазон был проанализирован с применением метода главных компонент (PCA) и линейного дискриминантного анализа (QDA). Точность полученных данных была подтверждена применением ROC-кривой, специфичность и чувствительность которой в оценке точности PCA-QDA анализа составили 80,25% и 87,50% соответственно. По итогам проведения программы ЭКО у 15 пациенток из 31 была зафиксирована клиническая беременность, остальные 16 пациенток имели отрицательный результат переноса. При применении Рамановской спектрометрии прогнозирование наступления беременности соответствовало 93% всех положительных результатов (14 из 15), прогнозирование отрицательного результата программы ЭКО соответствовало 65,2% всех отрицательных результатов (10 из 16). Чувствительность и специфичность метода исследования составили 93% и 65,2% соответственно [37].
Многие методы анализа биологической среды, используемые сегодня, сложны в исполнении, требуют длительности по времени и часто не могут обеспечить истинности полученных данных [38]. Следовательно, возникает необходимость в создании и использовании простых, быстрых, но точных технологий. Одним из таких методов является матрично-активированная ионизация лазерной десорбции с применением времяпролетного масс-анализатора (MALDI ToF MS) [39, 40]. Данный метод был применен в оценке секретома среды культивирования и показал быстроту техники и значимость в прогнозировании жизнеспособности эмбриона и наступления беременности после переноса [41]. В данном исследовании было проанализировано 136 образцов культуральной среды эмбрионов 5-х суток культивирования непосредственно перед переносом. Объем каждого образца среды составил 50 мкл, однако в дальнейшем, в ходе непосредственного изучения образцов, потребовался всего 1 мкл смеси культуральной среды и дитиотреитола (DDT). Исходами в исследовании считался результат переноса: наступление (95 случаев) или отсутствие наступления беременности (41 случай). Исследование образцов методом MALDI ToF MS определило значимый для работы диапазон спектральных данных 2000–17 000 масса/заряд (m/z), при анализе которого было определено 150 пиков по 100 m/z каждый. Средние величины данных пиков, рассчитанные при помощи ROC-кривой, были различны для обеих групп исхода. Для каждого из 150 пиков был рассчитан относительный риск положительного исхода программы (наступление беременности). Затем при помощи многочисленных пиковых комбинирований была определена модель спектральной оценки, включающая 9 пиков с максимальной точностью прогнозирования положительного результата и положительной прогностической ценностью (P=0,0018; PPV=82,9%). Примечательно, что исследование образцов сред занимало не более 20 минут и осуществлялось непосредственно перед переносом, что существенно увеличивает шанс для переноса одного эмбриона, обладающего максимальным потенциалом к развитию.
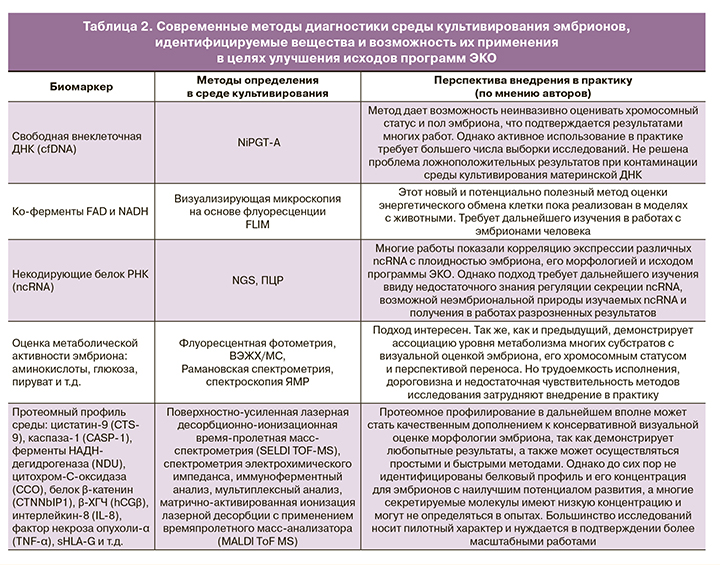
Перечисленные в статье подходы к исследованию сред культивирования эмбрионов в целях идентификации неинвазивного маркера их качества, имплантационной компетентности и успешного исхода программы ВРТ представлены в таблице 2.
Обработка спектральных характеристик с помощью машинного обучения
Очередным шагом для разработки более точного, безопасного и индивидуализированного предиктора исходов программы ВРТ стало внедрение в репродуктивную медицину технологий машинного обучения. Принцип работы машинного обучения базируется на методах ИИ, когда решение определенной задачи основывается не на прямом выводе, а на оценке библиотеки решений множества подобных задач. Эффективность применения ИИ в прогнозировании успешности исходов программ ВРТ была показана в результатах многих исследований. И, несмотря на определенные пока еще существующие препятствия (проблема «черного ящика», вероятность предвзятости системы), для более широкого внедрения в рутинную практику метод представляется крайне перспективным [42].
Более 20 лет назад Kaufmann S.J. et al. предложили использовать в программах ВРТ программное обеспечение Cortex Pro, созданное на основе нейронных сетей и состоящее только из четырех критериев оценки (число полученных ооцитов, возраст пациентки, число перенесенных эмбрионов, число замороженных эмбрионов). Точность программы составляла 59%. С тех пор был достигнут значительный прогресс в использования ИИ и машинного обучения в области репродукции человека [43].
Авторы из Японии Miyagi Y. et al. в 2019 г. опубликовали результаты работы по созданию системы, использующей машинное обучение и ИИ, которая с высокой точностью (до 67%) оценивает вероятность положительного исхода беременности по изображению бластоцисты. Они сравнили шесть методов машинного обучения, на основе лучшего из них – логистической регрессии с L2-регуляризацией – создали программу-классификатор, которая показывает вероятность живорождения эуплоидного эмбриона. Для обучения алгоритма использовалось по 80 изображений бластоцист, приведших к положительному и отрицательному исходу беременности [2, 44].
Значительный объем данных метаболомного профилирования биологических сред сегодня предоставляют такие аналитические платформы, как масс-спектрометрия и ее вариации (прямая (MS), жидкостная (LC-MS) или газовая (GC-MS)), капиллярный электрофорез (CE-MS), спектроскопия ядерного магнитного резонанса (NMR), рамановская спектрометрия. Для более качественной оценки среды разрабатываются новые многомерные системы разделения (комплексные двумерные GC или LC (GC×GC, LC×LC) или LC в сочетании со спектрометрией подвижности ионов (LC-IMS)). В целях автоматизированной и качественной обработки огромного количества комплексных исходных данных современные исследования, использующие данные методы, нуждаются в разработке и внедрении программного обеспечения с необходимыми этапами анализа спектральных данных. На первом этапе программной обработки спектральных данных происходят конвертирование исходных данных в матрицу открытых данных и их предварительная обработка для последующего анализа (поиск и сравнение/сопоставление спектров/признаков, выравнивание спектров/признаков с последующей сегментацией данных в ячейки или пиковой подгонкой, нормализация размера выборки, проверка одномерных гипотез, многовариантное моделирование и т.д.). Обработка спектральных данных, полученных при применении NMR, включает в себя, помимо перечисленного, элемент фазирования и базовой коррекции спектра. Далее следует этап обработки полученных данных статистическими методами (анализ главных компонент-дискриминантных функций (PC-DFA), метод Random forests, метод опорных векторов, дисперсионный анализ (ANOVA), t-критерий Стьюдента и их непараметрические эквиваленты). На третьем этапе осуществляются поиск и идентификация метаболитов в базе данных по физическим характеристикам (обычно недостаточным) – соотношению «масса/заряд», времени удержания, химическому сдвигу, интенсивности. Более точными параметрами поиска являются фрагментация моделей с последующим анализом при помощи вычислительного алгоритма и установление структуры de novo при комбинировании с данными NMR (1D или 2D).
Сегодня существует большое количество пакетов программного обеспечения для реализации исследований современной науки. Часть из них разработана и стандартизирована для решения определенных задач; например, идентификации малых молекул (CASMI (Critical Assessment of Small Molecule Identification, Schymanski and Neumann 2016)) или анализа протеомного состава среды (Ms-utils (ms-utils.org–Software List)), но большинство программ ориентировано на автоматизированную обработку метаболомного профиля биологических сред (MetaboAnalyst 3.0 (Xia et al., 2015), MAVEN (Melamud et al., 2010), MZmine 2 (Pluskal et al., 2010) и т.д.) [45].
Очевидно, что машинное обучение, несмотря на определенные недостатки, имеет огромный потенциал к расширению использования своих возможностей в будущем, предоставляя уже сейчас значительный объем новых научных данных. Кроме того, совершенствование и интеграция элементов ИИ, например, глубоких нейронных сетей, в процесс обработки улучшают качество экспериментальных данных, снижают частоту ложных идентификаций, способствуют постоянному пополнению библиотеки данных и, как следствие, делают машинное обучение более адаптированным к практике инструментом, предоставляющим обоснованные данные [46].
Заключение
Неудачные попытки ЭКО – это совокупность стечения многих факторов, в том числе и отсутствие точного метода диагностики качества эмбриона. Традиционная морфологическая характеристика эмбрионов, как и проведение ПГТ, демонстрируют ограниченность своих возможностей, инвазивные риски и остаются недостаточными в прогнозировании успешности исхода программы. Изучение молекулярного профиля культуральной среды является актуальным и перспективным направлением для идентификации неинвазивного показателя качества эмбриона.
С развитием омиксных технологий наметился прогресс в оценке качества переносимого эмбриона, а также в определении его репродуктивного потенциала. Исследование метаболома культуральных сред эмбрионов дает представление о процессах синтеза и распада специфических веществ и позволяет установить метаболомный профиль наиболее жизнеспособного эмбриона. Во многих работах подтверждена важность уровня концентрации энергетических субстратов и многочисленных белков, коррелирующих с морфологией эмбриона, его качеством и имплантационным потенциалом. Перспективным в данном вопросе представляется изучение эпигенетических регуляторов дифференцирования, пролиферации и межклеточного контакта – некодирующих белок РНК (ncRNA), а также главных коферментов энергетического обмена – NADH и FAD.
В перспективе повышение эффективности методов оценки молекулярного профиля культуральной среды эмбриона вкупе с более полной интеграцией полученных данных помогут преодолеть трудности широкого внедрения метода в клиническую практику и позволят повысить продуктивность селекции эмбрионов на этапе переноса. Это в конечном итоге позволит индивидуализировать подход к проведению программы ЭКО и увеличить успешные показатели исходов.



