Экстракорпоральное оплодотворение (ЭКО) в настоящее время является наиболее эффективным способом преодоления бесплодия. Согласно отчету Российской ассоциации репродукции человека (РАРЧ), частота наступления беременности при применении ЭКО составляет 34,8% в расчете на перенос эмбриона [1].
Установлено, что применение препаратов прогестерона в лютеиновую фазу цикла в программах ЭКО значимо повышает частоту наступления беременности в сравнении с плацебо [2].
Согласно клиническим рекомендациям Минздрава России «Женское бесплодие», после переноса эмбриона пациентке рекомендовано назначить препараты прогестерона или дидрогестерон [3]. Опубликованные метаанализы и систематические обзоры не показали отличий эффективности программ вспомогательных репродуктивных технологий (ВРТ) в зависимости от способа введения препаратов прогестерона (внутримышечный, подкожный, вагинальный, пероральный) [2, 4–8]. По данным глобального веб-опроса экспертов из 82 стран, вагинальный путь введения прогестерона является наиболее распространенным вариантом поддержки лютеиновой фазы [9].
Вагинальная форма использования прогестерона имеет такие неоспоримые преимущества, как хорошая абсорбция и высокая биодоступность, прямое влияние на эндометрий, отсутствие эффекта первичного прохождения через печень и снижение риска системных побочных эффектов (сонливость, седативный эффект), как при пероральном приеме, отсутствие инфильтратов и локальной болезненности, как при внутримышечном введении масляного раствора прогестерона [10]. Однако, несмотря на перечисленные преимущества, введение препарата прогестерона во влагалище в виде капсул в некоторых ситуациях приводит к возникновению случаев побочных реакций, таких как ощущение жжения и зуда во влагалище, гиперемия и отечность наружных половых органов. Также зафиксированы жалобы пациенток на дискомфортные ощущения из-за чувства «вытекания» препарата и неудобство его использования из-за необходимости неоднократного применения в течение дня [11, 12].
Понимание преимущества вагинального пути введения лекарств и физиологии влагалища привело к разработке специфических интравагинальных систем доставки лекарств для преодоления ограничений применения традиционных лекарственных форм, вводимых вагинальным путем. Были разработаны новые подходы, такие как использование мукоадгезивных или биоадгезивных полимеров, позволяющих продлевать высвобождение препарата [13, 14] и применять его в виде геля 1 раз в сутки.
Michnova L. et al. в 2017 г. в рамках рандомизированного клинического исследования продемонстрировали отсутствие отличий в отношении эффективности и безопасности при использовании микронизированного прогестерона в виде вагинального геля в сравнении с капсулами. Оценка переносимости препарата была определена после анализа анкет, заполненных пациентками. Биоадгезивный гель вызывал меньше субъективных жалоб, чем прогестерон в капсулах [15].
Ранее опубликованные нами промежуточные результаты сравнительного исследования эффективности вагинальных форм прогестерона по показателю частоты наступления клинической беременности в расчете на перенос эмбриона в программах ЭКО продемонстрировали отсутствие статистически значимых различий между группами, использующими прогестерон в виде вагинального геля или капсул [16].
Цель исследования: сравнить эффективность и переносимость двух форм вагинального микронизированного прогестерона – в виде капсул и геля – в программах ЭКО.
Материалы и методы
На базе ООО «Клинический институт репродуктивной медицины» с мая 2022 г. по декабрь 2023 г. был проведен сравнительный анализ эффективности и переносимости двух форм вагинального микронизированного прогестерона (в виде капсул и геля) в программах ЭКО, включивший 309 женщин.
Пациентки были обследованы согласно приказу Минздрава России № 803н от 31.07.2021 г. Всем пациенткам проводилась программа ЭКО с переносом 1 эмбриона стадии бластоцисты на 5-е сутки после пункции фолликулов. Полностью завершили исследование 307 женщин, 2 пациентки были исключены из исследования по причине потери связи с ними.
Критерии включения в исследование: возраст 25–35 лет, индекс массы тела (ИМТ) 18,5–34,9 кг/м2, нормальный овариальный резерв (уровень антимюллерова гормона (АМГ) не менее 1,2 нг/мл, число антральных фолликулов на 2–5-й день менструального цикла по данным ультразвукового исследования (УЗИ) не менее 5), отсутствие маточного фактора бесплодия/патологии эндометрия, отсутствие тяжелого мужского фактора бесплодия (азооспермия, олигоспермия), перенос 1 эмбриона 5-х суток развития в цикле стимуляции яичников качества 3–4 по классификации Гарднера с оценкой KIDScore не менее 7 баллов, отсутствие риска развития синдрома гиперстимуляции яичников.
Критерии исключения: возраст 36 лет и старше, ожирение 2–3 степени, патология матки/эндометрия, тяжелый мужской фактор бесплодия, получение более 15 ооцитов при пункции (риск развития синдрома гиперстимуляции яичников), показания к отмене переноса в «свежем» цикле ЭКО.
Эффективность программ ЭКО была определена по следующим показателям: частота клинической беременности, частота ранних репродуктивных потерь, частота живорождения.
Пациентки, подписавшие информированное согласие на участие в исследовании, согласно Федеральному закону «Об обращении лекарственных средств» от 12.04.2010 № 61, случайным образом были распределены на 2 группы. Пациенткам 1-й группы (n=154) в качестве гормональной поддержки был назначен препарат прогестерона в виде вагинального геля в дозе 90 мг в сутки («Миражэль», АО «Вертекс») со следующего дня после пункции фолликулов и далее в течение 14 дней после переноса эмбриона. Пациентки 2-й группы (n=155) в качестве гормональной поддержки второй фазы цикла получали микронизированный прогестерон в капсулах 200 мг 3 раза в сутки вагинально («Утрожестан», Besins Healthcare) со следующего дня после пункции фолликулов и далее в течение 14 дней после переноса эмбриона.
Контролируемая стимуляция яичников проведена по протоколу с антагонистами гонадотропин-рилизинг-гормона (ГнРГ), для стимуляции был использован препарат рекомбинантного ФСГ (рФСГ, «Гонал Ф», Merck Healthcare) в дозе 150–200 МЕ/сут. Антагонист ГнРГ («Цетротид», Merck Healthcare) в дозе 0,25 мг/сут назначался по гибкому протоколу (размер доминантных фолликулов 13–14 мм) и применялся до дня введения триггера включительно. При достижении 3 и более фолликулов размеров 17–19 мм был назначен хориогонадотропин альфа в дозе 6500 МЕ («Овитрель», Merck Healthcare); через 35–36 ч после назначения триггера проводилась пункция фолликулов трансвагинальным доступом под контролем УЗИ. Культивирование эмбрионов проведено в инкубаторе Embryoscope+ с системой искусственного интеллекта KIDScore. Классификация эмбрионов, достигших стадии бластоцисты, проводилась по классификации D.K. Gardner и W.B. Schoolcraft, дополнительно каждый эмбрион получал балльную оценку по шкале от 1 до 10 (показатель KIDScore). Эмбрионы, имеющие оценку более 7 баллов, относили к эмбрионам хорошего качества с высоким потенциалом для имплантации. На 5-е сутки после пункции фолликулов проводился перенос 1 эмбриона в полость матки. Через 14 дней после переноса эмбрионов проведен анализ сыворотки крови с целью определения концентрации хорионического гонадотропина человека (ХГЧ). Показатель более 100 мМЕ/мл расценивался как положительный результат. При отрицательном значении ХГЧ гормональная поддержка препаратами прогестерона была отменена; при положительном значении – прием препаратов прогестерона был рекомендован до 12 недель беременности. Частота клинической беременности оценивалась методом УЗИ через 24–30 дней после переноса эмбриона по визуализации плодного яйца в полости матки. Постановка на учет по беременности проводилась в сроке 7–8 акушерских недель беременности.
Оценка приверженности к проводимой терапии препаратами прогестерона осуществлялась путем анкетирования пациенток, которое проводилось через 14 дней после переноса эмбрионов; пациентам предлагалось ответить на 10 вопросов в формате «да/нет». Анкета содержала следующие вопросы.
1. Вас беспокоили вагинальные выделения после введения препарата?
2. Было ли у Вас раздражение в области наружных половых органов при применении препарата?
3. Беспокоил ли Вас зуд в области наружных половых органов при применении препарата?
4. Было ли ощущение «вытекания» препарата из влагалища?
5. Удобно ли Вам использовать препарат?
6. Были ли у Вас жалобы на тошноту при применении препарата?
7. Были ли у Вас жалобы на головную боль при применении препарата?
8. Были ли у Вас жалобы на нарушение стула (диарея, запор) при применении препарата?
9. Были ли у Вас жалобы на сонливость при применении препарата?
10. Было ли у Вас чувство уверенности в полном «усвоении» введенной дозы препарата?
Статистический анализ
Качественные признаки описывали простым указанием количества пациентов и доли (%) для каждой категории. Статистическую достоверность между этими признаками оценивали с помощью критерия Хи-квадрат с поправкой Йейтса и точного критерия Фишера. Все количественные признаки тестировались на нормальность распределения с помощью критерия Шапиро–Уилка. Учитывая, что распределение количественных признаков являлось нормальным, статистический анализ проводили с помощью критерия Стьюдента. Признаки описаны в виде среднего арифметического и стандартного отклонения. Различия считались значимыми при p<0,05.
Результаты
Пациентки обеих групп не отличались по основным клиническим характеристикам: возраст, ИМТ, уровень овариального резерва и запаса яйцеклеток (количество антральных фолликулов, данные АМГ, фолликулостимулирующего гормона (ФСГ)), а также по числу программ ЭКО в анамнезе (табл. 1). Также не выявлено статистически значимых отличий при анализе протоколов ЭКО. Суммарная доза рФСГ, число фолликулов, ответивших на стимуляцию, число ооцит-кумулюсных комплексов, число зрелых ооцитов стадии МII и показатель KIDScore, применяемый для оценки качества эмбриона, не отличались между группами. В день переноса эмбриона всем пациенткам проведено УЗИ органов малого таза и измерение толщины эндометрия, которая также не имела статистически значимых отличий между группами сравнения.
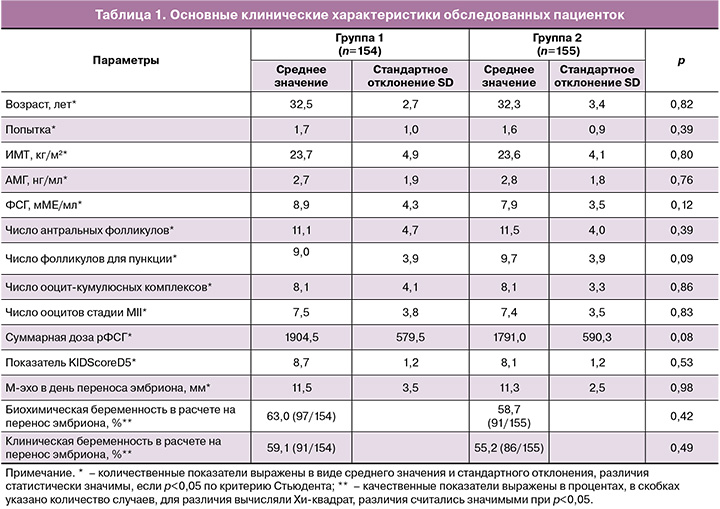
Частота клинической беременности в расчете на перенос эмбриона не имела статистически значимых отличий между группами и составила 59,1% (91 беременность после 154 переносов эмбрионов) и 55,2% (86 беременностей после переноса 155 эмбрионов) в 1-й и 2-й группах соответственно. Частота ранних репродуктивных потерь составила 14,2% (13 потерь беременности из 91) у пациенток 1-й группы и 15,1% – во 2-й группе (13 потерь беременности из 86); статистически значимых отличий между группами не установлено. Поздний выкидыш в сроке 18 недель беременности был зафиксирован у 1 пациентки из 1-й группы (причина – истмико-цервикальная недостаточность); у 2 пациенток 2-й группы потери беременности произошли в сроках 15 и 19 недель (2 выкидыша из 86 беременностей), также по причине истмико-цервикальной недостаточности; статистически значимых отличий между группами также не установлено. Частота живорождения в 1-й группе составила 49,4% (76 беременностей после 154 переносов эмбрионов завершились родами), во 2-й группе – 45,2% (70 беременностей после 155 переносов завершились родами), статистически значимых отличий между группами не выявлено. Также между группами не выявлено различий по способу родоразрешения: в 1-й группе доля абдоминальных родов составила 55,3%, во 2-й группе – 50%, доля естественных родов – 44,7% в 1-й группе и 50% – во 2-й группе. В 1-й группе все 76 родов были срочными (100%), а во 2-й группе срочными родами завершились 65/70 (92,9%); доля преждевременных родов во 2-й группе составила 7,1% (5/70): преждевременные роды произошли в сроках 32, 33, 34 (2 случая) и 36 недель; по сроку родоразрешения между группами были выявлены статистически значимые отличия (табл. 2).
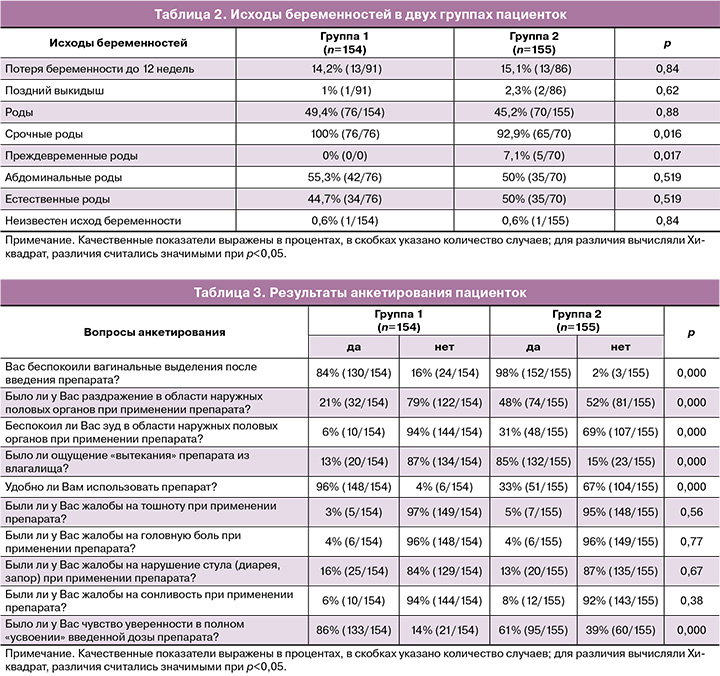
При оценке переносимости проводимой терапии препаратами прогестерона, согласно опросу, пациентки, использующие вагинальный гель, отмечали удобство применения и дали больше положительных ответов на вопрос «Было ли у Вас чувство уверенности в полном "усвоении" введенной дозы препарата?» Пациентки, применявшие вагинальный прогестерон в виде капсул, чаще отмечали такие нежелательные реакции, как вагинальные выделения после введения препарата, ощущение раздражения и зуда в области наружных половых органов, ощущение «вытекания» препарата из влагалища (табл. 3).
Обсуждение
В естественном цикле подготовка эндометрия к имплантации эмбриона осуществляется под влиянием эстрадиола и прогестерона, продуцируемых клетками растущего фолликула. Резкое повышение уровня лютеинизирующего гормона в поздней фолликулярной фазе приводит к созреванию ооцита, разрыву доминантного фолликула, формированию желтого тела, клетки которого начинают вырабатывать прогестерон. После имплантации эмбриональный ХГЧ стимулирует желтое тело посредством индукции антиапоптотического белка Mcl-1, которое продолжает секретировать эстроген и прогестерон для поддержания беременности [17].
В циклах ЭКО необходимым этапом успешного лечения бесплодия после стимуляции роста фолликулов и забора яйцеклеток следует назначение высоких доз прогестерона, что обусловлено следующими факторами: суперфизиологическая продукция стероидов тека-лютеиновыми кистами после пункции фолликулов провоцирует преждевременный лютеолиз и, как следствие, снижение выработки ЛГ гипофизом по принципу отрицательной обратной связи [18]; использование в циклах стимуляции агонистов и антагонистов ГнРГ для предотвращения «паразитарного» пика ЛГ также подавляет необходимую для активации желтого тела выработку ЛГ [19]; травма фолликула при его пункции также способствует нарушению эндогенной продукции прогестерона [20].
Установлено, что применение препаратов прогестерона в лютеиновую фазу цикла в программах ЭКО значимо повышает частоту наступления беременности в сравнении с плацебо [2]. Рекомендовано назначать прогестерон в период до 48 ч или в период 48–96 ч после забора яйцеклеток [4]. При отсутствии беременности лекарственные препараты отменяются с началом менструальноподобного кровотечения. Длительность их назначения в случае наступления беременности определяется врачом акушером-
гинекологом в соответствии с инструкцией по применению, особенностями течения беременности и анамнезом пациентки, но обычно продолжается до 12 недель беременности [3].
В настоящее время не существует единого протокола для выбора того или иного препарата прогестерона в конкретной клинической ситуации [11]. Введение препаратов прогестерона может быть осуществлено в виде внутримышечных и подкожных инъекций, вагинальных капсул, геля, пессария, а также таблеток и капсул, применяемых перорально.
Проведенные метаанализы и систематические обзоры не показали отличий эффективности программ ВРТ в зависимости от способа введения препаратов прогестерона (внутримышечный, подкожный, вагинальный, пероральный) [2, 4–8]. Вагинальный путь введения прогестерона является наиболее предпочитаемым специалистами во всем мире; такой путь удобен, эффективен и безопасен. Стандартные вагинальные формы лекарственных препаратов в виде капсул являются недорогими и простыми в использовании, но в ряде случаев сопровождаются жалобами пациенток на неприятные ощущения, связанные с выделением препарата из влагалища, а также неудобством в связи с необходимостью введения капсул 2–3 раза в сутки. Преимущество вагинального геля в том, что выделение прогестерона происходит с относительно постоянной скоростью в течение длительного времени, что на практике позволяет вводить препарат однократно в течение суток [11].
Во многих исследованиях проведена сравнительная оценка биоадгезивного геля с вагинальными капсулами и внутримышечной формой введения прогестерона. Результаты показывают сопоставимую эффективность биоадгезивного геля в сравнении с другими формами прогестерона и его лучшую переносимость [15, 21, 22]. В настоящем исследовании для поддержки лютеиновой фазы цикла применялся вагинальный гель «Миражэль» (АО «Вертекс», Россия), который доказал биоэквивалентность оригинальному препарату «Крайнон» (Мерк Сероно Лимитед, Великобритания), а также в предыдущих наблюдениях показал сопоставимую эффективность [12, 23]. В препарате «Миражэль», как и в оригинальном препарате, прогестерон в виде вагинального геля включен в полимерную систему доставки, которая связывается со слизистой оболочкой влагалища и обеспечивает непрерывное высвобождение прогестерона в течение суток.
В нашем исследовании сравнительный анализ применения прогестерона в виде вагинального геля в дозе 90 мг в сутки («Миражэль», АО «Вертекс) и микронизированного прогестерона в капсулах 200 мг 3 раза в сутки вагинально («Утрожестан», Besins Healthcare) показал сопоставимые результаты по частоте клинической беременности, частоте ранних репродуктивных потерь, частоте живорождения. В группе пациенток, применявших «Миражэль» после переноса эмбриона и до 12 недель беременности, была выше частота срочных родов, в сравнении с группой, использующих «Утрожестан»; но на течение беременности и исход родов влияет большое число других факторов, поэтому, выявленные отличия по исходам беременностей требуют дальнейшего изучения.
Анкетирование пациенток показало, что применение препарата в виде геля удобнее и комфортнее, что подтверждают предыдущие сравнительные исследования [16, 18, 21, 22]. Для акушеров-гинекологов при выборе препарата вагинального микронизированного прогестерона для поддержки лютеиновой фазы в протоколах ЭКО, при наличии сопоставимой эффективности, важными критериями могут стать переносимость и удобство для пациентки.
Заключение
Сравнительная оценка вагинального применения препаратов микронизированного прогестерона в виде геля и капсул продемонстрировала высокую эффективность. Использование вагинального геля переносилось лучше и было удобнее согласно опросу пациенток. Гель «Миражэль» может применяться для поддержки лютеиновой фазы в программах ЭКО.



