Эндометриоз является распространенным гинекологическим заболеванием, характеризующимся болью и бесплодием и поражает во всем мире практически каждую десятую женщину репродуктивного возраста [1]. Отмечено, что в структуре больных наружным генитальным эндометриозом неуклонно возрастает число больных с глубоким инфильтративным эндометриозом (ГИЭ), а также его рецидивов. ГИЭ характеризуется инвазивным прогрессирующим ростом с вовлечением в патологический процесс смежных органов, сопровождающимся выраженным болевым синдромом, оказывающим негативное влияние на качество жизни больных, что обусловливает необходимость углубленного изучения патогенеза заболевания и разработку новых эффективных схем терапии [2].
Молекулярные основы этого заболевания недостаточно известны. Существует большая гетерогенность среди пациентов в отношении фенотипических проявлений заболевания и связанных с ними тяжести симптомов. Эктопическая ткань эндометрия ведет себя подобно эутопическому эндометрию и имеет ту же реакцию на эндокринные раздражители. С гистологической точки зрения эндометриоидные поражения образуют сложную сеть железистых и стромальных структур, смешанных с сосудистыми, воспалительными и фибромышечными элементами [3]. Несмотря на многолетние исследования в лучших лабораториях мира, не разработаны неинвазивные диагностические маркеры эндометриоза и отсутствуют эффективные методы лечения.
Эндометриоз, особенно его инфильтративные формы, имеет много общих свойств с раком. Особенностью глубокого эндометриоза является его способность проникать в окружающие ткани и иногда метастазировать в лимфатические узлы и за пределы брюшной полости [4]. Повреждения клональные, происходящие из отдельных клеток, имплантируемых в нетипичных местах. В обоих процессах важную роль играет активация воспалительного процесса, наряду с окислительным стрессом, повышенной пролиферативной активностью, нарушенной регуляцией апоптоза и ангиогенеза [5]. Многие факторы, используемые сегодня в качестве мишени для терапии рака, могут проявлять себя аналогично и при эндометриозе.
Eph-рецепторы и их лиганды действуют как промотор опухоли, связанный с пролиферацией, инвазией и метастазированием. В этом отношении особый интерес представляет эритропоэтин-продуцирующий гепатоцеллюлярный рецептор А2 (EphA2), являющийся членом крупнейшего семейства трансмембранных рецепторов тирозинкиназ и показавшего себя в качестве перспективной мишени для лечения рака [6]. В связи с этим целью настоящей работы явилось исследование характера экспрессии EphA2 в эндометрии здоровых женщин и в эктопических эпителиальных клетках при ГИЭ.
Материалы и методы
Ретроспективно были исследованы образцы ткани эндометрия у 22 пациенток, которые были разделены на 4 группы: с колоректальным ГИЭ – 4 пациентки, с раком эндометрия – 9; в качестве контроля обследованы женщины с трубно-перитонеальным фактором бесплодия, из которых 5 – в пролиферативной фазе и 4 – в секреторной фазе цикла. Были взяты парафинированные образцы ткани эндометрия толщиной 4 мкм. У пациенток с ГИЭ исследовали срез эктопического эндометрия в зоне поражения, у женщин с раком эндометрия срезы пораженного участка изучались в области аденокарциномы эндометрия.
Образцы тканей эктопического эндометрия (эндометриоидный инфильтрат) были взяты во время операции с помощью механических ножниц и мягкого зажима. Эутопический эндометрий был собран с помощью биопсии эндометрия (кюретажа). Диагнозы эндометриоз и рак эндометрия были установлены на основе гистологического и визуального осмотра возможных поражений ткани, степень тяжести эндометриоза – согласно пересмотренной классификации Американского общества фертильности (rAFS) и классификации ENZIAN. Показатель ENZIAN (ENZIAN score) позволяет не только описать локализацию, но и оценить тяжесть ГИЭ.
Для количественной оценки экспрессии EphA2 использовали стандартную технику иммуногистохимического (ИГХ) окрашивания депарафинизированных препаратов моноклональными антителами к рецептору EphA2, фирмы Abcam: Rabbit monoclonal [SP169] to Eph receptor A2, разведение 1:100. После депарафинизации восстановление антигенной активности проводили в PT Link («Dako») при температуре 97 °С в течение 20 мин в 10 мМ цитратном буфере рН 8,0. Остывшие стекла помещали во влажные камеры (для предотвращения высыхания срезов) и инкубировали 15 мин в 3% растворе перекиси водорода для блокирования эндогенной пероксидазы. Реакцию с первичными антителами проводили в течение 30 мин при комнатной температуре. Для визуализации мест связывания антител с антигенами использовали реакцию окисления субстрата 3,3-диаминобензидина (ДАБ) пероксидазой хрена (HRP) в присутствии перекиси водорода с образованием водонерастворимого конечного продукта коричневого цвета системы «EnVision» («Dako Cytomation»). Для правильной постановки ИГХ- реакций ставили положительные и отрицательные контроли. В качестве отрицательных контролей брали образцы исследуемых срезов, которые подвергали стандартной процедуре ИГХ-реакции, но без добавления первичных антител. Положительные контроли для каждого антитела выбирали в соответствии со спецификациями от фирмы-производителя
Все срезы ИГХ-окрашивания для EphA2 оценивали полуколичественным способом в соответствии с методом, описанным McCarty и соавт. [7], которая учитывает как интенсивность, так и процент клеток, окрашенных при каждой интенсивности. Интенсивности были классифицированы как 0 (без окрашивания), 1 (слабое окрашивание), 2 (отчетливое окрашивание), 3 (сильное окрашивание) и 4 (очень сильное окрашивание).
Статистический анализ проводили с использованием пакета программ MedCalc Statistical Software 11.5.0. Достоверность различия между сравниваемыми группами проводили с применением непараметрического U-критерий Манна–Уитни. Данные представлены в виде медианы (Ме) и квартилей Q1 и Q3 в формате Ме (Q1;Q3) Уровень статистической значимости при проверке нулевой гипотезы считали соответствующим p<0,5.
Результаты
ИГХ-исследования показали, что EphA2 присутствует в эпителиальных клетках нормального эндометрия в пролиферативной фазе (рис. 1, Б), в то время как в секреторной фазе он практически отсутствует (рис. 1, А).
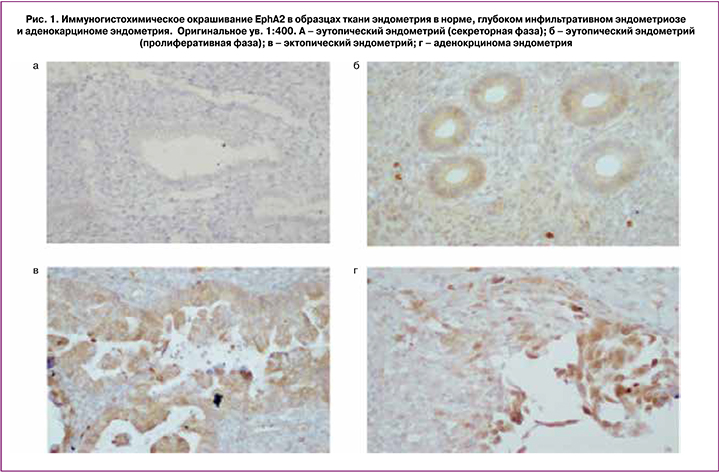
В эпителиальных клетках эктопического эндометрия (инфильтрат кишки) у пациенток с ГИЭ интенсивность окрашивания значительно выше и сравнима с интенсивностью экспрессии EphA2 в раковых клетках эндометрия (рис. 1, В, Г). При этом наиболее интенсивная окраска на внешней (апикальной) мембране.
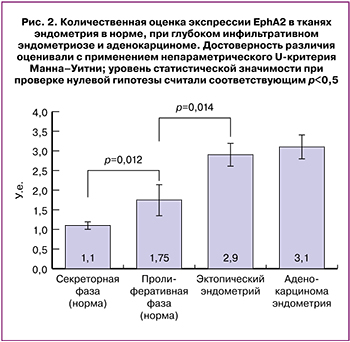 Результаты количественной оценки экспрессии EphA2 подтвердили значительно более высокую экспрессию рецептора в нормальном эндометрии в пролиферативной фазе, чем в секреторной: 2,0 (1,9;2,1) и 1,0 (1;1) соответственно, р=0,012. При этом в пролиферативной фазе экспрессия рецептора в эпителии эктопического эндометрия при ГИЭ статистически значимо выше, чем в эутопическом эндометрии, – 3,0 (2,9;3), р=0,01, и была сравнима с экспрессией в эпителиальных клетках аденокарциномы эндометрия – 3,0 (2,6;3,9). Эти результаты говорят о гиперэкспрессии EphA2 в эпителиальных клетках инфильтративного эктопического эндометрия.
Результаты количественной оценки экспрессии EphA2 подтвердили значительно более высокую экспрессию рецептора в нормальном эндометрии в пролиферативной фазе, чем в секреторной: 2,0 (1,9;2,1) и 1,0 (1;1) соответственно, р=0,012. При этом в пролиферативной фазе экспрессия рецептора в эпителии эктопического эндометрия при ГИЭ статистически значимо выше, чем в эутопическом эндометрии, – 3,0 (2,9;3), р=0,01, и была сравнима с экспрессией в эпителиальных клетках аденокарциномы эндометрия – 3,0 (2,6;3,9). Эти результаты говорят о гиперэкспрессии EphA2 в эпителиальных клетках инфильтративного эктопического эндометрия.
Обсуждение
Несмотря на то, что хроническое воспаление и значительно повышенная концентрация эстрогена являются общепризнанными характеристиками эндометриоза, точная этиология заболевания остается невыясненной. В первую очередь, это обусловлено мультифакторным характером заболевания, в котором участвуют генетические, эндокринные, иммунологические факторы [5, 8]. Эндометриоз, как и рак, характеризуется клеточной инвазией и неограниченным ростом. Кроме того, эндометриоз и рак сходны в других аспектах, таких как развитие новых кровеносных сосудов, уменьшение количества клеток, подвергающихся апоптозу, способность к инвазии и метастазированию [9]. Патогенез включает в себя потерю контроля над пролиферацией клеток.
Во многих раковых клетках выявлена повышенная экспрессия EphA2 как на поверхности мембраны, так и в цитоплазме; при этом повышенный уровень экспрессии ассоциируется с агрессивностью заболевания и плохим прогнозом выживания [6, 10, 11]. Исследования in vitro показали, что EphA2 является мощным онкопротеином, способным передавать злокачественный потенциал нетрансформированным эпителиальным клеткам [10]. В то же время, рядом авторов на экспериментальной модели было показано, что введение в кровь экспериментальных мышей пептидных лигандов к EphA2 приводит к элиминации опухоли и метастазов [6, 12–14]. Активация EphA2 осуществляется путем его фосфорилирования в результате связывания с лигандом эфрином (EphrinА1), приводящего к включению сигнального каскада для активации клеточной миграции, адгезии, ангиогенеза [15]. В отличие от других эфриновых рецепторов EphA2 экспрессируется только в эпителиальной ткани взрослых [16].
Обнаружено, что EphA2 эспрессируется на внешней мембране эпителиальных клеток эндометрия, тогда как его лиганд EphrinА1, выявляется на внешней мембране эмбриональных трофобластов. Предполагается, что взаимодействие между рецептором и лигандом опосредует установление маточной имплантации путем регуляции эмбрио-материнского контакта [17]. Предполагается также, что контакт между EphA2 и EphrinА1 обеспечивает пролиферацию и инвазию трофобласта в толщу децидуа. Этот же механизм взаимодействия между рецептором и лигандом, по-видимому, может участвовать и в процессе формирования эктопического эндометрия. Однако, данные об экспрессии EphA2 в эктопическом эндометрии человека до сих пор не описаны, и роль EphA2 в развитии эндометриоза и, особенно, агрессивного инфильтративного, по многим признакам похожего на раковую опухоль, остается неизвестной.
Учитывая тот факт, что поведение эктопического и, в особенности, инфильтративного эндометрия имеет много общих характеристик с злокачественной опухолью, представляет интерес оценить экспрессию эфринового рецептора в эндометриоидной ткани. Проведенные в настоящей работе ИГХ-сследования показали, что, действительно, в эпителиальных клетках инфильтративного эндометрия выявляется гиперэкспрессия EphA2, значимо более интенсивная, чем в эутопическом эндометрии, и сравнимая с уровнем экспрессии его в эпителии раковой ткани эндометрия.
Заключение
Таким образом, результаты, полученные в настоящей работе, еще раз подтверждают, что эндометриоз, по крайней мере, инфильтративный, имеет общие механизмы развития с неопластическими процессами. Рецептор EphА2, по- видимому, играет существенную роль в патогенезе эндометриоза. Эти предположения дают возможность для разработки новых диагностических и терапевтических подходов для лечения эндометриоза.



