Prediction of spontaneous pregnancy in patients with chronic endometritis and reproductive dysfunction using neural network technology (secondary analysis of the results of the "TULIP" randomized controlled trial)
Sukhanov A.A., Dikke G.B., Mudrov V.A., Kukarskaya I.I.
Relevance: The patients with chronic endometritis (CE) in comparison with patients without it have significantly lower rates of pregnancy (30.8% vs. 63.0%) and live births (7.7% vs. 51.9%, respectively). The prediction of pregnancy in patients with CE after treatment is of scientific and practical interest.
Objective: To develop a prognostic model of the probability of spontaneous pregnancy in patients with CE and reproductive dysfunction using neural network technology and evaluate its effectiveness.
Materials and methods: The secondary analysis of the results of the "TULIP" randomized controlled trial was carried out. A total of 875 patients with the results of a comprehensive examination were selected from the electronic database. The patients were divided into two comparison groups: group I (n=461, 52.7%) included patients who did not become pregnant, group II (n=414, 47.3%) included those who became pregnant.
Results: A prognostic model was created on the basis of neural network technology; 12 of the most significant parameters were used for this model. The prognosis was positive in 94.2% of patients in group II, and it was negative in 5.8% of women. The accuracy of the prediction was 88.0% (sensitivity is 94.2%, specificity is 82.4%). The information value of the model was confirmed by ROC analysis, the area under the curve (ROC-AUC) was 0.88, p<0.001. The use of the Superlymph medication was shown to have a significant effect on the rate of spontaneous pregnancy and it was an important parameter in the prognostic model. The oxygenation index obtained using the Photon-Bio spectrometer plays a significant role since the accuracy of the prediction decreases to 83.2% when the index is absent in the model. An online calculator was developed for the practical use of the model.
Conclusion: The model for predicting spontaneous pregnancy in patients with CE using neural network technology has an accuracy of 88% and it allows the clinicians to determine the need for either repeated courses of treatment for CE (if the prognosis is negative), or to make a decision on pregnancy planning (if the prognosis is positive).
Authors’ contributions: Sukhanov A.A. – collection of clinical material, formation of an electronic database, writing fragments of the article and editing the article; Dikke G.B. – development of the concept, design and program of the study, supervision during the study, analysis of the results of statistical processing of clinical material and their interpretation, search for literary sources, writing fragments of the article and editing the article after reviewing; Mudrov V.A. – development of the study program, statistical processing of clinical material, analysis of results, development of the prognostic model using neural network technology and its interpretation, writing the program for an online calculator, writing a fragment of the article and editing the article after reviewing; Kukarskaya I.I. – conducting the study in the clinic, supervision during the study.
Conflicts of interest: The authors report no conflicts of interest and guarantee that the article is the original work of the authors.
Funding: The study was carried out using own resources. The publication of the article was supported by Biotechpharm LLC, Moscow, Russia.
Ethical Approval: The study was approved by the Ethical Review Board of the Perinatal Medical Center (Tyumen, Russia).
Authors' Data Sharing Statement: The data supporting the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author after approval from the principal investigator.
For citation: Sukhanov A.A., Dikke G.B., Mudrov V.A., Kukarskaya I.I. Prediction of spontaneous pregnancy in patients with chronic endometritis and reproductive dysfunction using neural network technology (secondary analysis of the results of the "TULIP" randomized controlled trial).
Akusherstvo i Ginekologiya/Obstetrics and Gynecology. 2024; (2): 106-116 (in Russian)
https://dx.doi.org/10.18565/aig.2024.20
Keywords
The prevalence of chronic endometritis (CE) in patients with impaired fertility ranges from 2.8% to 56% [1]. Low pregnancy rate (30.8% versus 63.0%) and live birth rate (7.7% versus 51.9%, respectively) is among the patients with CE versus women, who have no CE [2]. The researchers associate the decline in fertility due to CE with endometrial receptivity and failed implantation of fertilized egg [3].
Assessments of the effectiveness of treatment of chronic endometritis for restoration of fertility is controversial. However, the meta-analysis of 12 studies concluded that treatment effectiveness for resolution of CE, in contrast to persistent CE, provides a greater chance of successful pregnancy and live birth (OR=6.82 and 9.75, respectively, p<0.0001) [4]. On the other hand, absence of resolution of CE after treatment, determine the necessity of repeated treatment courses and/or using other treatment methods for normalization of endometrium and restoration of its receptivity, since even assisted reproduction technologies (ART) do not provide a positive result, when chronic endometritis was not cured after treatment.
Assessment of the prospects for treating infertility associated with failed implantation of fertilized egg is based on the outcomes (spontaneous pregnancies, live birth rates) and appears to be uncertain in clinical practice. Prediction of treatment success or failure remains an open question, and current guidelines for CE do not provide any prognostic estimates for the couples planning to conceive.
The markers of chronic endometritis are very important for the practicing physicians due to the fact that they can help to predict the onset of pregnancy and make it possible to monitor treatment effectiveness aimed at improving endometrial receptivity. According to Krasnopol’skaia K.V. (2016), for these purpose, routine use of ultrasound is probably the only preferred technique for imaging endometrial thickness and macrostructure [5]. Currently, electron microscopy imaging, immunological, molecular and genetic, and many other parameters are being actively explored as markers of EC. However, all of them rather provide insight into the fundamental aspects of the process of implantation, but are not appropriate for the routine use in clinical practice [5]. In addition, it is suggested that there are different levels of CE during the window of implantation, and different signatures may reflect different levels of endometrial receptivity, that can be associated with different pregnancy outcomes. Extreme values of biomarkers (as opposed to average values) can have significant prognostic and diagnostic differences that are not reflected in the average values [6]. Obviously, the complexity of implementation, additional material costs and doubtful diagnostic value limits the clinical use of these methods.
Currently, several machine learning programs have been created to determine predictors of getting pregnant, but they predict exclusively the success of in vitro fertilization (IVF) [7–9]. Some predictive models that are described in literature, are based on modern algorithms, such as ranking algorithms, Bayesian networks and neural networks, and are being actively introduced in medical practice. Deep machine learning or neural network models with multiple layers of variables that predict the outcomes, are the most promising [10]. However, scientific and practical interest in assessment of the likelihood of spontaneous pregnancy in patients with CE remains unmet.
Thus, the need to search for the models predicting treatment success in CE in patients with impaired reproductive function is a topical issue in modern medicine.
The objective of the study was to develop a prognostic model of the likelihood of spontaneous pregnancy in patients with CE and impaired reproductive function using neural network model and to evaluate the effectiveness of this method.
Material and methods
Design. The secondary analysis of the results of randomized controlled trial TULUP “The course and outcomes of pregnancy in patients with chronic endometritis and impaired reproductive function, who received the complex treatment with Superlymph (a complex of natural antimicrobial peptides and cytokines)” was carried out [11].
The research was based on patient data (n=2 252) obtained from electronic database, who sought medical care at women’s clinic of Perinatal Center (Tyumen, Russia) from September, 2019 to February 2023 due to complaints of inability to conceive for 1–10 years and established diagnosis of uterine factor infertility (N97.2 Infertility of female origin, failed implantation of fertilized egg) and confirmed histological and immunohistochemical diagnosis of CE (N71.1 Chronic inflammatory disease of the uterus), that conformed to inclusion/exclusion criteria for the study. Data of 875 patients conforming to the purpose of the study, were selected from the database. Assessment of the results of complex examination of patients included clinical gynecological examination, functional and laboratory tests, such as real-time polymerase chain reaction to identify microbial agents, viruses and exclude sexually transmitted infections, morphological evaluation of endometrial aspirates, immunohistology of plasma cells (CD138+), enzyme immunoassay for detection of cytokine levels in serum; laser-based conversion testing (spectrometer Photon Bio, Russia).
The patients received treatment, including antimicrobial therapy during 10 days (875 patients, 100%) with complex of exogenous natural cytokines and chemokines (Superlymph 25 units once a day vaginally for 20 days) (476/875 patients, 54.4%), gestagen during the second phase of the menstrual cycle for 1–6 cycles before getting pregnant (428/875 patients, 48.9%).
Comparison groups. The patients were divided into two comparison groups. Group 1 (n=461, 5,7%) was composed of the patients, in whom spontaneous pregnancy did not occur. Group 2 (n=414, 47.3%) was composed of the patients, in whom spontaneous pregnancy occurred after treatment (patient surveillance was performed during 6 months after receiving treatment).
Major results. A prognostic model and predictors for spontaneous clinical pregnancy (according to ultrasound results at 7–8 weeks of pregnancy) in women with impaired reproductive function that was associated with CE. Online calculator was used for clinical prediction and evaluation of the individual likelihood of spontaneous pregnancy in patients with CE.
Statistical analysis
SPSS Statistics Version 25,0 (IBM, USA; license No. Z125-3301-14) was used for statistical analysis. The Kholmogorov–Smirnov test was used to assess distribution of the parameters. The quantitative parameters were presented as median (Me) and interquartile range (Q1; Q3). The qualitative parameters were shown as absolute (n) and relative values (%). The Mann–Whitney U test was used to compare the differences between quantitative indicators in independent samples, and Pearson’s chi-square (χ2) test was used for qualitative indicators. The significance of dynamic changes in quantitative indicators was assessed using the Wilcoxon test. The differences were considered to be significant at р<0.05 (type I and type II error rates α=5% and β=20%, respectively).
Neural network analysis was performed using 12 critical parameters, which were selected using neural data analysis. These parameters were then entered into the Neural Network module in SPSS Statistics, and evaluation of the likelihood of spontaneous pregnancy occurrence was obtained.
Results
Patient Overview. The age of patients ranged from 18 to 45 years (36.0 (35.0; 36.0) years). Table 1 represents the social and clinical characteristics of the patients. Comparison analysis showed that there were differences between group 1 and 2 in the educational level and in the number of pelvic laparoscopies. The other parameters had no statistically significant differences.
The average infertility duration was 2.0 (2.0; 2.8) years and 1.0 (1.0; 2.5) year, respectively, р=0.06. Infertility duration was less than 5 years in 79.0% (367/461) and in 84.5% (350/414) of patients. Infertility duration was 5 years and more in 21.0% (97/461) and 15.5% (64/414) of patients, respectively, р=0,03. That is, the number of patients with infertility duration of 5 years and more was significantly less in group 2.
There was statistically significant difference between the groups in the number of patients, who received treatment with a complex of natural antimicrobial peptides and cytokines (Superlymph) at the pregravid stage, that is, the number of patients was higher in group 2 (212/414, 62.6%) versus group 1 (217/461, 47.1%), р<0.001. There were no statistically significant differences between other types of treatments.
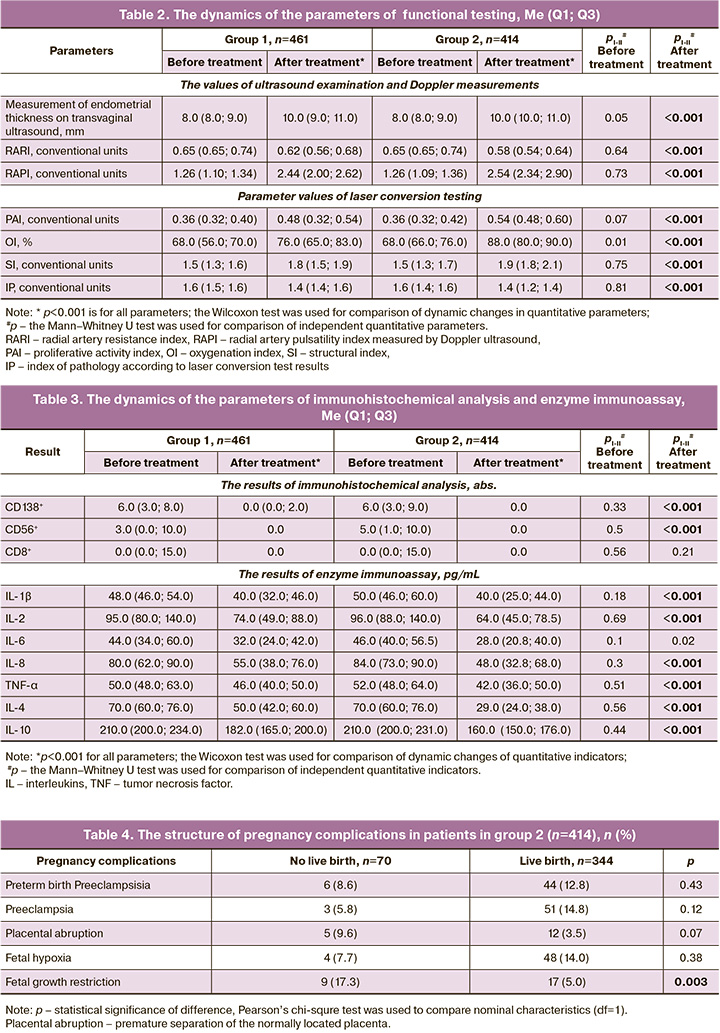
Table 2 represents the results of functional testing and the dynamics of the parameters after treatment.
After treatment in both groups, parameter values of ultrasound and Dopplerometry as well as laser conversion testing improved significantly, but in patients in group 2, they appeared to be significantly better versus group 1.
Similar conclusion can be made about the results of immunohistochemical analysis and enzyme immunoassay (Table 3).
Spontaneous conception with favorable pregnancy outcome happened in patients the average of 3.0 (3.0; 3.5) months, and in patients with adverse pregnancy outcomes 2.0 (2.0; 2,5) months after completion of the course of treatment (U=6868.0, p<0.001). Completion of pregnancy happened on average at 39.0 (38.5; 39.0) and 14.0 (14.0; 19.6) weeks of gestation, respectively (U=509.5, p<0.001).
Spontaneous pregnancies that resulted in live births was in 83.1% (344/414) of patients, or in 39.3% (344/875) of the total number of patients, who underwent treatment. Failure to achieve live birth associated with spontaneous miscarriage before 12 weeks was in 67.1% (47/70), before 22 weeks in 14.3% (10/10) of observations. Failure to achieve live birth due to antenatal fetal death was in 18.6% (13/70) of observations. The structure of other pregnancy complications is shown in Table 4. It can be seen that fetal growth restriction was the only cause of pregnancy loss, and the difference was statistically significant compared to live birth – 17.3% versus 5.0% (р=0.003).
Fetal weight in live births was 3500.0 (3288.3; 3508.9) g (U=378.5, p< 0.001). The Apgar score to evaluate the newborns’ condition was 8.0 (7.6; 8.0) points at the end of the first minute, and 8.0 (8.0; 8.1) points at the end of the fifth minute after birth.
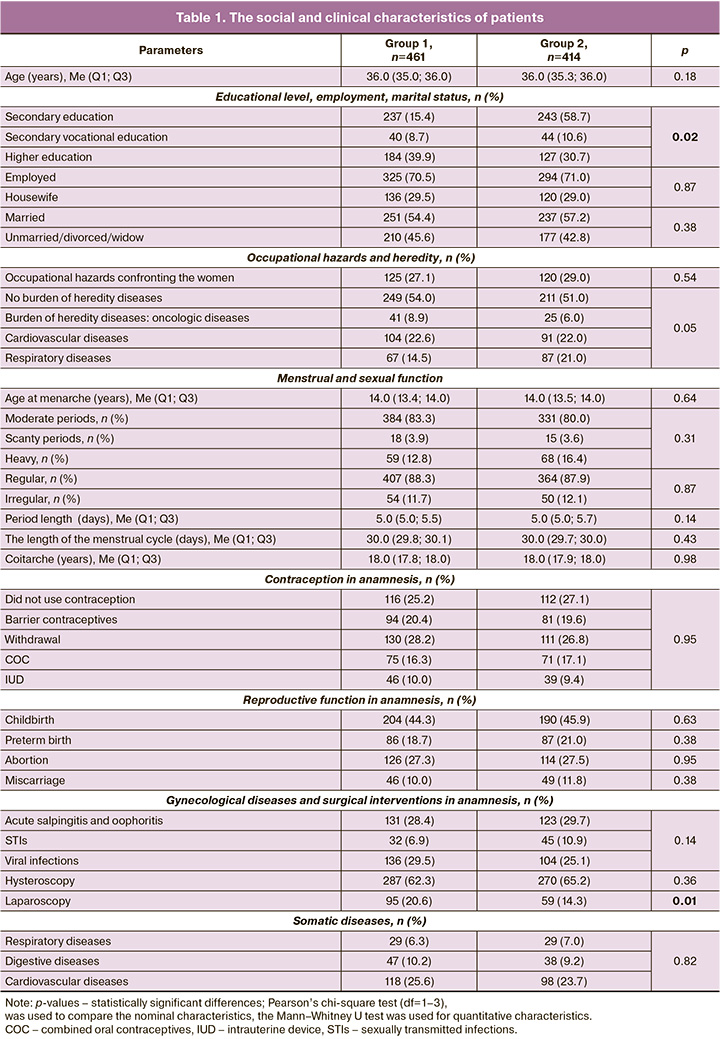
A prognostic model of the likelihood of spontaneous pregnancy. Given the need to exclude multicollinearity between the correlating parameters of the research methods used, it was decided that the most important parameters will be used for development of the prognostic model of the likelihood of spontaneous pregnancy in infertile patients after treatment of CE. For this purpose, neural network data analysis was used. Based on the results, the multilayer perceptron was chosen to create a prognostic model for predicting spontaneous pregnancy. The number of neurons in the input layer was 12. They were the study parameters (infertility duration less than 5 years, or 5 years and more, the educational level of women, the presence or absence of a complex of antimicrobial peptides and cytokines in treatment structure, the numerical values of radial artery pulsatility index measured by Doppler ultrasound, oxygenation index according to laser conversion test results, CD138, interleukins (IL-1β and IL-4 after treatment), and they had not only significant differences in comparison between the study groups, but also pathogenetic significance.
Given the number of neurons in the input layer, 2 hidden layers were included in the architecture of the multilayer perceptron. The choice of architecture of the multilayer perceptron was performed automatically, that enabled to calculate the optimal number of neurons in the specified hidden layers, equal to 8 and 6, respectively, and most effectively predict the outcome.
Sigmoid activation function was used in both hidden layers and in the output layer, that determined the relationship of the weighted sums of the objects with the subsequent data layer objects. The sigmoid function in the output layer converted real variables into range variables (0; 1), that met the design of the study. The sum of squares served as the error function. The output layer contained 2 target (dependent) variables – the presence or absence of spontaneous pregnancy. Figure 1 represents the architecture of the developed neural network.
Predicting outcomes. In group 1, the prognostic prediction was positive in 81 (17.6%) out of 461 patients, negative in 380 (82.4%) patients. In group 2, the prognostic prediction was positive in 390 (94.2%) out of 414, and negative in 24 (5.8%) patients. The accuracy of developed predictive model was 88.0% (94.2% sensitivity, 82.4% specificity). The value of information flow in neural network data analysis for predicting spontaneous pregnancy in patients with infertility associated with CE is represented by ROC analysis (Fig. 2). The area under the ROC curve (AUC ROC) was 0.88; p<0.001.
Assessment of the importance of the selected parameters in the structure of the developed neural network enabling to predict the likelihood of spontaneous pregnancy in patients with infertility and CE, showed that among the laboratory and functional indicators, the most important indicators were IL-4 according to the results of immunohistochemical analysis (26%), and oxygenation index that was obtained using laser conversion test (22). It should be noted that the importance of the parameters is determined not only by their share in the structure of all parameters, but also by the influence of a full set of parameters on each other, and the neural network takes it into account.
Thus, the analysis showed that among the patients with impaired fertility associated with CE, spontaneous pregnancy happened within 6 months after treatment in 47.3% of women, and live birth rate was 39.3%. Based on neural network technology, 12 most important parameters were identified and used to create the prognostic model for predicting spontaneous pregnancy in patients with CE. The elaborated model is effective for predicting spontaneous pregnancy and is characterized by prognostic accuracy of 88.0 %, 94.2% sensitivity, 82.4% specificity.
For practical use of the prognostic model for predicting spontaneous pregnancy in patients with CE, оnline calculator was developed. It contained all parameters that were included in the prognostic model and calculated using neural network technology for accurate identification of CE and making a decision about treatment, necessity of repeated courses of treatment, spontaneous pregnancy planning or using ART.
The interface of online calculator shown in Figure 3.
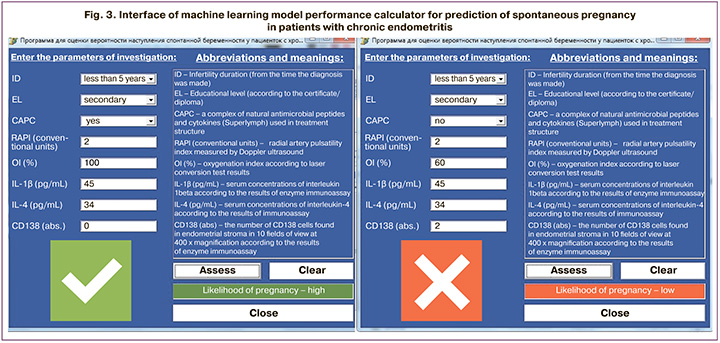
The obstetrician-gynecologist enters the study parameters (which are included in source network and are represented below), clicks on the command button “Assess”; the calculator automatically calculates the likelihood of a spontaneous pregnancy and displays the result (the likelihood of spontaneous pregnancy is high or low).
The prognosis enables to take a decision about planning spontaneous pregnancy (if the prognosis is positive), or to determine the necessity of repeated course/courses of treatment of CE (if the prognosis is negative).
Discussion
Some previous studies assessed the individual or combined prognostic value of a number of variables in the ART programs [12–14]. The variables included anti-Mullerian hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, ovarian reserve tests, antral follicle count, age, inhibin B, the number of oocytes retrieved, and serum luteinizing hormone concentration on day 1 of ovarian stimulation, but had limited prognostic accuracy. However, limited prognostic accuracy based on these variables was less than 60% [13, 14]. Xu T. et al. (2022) reported the predictors of the onset of pregnancy after the first IVF cycle and a fresh embryo transfer using fertility clinic software system eIVF [9]. Hansen K.R. et al. (2016) determined the initial characteristics in couples with unexplained infertility, who underwent intrauterine insemination after four cycles of ovarian stimulation, which can predict the outcomes, such as conception, clinical pregnancy and live birth. They found that age, waist circumference, income level, infertility duration, and pregnancy loss in medical history were significantly associated with at least one of these pregnancy outcomes [15]. However, no studies have been conducted to search for the predictors of spontaneous pregnancy after treatment of CE.
In contrast to the study by Hansen K.R. et al. and many other authors, where age was indicated as an important factor for both natural conception and using ART cycles, in our study, age was not identified as a prognostic parameter, since the age range of patients included in the analysis was very narrow (35.0; 36.0 years).
On the contrary, the parameter “infertility duration” appeared to be very significant, and this correlates with other authors’ point of view [16–18]. Thus, a nonlinear relationship was identified between infertility duration and fertilization rate in IVF programs, which decreased with years of infertility until the “turning point” equal to 4.8 years [17]. Abdelazim I. et al. (2018) suggested that if pregnancy did not happen after 2 years, then each additional year of infertility reduces the likelihood of pregnancy by 25% annually [18]. Our study confirmed this fact. The expected pregnancy rate was significantly higher when infertility duration was less than 5 years and depended on treatment carried out, and was 61.0% versus 19.2% (р <0.001). In patients with infertility duration 5 years or more, the significant association was found between taking a complex of natural antimicrobial peptides and cytokines (Superlymph) as part of complex treatment and increased chances of getting pregnant by almost 3 times in comparison with the patients, who received only gestagen/AB (OR=2.91 (95% CI 1.55–5.47) [11].
Resolution of CE with the absence of plasma cells in endometrial microspecimen (the study TULIP) was observed in the group of patients, who were treated with Superlymph complex, gestagen and AB – in 86.0% versus 58.0% of patients, who were treated with gestagen/AB (p <0.001; OR=1.61; 95% CI 1.52–1.71). Simultaneously, the severity of fibrosis decreased according to the results of histological analysis of endometrial aspirates, that naturally led to increased rate of spontaneous pregnancies and live births [11]. During 12 months the results were studied, and it was found that after complex treatment with Superlymph, pregnancies happened in 83.3 % (472/563) of patients, out of them spontaneous pregnancies occurred in 78% (368/472), pregnancies ended in live births in 87.7% (323/368) of patients. Our observation correlates with the conclusions made by other researchers, that treatment with resolution of CE provides a greater chance of successful pregnancy and live birth in contrast to persistent CE [4]. At the same time the use of Superlymph demonstrates high effectiveness compared with other types of treatment that were used by other authors.
The indicators, such as the use of a complex of natural peptides and cytokines, uterine radial artery pulsatility index according to Doppler ultrasound measurements, IL-4 and IL-1β concentrations according to enzyme immunoassay in serum specimens, oxygenation index according to laser conversion test, as predictors of the onset of pregnancy have not been previously explored. In our study, their significance for the purpose of prognosis was determined using neural network analysis, and it was identified that these indicators are important in terms of the pathogenesis of CE.
The important parameter for prediction of spontaneous pregnancy was the use or not use of Superlymph in the program of complex treatment of CE. It should be noted that treatment with Sperlymph is pathogenetically substantiated therapy, since in the pathogenesis of this disease, the leading role is currently assigned to the immune response to infection and excessive local production of cytokines and leukocytes, that was reported in the systematic review in 2020 [19] and was demonstrated in recent domestic studies [20–22]. These studies showed the positive effect of the complex treatment on elimination of pathogens and resolution of CE, expression of specific genes, restoration of expression of innate immune regulators, normalization of the balance of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, increased progesterone receptor expression in endometrial epithelial cells and endometrial stromal cells by 3 and 2.7 times, respectively, enhancement of angiogenesis and vascularization of endometrial tissue.
Superlymph is obtained from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) – blood leukocytes in pigs. Previously, the network meta-analysis of 16 randomized clinical trials reported that intrauterine administration of autologous PBMCs leads to increased chances of getting pregnant with IVF by 2.4 times compared with the control group (without administration of PBMCs) (OR=2.44; 95% CI 1.67–3.57), and of live birth by 2.9 times (OR=2.86; 95% CI 1.64–5.00) [23]. The advantage of Superlymph, in contrast to intrauterine administration of autologous PBMCs, is the local effect and ease of self-administration of vaginal or rectal suppositories by the patients, and increased chances of getting pregnant after IVF by 3 times (OR=3.08, 95% CI 2.31–4.10) and live birth by 3.8 times (OR=3.75, 95% CI 2.86–4.92) versus the patients in the control group, who were not treated with Superlymph.
Pulsatility index according to Doppler ultrasound measurement reflects reduction in endometrial blood flow, and is also reported to be one of the causes of impaired reproduction function in patients with CE [19].
The significance of laser conversion diagnostics of endometrium conditions using the FOTON-BIO spectrometer is currently being actively explored and yields encouraging results [24–26]. The new express-diagnostics method that was elaborated by domestic researchers is based on the spectral analysis of reflected light from endometrial tissue enables to evaluate the condition of endometrium and its readiness for fertilized egg implantation in patients with CE using four parameters – oxygenation index, proliferative activity, structure and pathology. Our study found that oxygenation index is a significant indicator acting as a prognostic factor and its efficiency in the structure of most important parameters along with IL-4 is more than 20%. Oxygenation index demonstrates saturation of the endometrium with oxygen (the normal range of oxygen saturation is more than 80%) and indirectly reflects the degree of vascularization in the endometrium. Low level of oxygen tissues was up to 46–50% in women with CE and intrauterine synechiae [24]. Previously we have developed the prognostic method for IVF cycles in patients with infertility caused by CE. It was based on two indicators –
oxygenation index and proliferative activity index of the endometrium with likelihood of a positive prognosis for occurrence of pregnancy and live birth (80%) [26]. It should be noted that when oxygenation index was excluded from the structure of neural network, the prognostic accuracy reduced up to 83,2%, and this fact determines its diagnostic significance.
The use of Superlymph is closely related to three other important prognostic indicators CD138, IL-1β and IL-4, which were identified by neural network analysis. The absence of CD138 indicates resolution of CE. The values of IL-1β and IL-4 indicate inflammatory and anti-inflammatory activity of local immunity, respectively. Previously, we also demonstrated the importance of IL-4 as a predictor of recurrence of bacterial vaginosis in patients infected with herpes viruses [27]. High concentrations of IL-1β and IL-4 after treatment indicate incomplete pathogen elimination, that creates the premise for persistence of CE.
Therefore, the prognostic model developed by us for spontaneous pregnancy after treatment in patients with CE and impaired reproductive function using neural network technology is a unique tool that helps to predict the success of treatment with a positive result and predictive accuracy of 88%, and this is the highest accuracy achieved among all other neural network models elaborated for IVF.
For practical use of the prognostic model for predicting spontaneous pregnancy in patients with infertility associated with CE, оnline calculator was developed. It helps to determine the necessity of either repeated treatment course/courses of CE (when the prognosis for successful spontaneous pregnancy is negative) or make a decision about planning pregnancy (when the prognosis is positive).
Conclusion
The model for predicting spontaneous pregnancy in patients with infertility associated with CE using neural network technology has an accuracy of 88% (94.2% sensitivity, 82.4% specificity) and enables to take a decision about planning spontaneous pregnancy or to determine the necessity of repeated treatment course/courses of CE.
Prospects for further researches
Given our experience of development of the prognostic model using neural network technology for predicting spontaneous pregnancy in patients with impaired reproductive function associated with CE, we believe that identification of predictive biomarkers of IVF success before embryo transfer for women with uterine infertility, and carrying out further research in this area is a promising diagnostic solution. The prognostic model of the onset of pregnancy and live birth as a result of IVF, using neural network technology, will improve prognostic possibilities compared with the existing foreign models. The program for online calculator of IVF success created on the basis of this model will enable its widespread use in routine clinical practice, that is the subject of our future research.
References
- Kimura F., Takebayashi A., Ishida M., Nakamura A., Kitazawa J., Morimune A. et al. Review: Chronic endometritis and its effect on reproduction. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2019; 45(5): 951-60. https://dx.doi.org/10.1111/jog.13937.
- Hirata K., Kimura F., Nakamura A., Kitazawa J., Morimune A., Hanada T. et аl. Histological diagnostic criterion for chronic endometritis based on the clinical outcome. BMC Women's Health. 2021; 21: 94. https://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12905-021-01239-y.
- Vitagliano A., Laganà A.S., De Ziegler D., Cicinelli R., Santarsiero C.M., Buzzaccarini G. et al. Chronic endometritis in infertile women: impact of untreated disease, plasma cell count and antibiotic therapy on IVF outcome – a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022; 12(9): 2250. https://dx.doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12092250.
- Liu J., Liu Z.A., Liu Y., Cheng L., Yan L. Impact of antibiotic treatment for chronic endometritis on pregnancy outcomes in women with reproductive failures (RIF and RPL): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Med. (Lausanne). 2022; 9: 980511. https://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2022.980511.
- Краснопольская К.В., Назаренко Т.А., Ершова И.Ю. Современные подходы к оценке рецептивности эндометрия (обзор литературы). Проблемы репродукции. 2016; 22(5): 61 9. [Krasnopol'skaia K.V., Nazarenko T.A., Ershova I.Yu. Modern approaches to endometrial receptivity assessment (a review). Russian Journal of Human Reproduction. 2016; 22(5): 61-9 (in Russian)]. https://dx.doi.org/10.17116/repro201622561-69.
- Craciunas L., Gallos I., Chu J., Bourne T., Quenby S., Brosens J.J., Coomarasamy A. Conventional and modern markers of endometrial receptivity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum. Reprod. Update. 2019; 25(2): 202-23. https://dx.doi.org/10.1093/humupd/dmy044.
- McLernon D.J., Steyerberg E.W., Te Velde E.R., Lee A.J., Bhattacharya S. Predicting the chances of a live birth after one or more complete cycles of in vitro fertilisation: population based study of linked cycle data from 113 873 women. BMJ. 2016; 355: i5735. https://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.i5735.
- Vaegter K.K., Lakic T.G., Olovsson M., Berglund L., Brodin T., Holte J. Which factors are most predictive for live birth after in vitro fertilization and intracytoplasmic sperm injection (IVF/ICSI) treatments? Analysis of 100 prospectively recorded variables in 8,400 IVF/ICSI single-embryo transfers. Fertil. Steril. 2017; 107(3): 641-8.e2. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2016.12.005.
- Xu T., de Figueiredo Veiga A., Hammer K.C., Paschalidis I.C., Mahalingaiah S. Informative predictors of pregnancy after first IVF cycle using eIVF practice highway electronic health records. Sci. Rep. 2022; 12(1): 839. https://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-04814-x.
- Ratna M.B., Bhattacharya S., Abdulrahim B., McLernon D.J. A systematic review of the quality of clinical prediction models in in vitro fertilisation. Hum. Reprod. 2020; 35(1): 100-16. https://dx.doi.org/10.1093/humrep/dez258.
- Дикке Г.Б., Суханов А.А., Остроменский В.В., Кукарская И.И. Течение и исходы беременности у пациенток с хроническим эндометритом и нарушением репродуктивной функции, получавших комплексное лечение с использованием препарата «Суперлимф» (рандомизированное контролируемое испытание в параллельных группах «ТЮЛЬПАН»). Акушерство и гинекология. 2023; 4: 132-44. [Dikke G.B., Sukhanov A.A., Ostromensky V.V., Kukarskaya I.I. Course and outcomes of pregnancy in patients with chronic endometritis and impaired reproductive function after receiving complex treatment with drug Superlymph: randomized control trial in parallel groups “TULIP”. Obstetrics and Gynecology. 2023; (4): 132-44. (in Russian)]. https://dx.doi.org/10.18565/aig.2023.74.
- Broer S.L., van Disseldorp J., Broeze K.A., Dolleman M., Opmeer B.C., Bossuyt P. et al. Added value of ovarian reserve testing on patient characteristics in the prediction of ovarian response and ongoing pregnancy: an individual patient data approach. Hum. Reprod. Update. 2013; 19(1): 26-36. https://dx.doi.org/10.1093/humupd/dms041.
- Lukaszuk K., Kunicki M., Liss J., Lukaszuk M., Jakiel G. Use of ovarian reserve parameters for predicting live births in women undergoing in vitro fertilization. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2013; 168(2): 173-7. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2013.01.013.
- Zhang Q., Wang X., Zhang Y., Lu H., Yu Y. Nomogram prediction for the prediction of clinical pregnancy in Freeze-thawed Embryo Transfer. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2022; 22(1): 629. https://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12884-022-04958-8.
- Hansen K.R., He A.L., Styer A.K., Wild R.A., Butts S., Engmann L. et al.; Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Reproductive Medicine Network. Predictors of pregnancy and live-birth in couples with unexplained infertility after ovarian stimulation-intrauterine insemination. Fertil. Steril. 2016; 105(6): 1575-83.e2. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2016.02.020.
- Kuru Pekcan M., Tokmak A., Ulubasoglu H., Kement M., Özakşit G. The importance of infertility duration and follicle size according to pregnancy success in women undergoing ovulation induction with gonadotropins and intrauterine insemination. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2023; 43(1): 2173058. https://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01443615.2023.2173058.
- Zhang L., Cai H., Li W., Tian L., Shi J. Duration of infertility and assisted reproductive outcomes in non-male factor infertility: can use of ICSI turn the tide? BMC Womens Health. 2022; 22(1): 480. https://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12905-022-02062-9.
- Abdelazim I., Purohit P., Farag R., Zhurabekova G. Unexplained infertility: prevalence, possible causes and treatment options. A review of the literature. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Investig. 2018; 1(1): 17-22. https://dx.doi.org/10.5114/jogi.2018.74250.
- Buzzaccarini G., Vitagliano A., Andrisani A., Santarsiero C.M., Cicinelli R., Nardelli C. et al. Chronic endometritis and altered embryo implantation: a unified pathophysiological theory from a literature systematic review. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2020; 37(12): 2897-911. https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10815-020-01955-8.
- Тапильская Н.И., Толибова Г.Х., Савичева А.М., Копылова А.А., Глушаков Р.И., Будиловская О.В., Крысанова А.А., Горский А.Г., Гзгзян А.М., Коган И.Ю. Эффективность локальной цитокинотерапии хронического эндометрита пациенток с бесплодием. Акушерство и гинекология. 2022; 2: 91-100. [Tapilskaya N.I., Tolibova G.Kh., Savicheva A.M., Kopylova A.A., Glushakov R.I., Budilovskaya O.V., Krysanova A.A., Gorskii A.G., Gzgzyan A.M., Kogan I.Yu. The effectiveness of local cytokine therapy for chronic endometritis in patients with infertility. Obstetrics and Gynecology. 2022; (2): 91-100. (in Russian)]. https://dx.doi.org/10.18565/aig.2022.2.91-100.
- Доброхотова Ю.Э., Ганковская Л.В, Боровкова Е.И., Зайдиева З.С., Скальная В.С. Модулирование локальной экспрессии факторов врожденного иммунитета у пациенток с хроническим эндометритом и бесплодием. Акушерство и гинекология. 2019; 5: 125-32. [Dobrokhotova Yu.E., Gankovskaya L.V., Borovkova E.I., Zaidieva Z.S., Skalnaya V.S. Modulation of the local expression of innate immune factors in patients with chronic endometritis and infertility. Obstetrics and Gynecology. 2019; (5): 125-32. (in Russian)]. https://dx.doi.org/10.18565/aig.2019.5.125-132.
- Дикке Г.Б., Суханов А.А., Кукарская И.И., Остроменский В.В. Цитокиновый профиль пациенток с хроническим эндометритом и нарушением репродуктивной функции. Вопросы гинекологии, акушерства и перинатологии. 2021; 20(6): 82-91. [Dikke G.B., Sukhanov A.A., Kukarskaya I.I., Ostromensky V.V. Cytokine profile in patients with chronic endometritis and reproductive dysorders. Gynaecology, Obstetrics and Perinatology. 2021; 20(6): 82-91. (in Russian)]. https://dx.doi.org/10.20953/1726-1678-2021-6-82-91.
- Liu M., Yuan Y., Qiao Y., Tang Y., Sui X., Yin P., Yang D. The effectiveness of immunomodulatory therapies for patients with repeated implantation failure: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2022; 12(1): 18434. https://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-21014-9.
- Зуев В.М., Александров М.Т., Хомерики Т.А., Чернышов Г., Метревели Б.Г., Попов С.Н., Ибоян И.И., Калинина Е.А. Клиническое значение лазерного конверсионного тестирования в диагностике и лечении хронического эндометрита. Вестник РУДН. Серия: Медицина. 2012; 6: 95-101. [Zuyev V.M., Aleksandrov M.T., Khomeriki T.A., Tchernyshov G., Metreveli B.G., Popov S.N., Iboyan I.I., Kalinina E.A. Clinical value of laser conversion testing in diagnostics and treatment of a chronic endometritis. RUDN Journal of Medicine. 2012; (6): 95-101. (in Russian)].
- Осипова А.Д., Зуев В.М., Александров М.Т. Значение экспресс-метода лазерной конверсионной диагностики (раман-флуоресцентной составляющей) патологических процессов эндометрия у женщин в перименопаузе. Архив акушерства и гинекологии им. В.Ф. Снегирева. 2019; 6(2): 85-9. [Osipova A.D., Zuyev V.M., Aleksandrov M.T. The value of the express method of laser conversion diagnostics (raman-fluorescent component) of the pathological processes of endometrium in women in the perimenopause. V.F. Snegirev Archives of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 2019; 6(2): 85-9. (in Russian)]. http://dx.doi.org/10.18821/2313-8726-2019-6-2-85-89.
- Суханов А.А., Дикке Г.Б. Дефект имплантации эмбриона. Положительный прогноз – залог успешного ЭКО. Акушерство и гинекология сегодня. 2023; 4: 10-1. [Sukhanov A.A., Dikke G.B. Embryo implantation defect. A positive prognosis is the key to successful IVF. Obstetrics and Gynaecology Today. 2023; 4: 10-1. (in Russian)]. https://medvedomosti.media/articles/defekt-implantatsii-yaytsekletki-polozhitelnyy-prognoz-zalog-uspeshnogo-eko/
- Дикке Г.Б., Суханов А.А., Кукарская И.И., Остроменский В.В. Способ прогнозирования рецидива бактериального вагиноза у женщин, инфицированных герпес-вирусами. Патент на изобретение RU №2810428 от 27.12.2023. Опубликовано 27.12.2023, Бюл. № 36. [Dikke G.B., Sukhanov A.A., Kukarskaya I.I., Ostromensky V.V. A method for predicting recurrence of bacterial vaginosis in women infected with herpes viruses. Patent RU No.2810428 of 27.12.2023. Publ. 27.12.2023, Bul. No. 36. (in Russian)].
Received 30.01.2024
Accepted 07.02.2024
About the Authors
Anton A. Sukhanov, PhD, Head of the Department of Family Planning and Reproduction, Tyumen Regional Perinatal Center, 1 Daudelnaya str., Tyumen, 625002, Russia; Associate Professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Tyumen State Medical University, Ministry of Health of Russia,10 Permyakov str., Tyumen, 625013, Russia, saa2505anton@yandex.ru, https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9092-9136
Galina B. Dikke, Dr. Med. Sci., Professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology with a Course of Reproductive Medicine, F.I. Inozemtsev Academy of Medical Education, 22 Liter M, Moskovskiy Ave., Saint Petersburg, 190013, Russia, galadikke@yandex.ru, https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9524-8962
Viktor A. Mudrov, Dr. Med. Sci., Associate Professor, Associate Professor of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Faculty of Pediatrics and Faculty of Additional Professional Education, Chita State Medical Academy, Ministry of Health of Russia, 39a, Gorkogo str., Chita, 672000, Russia,
mudrov_viktor@mail.ru, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5961-5400
Irina I. Kukarskaya, Dr. Med. Sci., Professor of the Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reanimatology with a Course of Clinical Laboratory Diagnostics, Tyumen State Medical University, 10 Permyakov str., Tyumen, 625013, Russia; Chief Physician, Tyumen Regional Perinatal Center, 1 Daudelnaya str., Tyumen, 625002, Russia;
Chief Specialist in Obstetrics and Gynecology, Department of Health of the Tyumen Region, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8275-3553
Corresponding author: Anton A. Sukhanov, such-anton@yandex.ru



