Differentiated approaches to surgical correction of post-caesarean uterine scar niche
Bezhenar V.F., Grigorian A.E., Romanova M.L.
Objective: To evaluate the effectiveness of laparoscopic metroplasty with hysteroscopic assistance and laparoscopic metroplasty combined with transabdominal cerclage in correcting the post-caesarean uterine scar niche.
Materials and methods: This randomized controlled trial included 38 patients with a post-caesarean uterine scar niche. Group 1 comprised of 18 patients who underwent laparoscopic metroplasty with simultaneous hysteroscopy and transabdominal cerclage. Group 2 included 20 patients who underwent laparoscopic metroplasty with simultaneous hysteroscopy. Scar thickness was assessed before and six months after surgery using pelvic MRI data.
Results: Six months after surgery, the study group exhibited greater scar thickness (6.0 [4.0; 7.3] mm) than the control group (5.0 [4.0; 6.65] mm), as determined by pelvic MRI. MRI data revealed a significant change in scar thickness in both groups before and after laparoscopic metroplasty (p=0.0002 and p=0.0001, respectively). Following the surgical procedure, a notable reduction in the severity of clinical symptoms was observed. In group 1, the duration of postmenstrual bleeding decreased from 5 to 2 days, while in group 2, the duration decreased from 4 to 2 days. Prior to surgery, the mean dyspareunia score according to the visual analog scale (VAS) was 6 in group 1, decreasing to 4 postoperatively. In group 2, the mean score was 5, which decreased to 3 after the metroplasty. No complications were observed after surgery in any of the patient groups.
Conclusion: Laparoscopic correction of the post-caesarean uterine scar niche using both methods increased the thickness of the uterine scar and reduced the severity of the clinical symptoms associated with a thinned uterine scar.
Authors’ contributions: Bezhenar V.F. – conception and design of the study, drafting and editing of the manuscript; Grigorian A.E. – material collection and processing, statistical analysis, editing of the manuscript; Romanova M.L. – drafting and editing of the manuscript.
Conflicts of interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Funding: There was no funding for this study.
Ethical Approval: The study was reviewed and approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Pavlov First Saint Petersburg SMU, Ministry of Health of Russia.
Patient Consent for Publication: All patients provided informed consent for the publication of their data.
Authors' Data Sharing Statement: The data supporting the findings of this study are available upon request from the corresponding author after approval from the principal investigator.
For citation: Bezhenar V.F., Grigorian A.E., Romanova M.L. Differentiated approaches to
surgical correction of post-caesarean uterine scar niche.
Akusherstvo i Ginekologiya/Obstetrics and Gynecology. 2024; (11): 118-127 (in Russian)
Authors’ contributions: Bezhenar V.F. – conception and design of the study, drafting and editing of the manuscript; Grigorian A.E. – material collection and processing, statistical analysis, editing of the manuscript; Romanova M.L. – drafting and editing of the manuscript.
Conflicts of interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Funding: There was no funding for this study.
Ethical Approval: The study was reviewed and approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Pavlov First Saint Petersburg SMU, Ministry of Health of Russia.
Patient Consent for Publication: All patients provided informed consent for the publication of their data.
Authors' Data Sharing Statement: The data supporting the findings of this study are available upon request from the corresponding author after approval from the principal investigator.
For citation: Bezhenar V.F., Grigorian A.E., Romanova M.L. Differentiated approaches to
surgical correction of post-caesarean uterine scar niche.
Akusherstvo i Ginekologiya/Obstetrics and Gynecology. 2024; (11): 118-127 (in Russian)
https://dx.doi.org/10.18565/aig.2024.231
Keywords
The formation of a uterine scar niche after cesarean section (CS) is a common complication that affects a significant proportion of women post-surgery [1]. Localized thinning of the uterine scar following CS has been described in the literature under various terms, including niche, isthmocele, scar defect, incomplete uterine scar, and diverticulum [2–4]. A standardized definition of niche was proposed by a consensus group of European experts who also provided guidelines for detailed measurements to enable the uniform assessment of CS scars. According to this definition, a niche is an indentation at the site of a CS scar with a depth of at least 2 mm [5].
The most common clinical symptoms associated with a niche include intermenstrual and postmenstrual bleeding as well as heavy, prolonged, and painful menstruation. Postmenstrual bleeding is characterized by bleeding lasting more than two days, with a total menstrual duration exceeding seven days [6]. Additionally, 18% of patients with a niche experience dyspareunia, 35% report chronic pelvic pain syndrome, and many develop secondary infertility [4, 7]. Studies indicate that secondary infertility related to a niche is diagnosed in 10–40% of cases, after ruling out other causes of decreased fertility. Factors contributing to secondary infertility include accumulation of blood and mucus within the niche, leading to reactive inflammation, impaired sperm motility, and subsequent disruption of the implantation process [8].
Beyond these clinical manifestations, a thinned uterine scar poses a heightened risk of complications during pregnancy and childbirth, such as abnormal placentation, ectopic pregnancy within the scar area, and incomplete or complete uterine rupture [9]. Recently, attention has shifted not only toward preventing complications during subsequent pregnancies, but also toward assessing quality of life and the impact of niche-related symptoms on patients' daily activities. A recent prospective study involving patients with a scar niche revealed decreased quality of life and social activity with significant improvements following surgical intervention [10].
With the global rise in CSs and increasing awareness of the clinical implications of scar niches, there is a corresponding expansion in diagnostic and treatment options for thinned uterine scars. Common surgical methods for niche correction include hysteroscopic and laparoscopic techniques [3, 11]. However, the persistent recurrence rate after metroplasty, along with the widespread prevalence of CS, underscores the need to explore new approaches for scar defect correction.
This article compares the efficacy of two laparoscopic metroplasty techniques in terms of niche-associated symptoms and scar thickness, as measured using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the pelvic organs.
This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of laparoscopic metroplasty with hysteroscopic assistance versus laparoscopic metroplasty supplemented by transabdominal cerclage for correcting the post-cesarean uterine scar niche.
Materials and methods
Study design
This randomized controlled trial aimed to evaluate the efficacy of laparoscopic correction of the uterine scar niche after cesarean section (CS). This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Pavlov First Saint Petersburg SMU of Minzdrav, Russia. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to their inclusion in the study. In the prehospital stage, all patients underwent standard clinical and laboratory examinations.
Study participants and main criteria for participation
The study included patients aged 18–45 years with reproductive plans and the presence of a scar niche after CS, confirmed by contrast pelvic MRI, with a residual myometrium thickness of less than 3 mm. Exclusion criteria included a history of fundal and corporal CS, pregnancy at the time of inclusion in the study, presence of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs in the acute stage, malignant neoplasms, and severe somatic comorbidities that would exclude laparoscopic surgery.
Surgical treatment, randomization, and blinding
Participants were randomly assigned to two groups using the envelope method. Group 1 (study group, n=18) underwent laparoscopic metroplasty with simultaneous hysteroscopy and transabdominal cerclage [12]. In group 2 (control group, n=20), laparoscopic metroplasty with simultaneous hysteroscopy was performed.
Blinding was not performed in the present study. The surgeon, medical staff, researchers, and study participants were not blinded to allocation.
The surgery consisted of the following stages.
Stage 1. The peritoneum and vesicouterine fold are opened using Lotus ultrasonic scissors (Bowa, Germany). The bladder is then separated downwards, allowing the visualization of the scar area (Fig. 1).
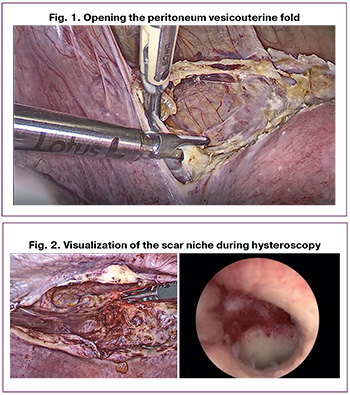
Stage 2. A hysteroscope is inserted into the uterine cavity to visualize the scar niche (Fig. 2).
Stage 3. During laparoscopic diaphanoscopy in a "dark field," the niche is clearly visualized. Without turning on the illumination in the abdominal cavity, the myometrium is opened at the thinnest part of the scar (Fig. 3, 4). A Hegar dilator No. 5 is inserted into the resulting defect, and the edges of the niche are excised with sharp scissors, avoiding the use of electrosurgery.
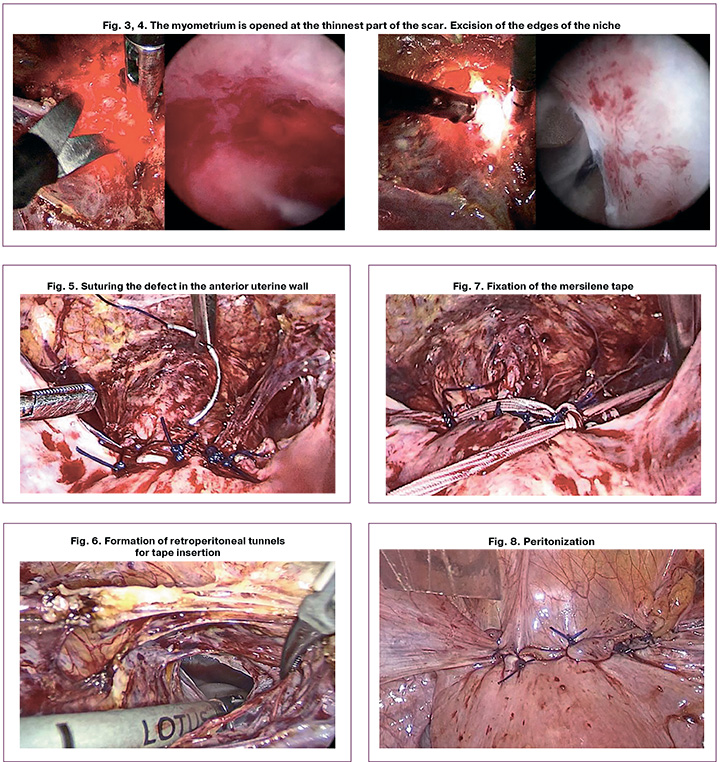
Stage 4. The defect in the anterior wall of the uterus is sutured in two rows. For the first row, synthetic suture material PDS Plus 0 (CT 40 mm, 1/2c, Ethicon) is used, and three separate sutures are applied to capture both the mucous and muscular layers (Fig. 5). In the second row, Monocryl Plus 0 (CT 40 mm, 1/2c, Ethicon) suture material is used, with Z-shaped interrupted muscular-serous sutures applied for layer-by-layer tissue alignment.
Stage 5. Transabdominal cerclage is applied. At the level of the internal os, Mersilene tape (5 mm, BP-1 65 mm 1/2c, Ethicon) without needles, measuring 40 cm long and 5 mm wide, is inserted. The tape is threaded through the created retroperitoneal tunnels, moving from the back to the front, lateral to the uterine vessels at the level of the internal os, with mandatory visualization of the ureters (Fig. 6, 7).
Stage 6. Peritonization is performed using a vesicouterine fold (Fig. 8).
A detailed description of the surgical technique is provided in the patent for invention dated 12/11/2023 No. 2023132595/14 (071930), titled "Method for surgical treatment of local thinning of the uterine scar with the formation of a niche after CS surgery" [12].
In the control group, patients underwent laparoscopic metroplasty with hysteroscopy. The surgical technique corresponded to the four stages described above.
Endpoints
The primary endpoint was the change in residual myometrium thickness six months after surgery, as assessed by MRI of the pelvic organs with contrast in both the study and control groups.
Secondary endpoints included the assessment of the severity of clinical symptoms, surgery time, blood loss, length of hospitalization, and intraoperative and postoperative complications.
Statistical analysis and sample size calculation
Based on the anticipated intergroup difference in myometrial thickness changes of 1 mm, standard deviation of 1.5, alpha error of 0.05, and power of 80%, the final sample size was determined to be 74 patients (37 patients in each group). This study presents the results of the recruitment phase, which reached the point where 50% of the expected sample has been enrolled.
The study tested the statistical hypothesis of the superiority of the study method over the control for the primary endpoint, which was the change in residual myometrial thickness six months after surgery according to MRI of the pelvic organs. An efficiency analysis was conducted on all randomized participants who underwent surgery. The study population complied with the intention-to-treat analysis. Qualitative variables are presented in frequency and contingency tables. Continuous variables were described using the median (Me), 25th, and 75th quantiles (Q1; Q3). The normality of continuous variables was evaluated using the Shapiro-Wilk test. The distribution was considered to deviate from normal at a significance level of 0.05. Owing to the limited number of observations in the groups (n<25), nonparametric criteria were employed to test the hypotheses. These included Pearson's χ2 test, Fisher's exact test for qualitative data, and the Mann–Whitney U test for comparing groups based on continuous variables, as well as the Wilcoxon test for paired samples to analyze changes in continuous variables before and after surgery. Data were analyzed using Statistica 10.0.
Results
Distribution of study participants
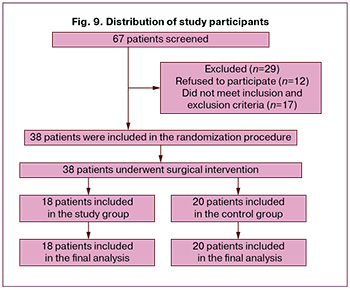
From September 2022 to March 2024, 67 patients aged 26–43 years with a post-cesarean scar niche were screened for surgical treatment. After randomization, 18 patients who underwent laparoscopic metroplasty with simultaneous hysteroscopy and transabdominal cerclage were included in group 1. The control group, which did not undergo transabdominal cerclage, consisted of 20 patients. The final distribution of study participants and reasons for dropout are shown in Figure 9.
Baseline demographic characteristics
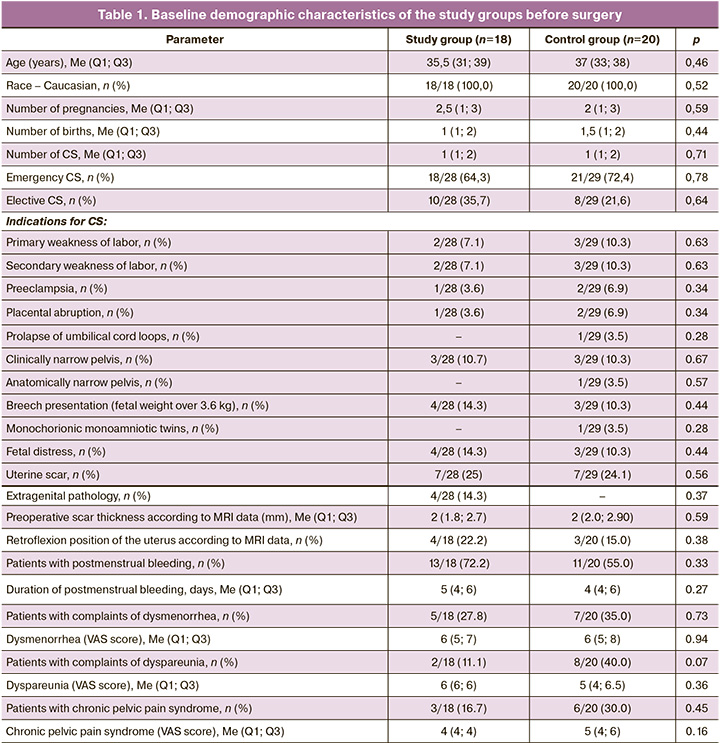
Baseline demographic characteristics of the study groups are presented in Table 1. The median age of patients was 35.5 (31; 39) years in the study group and 37 (33; 38) years in the control group. No statistically significant differences in age were found between groups (U=154.0, p=0.46). In the study group, 13/18 patients (72.2%) had one cesarean section (CS), 1/18 (5.6%) had two CSs, 3/18 (16.7%) had three CSs, and 1/18 (5.6%) had four CSs. In the control group, 11/20 (55.0%) patients had one CS, whereas 9/20 (45.0%) had two CSs in their medical history. No statistically significant differences were observed in these parameters (U=167.0, p=0.71). In the study group, 18/28 (64.3%) patients underwent emergency CS; in the control group, emergency CS was performed in 21 out of 29 women (72.4%). No statistically significant differences were observed (χ²=0.082, p=0.78).
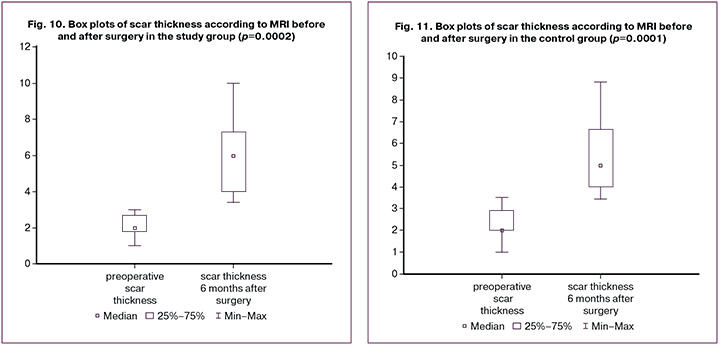
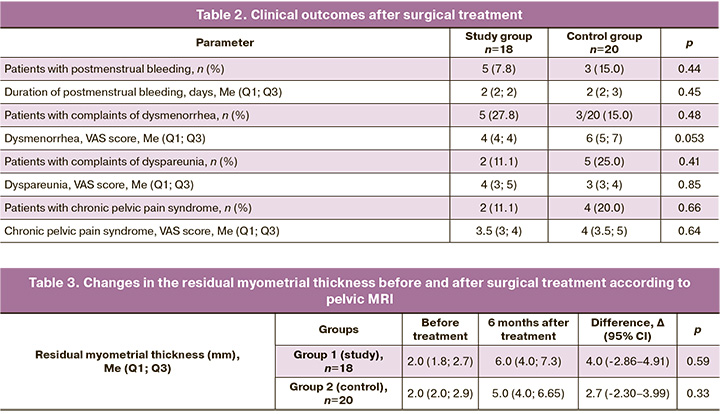
Preoperative scar thickness according to MRI was normally distributed (p=0.053), whereas other variables exhibited a distribution different from normal (p=0.047) according to the Shapiro–Wilk test. In the study group, the median scar thickness before surgery was 2.0 (1.8; 2.7) mm, 6 months post-surgery, it increased to 6.0 (4.0; 7.3) mm. When analyzed using Wilcoxon test, these differences were statistically significant (T (n=18) = 0.0, p=0.0002). In the control group, the median scar thickness before surgery was 2.0 (2.0; 2.9) mm, and after surgery, it was 5.0 (4.0; 6.65) mm; these differences were also statistically significant (T (n=20)=0.0, p=0.0001). This is further illustrated in the box plots (Fig. 10, 11). The median scar thickness at six months after surgery was 6.0 (4.0; 7.3) mm in the study group and 5.0 (4.0; 6.65) mm in the control group, with no statistically significant differences (U=146.5, p=0.33). There were also no statistically significant differences in thickness delta between the groups (U=146.0, p=0.33).
Before surgery, 13/18 (72.2%) patients in the study group and 11/20 (55.0%) in the control group complained of spotting postmenstrual bleeding, which did not differ significantly (Pearson χ2, p=0.33). In symptomatic patients, the duration of post-menstrual bleeding before surgery was 5 (4; 6) days in the study group and 4 (4; 6) days in the control group (U=52.0, p=0.27). After surgery, 5/18 (7.8%) patients in the study group reported spotting and postmenstrual bloody discharge from the genital tract, compared to 3/20 (15.0%) in the control group. The groups did not differ significantly in this regard (p=0.44). The median duration of post-menstrual bloody discharge was 2 (2; 2) days in the study group and 2 (2; 3) days in the control group (Mann–Whitney U-test = 5.5, p = 0.45). Before surgery, 5 /18 (27.8%) patients in the study group and 7/20 (35.0%) in the control group reported dysmenorrhea, with no significant difference between the groups using Fisher's exact test (p=0.73). The median dysmenorrhea score according to the VAS in the study group was 6 (5; 7), while that in the control group was 6 (5; 8) (U=16.5, p=0.94). After surgery, 5/18 (27.8%) patients in the study group and 3/20 (15.0%) patients in the control group reported dysmenorrhea; however, the groups did not differ significantly according to this measure using Fisher's exact test (p=0.48). The median dysmenorrhea score according to the VAS in the study group after the operation was 4 (4; 4), compared to 6 (5; 7) in the control group (U=0.5, p=0.053).
Before the operation, 2/18 (11.1%) patients in the study group and 8/20 (40.0 %) in the control group reported dyspareunia; this difference was not statistically significant according to Fisher's exact test (p=0.07). The median dyspareunia score according to the VAS prior to surgery was 6 (6; 6) in the study group and 5 (4, 6.5) in the control group (U=4.0, p=0.36). After the operation, 2/18 (11.1%) patients in the study group and 5/20 (25.0%) patients in the control group reported dyspareunia, with no significant difference between the groups using Fisher's exact test (p=0.41). The median dyspareunia score according to the VAS after surgery was 4 (3; 5) in the study group and 3 (3; 4) in the control group (U=4.0, p=0.85).
Before surgery, 3/18 (16.7%) patients had chronic pelvic pain syndrome in the study group, compared to 6/20 (30.0%) in the control group, and there was no significant difference between the groups using Fisher's exact test (p=0.45). The median chronic pelvic pain syndrome score according to the VAS prior to surgery was 4 (4; 4) in the study group and 5 (4; 6) in the control group (U=3.0, p=0.16). After the surgery, there were 2/18 (11.1%) patients in the study group and 4/20 (20.0%) in the control group had chronic pelvic pain syndrome, with no significant difference between the groups using Fisher's exact test (p=0.66). The median chronic pelvic pain syndrome VAS score following surgery was 3.5 (3; 4) in the study group and 4 (3.5; 5) in the control group (U=2.5, p=0.64) (Tabl. 2).
There was no statistically significant difference in the duration of the surgery: the average duration was 95 (85; 110) minutes in the study group and 87.5 (60; 110) minutes in the control group (U=144, p=0.30). The average blood loss was 100 (70–100) ml in the study group and 85 (70–100) ml in the control group (U=161, p=0.59). No significant differences were found between the groups in the number of postoperative hospital days; both groups had a median of 5 (4–6) days (U=152, p=0.43). No complications were noted intraoperatively or during the early postoperative period.
Data on the thickness of the residual myometrium before surgery and six months after laparoscopic metroplasty, categorized by group, are presented in Table 3. To assess the changes in these parameters, the delta indicator was calculated based on the scar thickness values before and after surgical intervention.
Discussion
In most cases, the postoperative cesarean scar niche is asymptomatic. Various treatment options are available for patients with clinical symptoms, as well as those preparing for pregnancy, to help alleviate symptoms and improve reproductive outcomes [13]. Conservative treatment with hormone-modulating drugs is the first-line therapy for patients with heavy and prolonged menstruation or postmenstrual bleeding. The use of combined oral contraceptives has been shown to significantly reduce these symptoms [14]. However, when comparing conservative therapy with minimally invasive surgical treatments, a more pronounced reduction in the postmenstrual discharge duration was observed in patients undergoing hysteroscopic metroplasty [15]. This minimally invasive procedure is recommended for symptomatic patients who do not plan future pregnancies. According to various studies, a minimum scar thickness of 2 to 3 mm is recommended for safe hysteroscopy [16, 17].
Several surgical techniques have been described, including resection of only the proximal or distal edges or resection of both edges with coagulation of dilated vessels at the niche base [18]. Many authors have highlighted that while the edges of the niche become smoother following hysteroscopy, scar thickness does not necessarily increase [16]. However, Casadio et al. observed an increase in residual myometrial thickness after hysteroscopy, which can be attributed to smooth muscle fiber contraction after defect correction [19]. For patients with reproductive plans and a scar thickness of <3 mm, as determined by ultrasound or MRI during pre-pregnancy preparation, scar niche correction is recommended. Several metroplasty approaches are available, including laparoscopic, laparotomic, vaginal, and robotic [20]. Vaginal metroplasty is commonly performed to correct thinned scars with niche formation. According to several studies, residual myometrial thickness improved from <3 mm to an average of 5.6±2.0 mm and 6.1±1.43 mm, respectively, following correction [21, 22]. In contrast, studies examining niche correction via laparotomy are limited; this method is associated with a higher risk of complications and a longer recovery period than less invasive approaches [23].
Robotic surgery offers advantages, such as enhanced three-dimensional visualization and increased precision during manipulation. A systematic review found that robot-assisted surgery provides excellent control and visualization in correcting cesarean scar defects, with minimal complications and favorable reproductive outcomes [24]. Unlike hysteroscopy alone, laparoscopy not only remodels the scar niche, but also aims to increase scar thickness, correct uterine retroflexion, and address concomitant gynecological conditions [25].
Various methods for identifying localized thinning of the uterine scar have been proposed. One approach involves one-stage hysteroscopy, which visualizes the thinnest part of the scar using diaphanoscopy [26]. Other authors have suggested the intraoperative use of a Foley catheter to delineate defect boundaries more accurately [27]. Laparoscopic visualization of the scar niche can also be enhanced with intrauterine administration of an indocyanine green solution, allowing precise identification of the resection line without excessive tissue dissection [28]. To optimize myometrial suturing, an intrauterine manipulator with a groove can be used to create an optimal angle for suturing [29].
Uterine retroflexion is a known risk factor for scar niche formation. Consequently, a combined surgical technique has been proposed involving correction of pathological retroflexion through plication of the round ligaments, which has been shown to improve tissue repair postoperatively [30]. Double-layer suturing is preferred for defect repair by most authors. This technique involves suturing two-thirds of the myometrium in the first layer, followed by closure of the remaining third along with the serous membrane in the second layer [13, 30].
According to various studies, clinical symptoms decrease in 79.2–92.7% of patients following surgical treatment. Nonetheless, some patients continue to experience chronic pelvic pain and dysmenorrhea after cesarean scar niche correction, as observed in our study. These symptoms may result from concurrent gynecological conditions such as endometriosis and uterine fibroids, which can contribute to persistent complaints [13, 20]. Findings from a prospective study by Vervoort et al. align with our results, demonstrating a reduction in postmenstrual discharge from 9 to 2 days and an increase in scar thickness from 1.2 mm to 5.3 mm (p<0.01) post-surgery [13]. Similar outcomes were noted when comparing two laparoscopic niche correction techniques, with and without scar edge resection, which showed an increase in residual myometrial thickness to 6 mm, with no significant difference between the groups [31]. These findings indicate that laparoscopic metroplasty is an effective method for correcting cesarean scar niches. However, the choice of surgical method should be tailored to each clinical situation, as scar niche recurrence remains a notable clinical challenge that necessitates further refinement of existing correction techniques for thinned scars [32].
Despite the randomized design, our study has several limitations, including its single-center setting, which may restrict the generalizability of the results, lack of blinding, absence of reproductive and obstetric outcome assessments due to short follow-up duration, and a small sample size. Further studies with larger cohorts are required to confirm our findings.
Conclusion
Cesarean scar niches are increasingly recognized as a common issue among reproductive-age patients and frequently result in outpatient visits, significantly affecting quality of life. Various surgical approaches have been developed to address these complications. In particular, laparoscopic metroplasty has shown promising results in increasing scar thickness, as evidenced by pelvic MRI findings, and in reducing symptom severity at six months post-surgery. Nevertheless, further studies are needed to evaluate the long-term surgical outcomes by including more patients in prospective trials.
References
- Tsuji S., Nobuta Y., Hanada T., Takebayashi A., Inatomi A., Takahashi A. et al. Prevalence, definition, and etiology of cesarean scar defect and treatment of cesarean scar disorder: A narrative review. Reprod. Med. Biol. 2023; 22(1): e12532. https://dx.doi.org/10.1002/rmb2.12532.
- Мартынов С.А., Адамян Л.В. Рубец на матке после кесарева сечения: терминологические аспекты. Гинекология. 2020; 22(5): 70-5. [Martynov S.A., Adamyan L.V. Cesarean scar defect: terminological aspects. Gynecology. 2020; 22(5):70-5. (in Russian)]. https://dx.doi.org/10.26442/20795696.2020.5.200415.
- Donnez O. Cesarean scar defects: Management of an iatrogenic pathology whose prevalence has dramatically increased. Fertil. Steril. 2020; 113(4): 704-16. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2020.01.037.
- Klein Meuleman S.J.M., Min N., Hehenkamp W.J.K., Post Uiterweer E.D., Huirne J.A.F., de Leeuw R.A. The definition, diagnosis, and symptoms of the uterine niche – a systematic review. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2023; 90: 102390. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2023.102390.
- Jordans I.P.M., de Leeuw R.A., Stegwee S.I., Amso N.N., Barri-Soldevila P.N., van den Bosch T. et al. Sonographic examination of uterine niche in non‐pregnant women: A modified Delphi Procedure. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2019; 53(1): 107-15. https://dx.doi.org/10.1002/uog.19049.
- Antila R.M., Mäenpää J.U., Huhtala H.S., Tomás E.I., Staff S.M. Association of cesarean scar defect with abnormal uterine bleeding: The results of a prospective study. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2020; 244:134-40. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2019.11.021.
- Zakherah M., Mohamed A.A., Rageh A.M., Abdel-Aleem M. Navigating uterine niche 360 degree: a narrative review. Middle East Fertility Society Journal. 2024; 29(1). https://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s43043-024-00185-7.
- Vissers J., Hehenkamp W., Lambalk C.B., Huirne J.A. Post-caesarean section niche-related impaired fertility: hypothetical mechanisms. Hum. Reprod. 2020; 35(7): 1484-94. https://dx.doi.org/10.1093/humrep/deaa094.
- Kremer T.G., Ghiorzi I.B., Dibi R.P. Isthmocele: An overview of diagnosis and treatment. Revista da Associação Médica Brasileira. 2019; 65(5): 714-21. https://dx.doi.org/10.1590/1806-9282.65.5.714.
- Stegwee S.I., Hehenkamp W.J.K., de Leeuw R.A., de Groot C.J.M.,Huirne J.A.F. Improved health-related quality of life in the first year after laparoscopic niche resection: A prospective cohort study. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2020; 245: 174-80. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2020.01.003.
- Armstrong F., Mulligan K., Dermott R.M., Bartels H.C., Carroll S., Robson M.et al. Cesarean scar niche: An evolving concern in clinical practice. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2022; 161(2): 356-66. https://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijgo.14509.
- Беженарь В.Ф., Трофимова Т.Н., Григорян А.Э., Кошелев Т.Е. Способ хирургического лечения локального истончения рубца на матке с формированием «ниши» после операции кесарева сечения. Патент №2823054 РФ; Заявл.11.12.2023; Опубл. 17.07.2024. [Bezhenar V.F., Trofimova T.N., Grigoryan A.E., Koshelev T.E. A method of surgical treatment of local thinning of the scar on the uterus with the formation of a "niche" after cesarean section surgery. Patent No. 2823054 of the Russian Federation; Application 11.12.2023; Publ. 17.07.2024. (in Russian)].
- Vervoort A., Vissers J., Hehenkamp W., Brölmann H., Huirne J. The effect of laparoscopic resection of large niches in the uterine caesarean scar on symptoms, ultrasound findings and quality of life: A prospective cohort study. BJOG. 2017; 125(3): 317-25. https://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.14822.
- Zhang X., Yang M., Wang Q., Chen J., Ding J., Hua K. Prospective evaluation of five methods used to treat cesarean scar defects. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2016; 134(3): 336-9. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2016.04.011.
- Van Horenbeeck A., Temmerman M., Dhont M. Cesarean scar dehiscence and irregular uterine bleeding. Obstet. Gynecol. 2003; 102(5, Pt 2): 1137-9.
- Di Spiezio Sardo A., Zizolfi B., Calagna G., Giampaolino P., Paolella F., Bifulco G. Hysteroscopic isthmoplasty: Step-by-step technique. J. Minim. Invasive Gynecol. 2018; 25(2): 338-9. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmig.2017.09.002.
- Harjee R., Khinda J., Bedaiwy M.A. Reproductive outcomes following surgical management for isthmoceles: A systematic review. J. Minim. Invasive Gynecol. 2021; 28(7): 1291-302.e2. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmig.2021.03.012.
- Zeller A., Villette C., Fernandez H., Capmas P. Is hysteroscopy a good option to manage severe cesarean scar defect? J. Minim. Invasive Gynecol. 2021; 28(7): 1397-402. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmig.2020.11.005.
- Casadio P., Raffone A., Alletto A., Filipponi F., Raimondo D. et al. Postoperative morphologic changes of the isthmocele and clinical impact in patients treated by channel-like (360°) hysteroscopic technique. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2023; 160(1): 326-33. https://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijgo.14387.
- Vitale S.G., Ludwin A., Vilos G.A., Török P., Tesarik J., Vitagliano A. et al. From hysteroscopy to laparoendoscopic surgery: What is the best surgical approach for symptomatic isthmocele? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2020; 301(1): 33-52. https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00404-020-05438-0.
- Chen H., Wang H., Zhou J., Xiong Y., Wang X. Vaginal repair of cesarean section scar diverticula diagnosed in non-pregnant women. J. Minim. Invasive Gynecol. 2019; 26(3): 526-34. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmig.2018.06.012.
- Zhou X., Yang X., Chen H., Fang X., Wang X. Obstetrical outcomes after vaginal repair of caesarean scar diverticula in reproductive-aged women. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2018; 18(1): 411. https://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12884-018-2015-7.
- Schepker N., Garcia-Rocha G-J., von Versen-Höynck F., Hillemanns P., Schippert C. Clinical diagnosis and therapy of uterine scar defects after caesarean section in non-pregnant women. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2014; 291(6): 1417-23. https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00404-014-3582-0.
- Gkegkes I.D., Psomiadou V., Minis E., Iavazzo C. Robot-assisted laparoscopic repair of cesarean scar defect: a systematic review of clinical evidence. J. Robot. Surg. 2022; 17(3): 745-51. https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11701-022-01502-w.
- Mashiach R., Burke Y.Z. Optimal isthmocele management: hysteroscopic, laparoscopic, or combination. J. Minim. Invasive Gynecol. 2021; 28(3): 565-74. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmig.2020.10.026.
- Nirgianakis K., Oehler R., Mueller M. The Rendez-vous technique for treatment of caesarean scar defects: a novel combined endoscopic approach. Surg. Endosc. 2016; 30(2): 770-1. https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4226-6.
- Akdemir A., Sahin C., Ari S.A., Ergenoglu M., Ulukus M., Karadadas N. Determination of isthmocele using a Foley catheter during laparoscopic repair of cesarean scar defect. J. Minim. Invasive Gynecol. 2018; 25(1): 21-2. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmig.2017.05.017.
- Krentel H., Lauterbach L.-K., Mavrogiannis G., De Wilde R.L. Laparoscopic fluorescence guided detection of uterine niche - the next step in surgical diagnosis and treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2022; 11(9): 2657. https://dx.doi.org/10.3390/jcm11092657.
- Макиян З.Н., Адамян Л.В., Карабач В.В., Чупрынин В.Д. Новый метод хирургического лечения несостоятельности рубца на матке после кесарева сечения с помощью манипулятора с желобом. Акушерство и гинекология. 2020; 2:104-10. [Makiyan Z.N., Adamyan L.V., Karabach V.V., Chuprynin V.D. A new method for surgical treatment of uterine scar insuffisiency after a previous cesarean section using an intrauterine manipulator with a groove. Obstetrics and Gynecology. 2020; (2): 104-10. (in Russian). https://dx.doi.org/10.18565/aig.2020.2.104-110.
- Donnez O., Donnez J., Orellana R., Dolmans M.M. Gynecological and obstetrical outcomes after laparoscopic repair of a cesarean scar defect in a series of 38 women. Fertil. Steril. 2017; 107(1): 289-96.e2. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2016.09.033.
- Zhang N.N., Wang G.W., Zuo N., Yang Q. Novel laparoscopic surgery for the repair of cesarean scar defect without processing scar resection. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2021; 21(1). https://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12884-021-04281-8.
- Ножницева О.Н., Беженарь В.Ф. Ниша рубца после операции кесарева сечения: новая проблема репродуктивного здоровья женщины. Журнал акушерства и женских болезней. 2020; 69(1): 53-62.[Nozhnitseva O.N., Bezhenar V.F. The niche in the uterine cesarean scar: a new problem of women’s reproductive health. Journal of Obstetrics and Women’s Diseases. 2020; 69(1): 53-62. (in Russian)]. https://dx.doi.org/10.17816/jowd69153-62.
Received 13.09.2024
Accepted 29.10.2024
About the Authors
Vitaly F. Bezhenar, Dr. Med. Sci., Professor, Head of the Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Neonatology/Reproductology, Head of the Clinic of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Pavlov First Saint Petersburg State Medical University, Ministry of Health of Russia, 197022, Russia, St. Petersburg, Leo Tolstoy str., 6-8, +7(812)338-78-66,bez-vitaly@yandex.ru, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7807-4929
Anna E. Grigorian, PhD Student at the Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Neonatology, Pavlov First Saint Petersburg State Medical University, Ministry of Health of Russia, 197022, Russia, St. Petersburg, Leo Tolstoy str., 6-8, +7(981)104-91-84, Annagrigoryan2112@mail.ru, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1674-7753
Maria L. Romanova, PhD, Associate Professor at the Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductology, Pavlov First Saint Petersburg State Medical University, Ministry of Health of Russia, 197022, Russia, St. Petersburg, Leo Tolstoy str., 6-8, +7(905)205-25-13, Mariaro@mail.ru, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4378-6424



