Разработка агонистов гонадотропин рилизинг-гормона (ГнРГ) позволила значительно расширить возможности лечения эстрогензависимых состояний в гинекологии, включая эндометриоз, лейомиому матки, преждевременное половое созревание и рак эндометрия [1–3]. Первоначально введение агонистов ГнРГ (фаза стимуляции до 10–15 суток) вызывает стимуляцию гонадотропинов гипофиза – фолликулостимулирующего гормона (ФСГ) и лютеинизирующего гормона (ЛГ), что приводит к усилению стероидогенеза в яичниках; таким образом, повышается уровень эстрадиола (Е2), но кратковременно. Дальнейший эффект пролонгированных форм агонистов ГнРГ снижает уровень гонадотропинов и гонадных стероидов путем ингибирования выработки ФСГ и ЛГ вследствие десенсибилизации рецепторов ГнРГ гипофиза, что является основой клинического эффекта агонистов. В свою очередь, это приводит к гипоэстрогении и другим физиологическим эффектам, связанным с этим [1, 4–6].
Агонисты ГнРГ, значительно подавляя стероидогенез, приводят к ановуляции и временной вторичной аменорее, что способствует регрессии эндометриоидных очагов поражения и уменьшению клинических симптомов заболевания. Однако гипоэстрогения, вызванная длительным применением агонистов ГнРГ, осложняется появлением побочных эффектов в виде симптомов менопаузы, таких как приливы, потливость, сухость влагалища, снижение либидо, головная боль и эмоциональная лабильность. Одним из серьезных последствий в результате долгосрочного лечения агонистами ГнРГ является остеопороз. После отмены длительной терапии минеральная плотность костной ткани долго восстанавливается до исходных значений [1, 6–9].
Агонисты ГнРГ могут применяться в качестве основного медикаментозного компонента лечения или адъювантной терапии; однако из-за вышеописанных негативных последствий на организм женщины курс введения данных препаратов ограничивается шестью месяцами при исключении приема add-back терапии [9–11]. В связи с этим важной задачей является осуществление поиска вариантов уменьшения побочных действий с одновременным сохранением эффективности агонистов ГнРГ, включая применение эстрогеновых добавок или модификацию режима назначения [3, 6, 12, 13].
Недавние исследования ряда авторов показывают возможность увеличения интервала между инъекциями до 5–6 недель. Кроме того, согласно исследованию Broekmans F.J. et al. [6] после однократного приема депо-формы трипторелина подавление секреции ЛГ сохраняется в течение 8 недель, уровень ФСГ нормализуется в течение 3–4 недель, а уровень 17β-Е2 начинает восстанавливается через 7–8 недель. Все сказанное послужило основанием для пробного удлинения интервала между инъекциями Бусерелина-депо 3,75 мг и исследования изменения профиля ряда гормонов.
В своем исследовании Vercelini P. et al. [14] провели поиск в системе MEDLINE PubMed и Embase в период с января 1980 г. по январь 2023 г., применяя следующие ключевые слова: (endometriosis OR adenomyosis) AND (GnRH-agonists OR gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists OR triptorelin OR leuprorelin OR goserelin OR buserelin OR nafarelin). Были отобраны только исследования, посвященные альтернативным режимам применения агонистов ГнРГ у женщин с эндометриозом и/или аденомиозом: интермиттирующая терапия, направленная на снижение эстрогенов (Chiu C.C. et al. [8]; Resta C. et al. [15]); режим снижения дозировки (Surrey E.S. et al. [16]; Gong L. et al. [17]); и режим увеличения межинъекционного интервала (Kang J.L. et al. [18]; Liu D.Y. et al. [10]). Общей целью проведенных исследований является снижение профиля и выраженности побочных эффектов и финансовой нагрузки лечения при сохранении его эффективности [14].
Цель исследования: оценка клинико-гормонального статуса пациенток с наружным генитальным эндометриозом при назначении Бусерелина-депо 3,75 мг с 6-недельными и 4-недельными интервалами между введением препарата в послеоперационном периоде.
Материалы и методы
В период с июня 2021 г. по март 2022 г. на базе ФГБОУ ВО СПбГПМУ МЗ РФ ПЦ и ГБУ НИИ СП им. И.И. Джанелидзе были прооперированы 20 пациенток с эндометриозом. Нами специально были отобраны для исследования формы с выраженным болевым синдромом (не менее 8 баллов по визуально-аналоговой шкале (ВАШ) до операции), с поверхностным эндометриозом, при котором выполнялась только вапоризация очагов (I и II стадии ASRM, 9 и 11 пациенток, соответственно). В исследование не были включены случаи эндометриом яичников и глубокого инфильтративного эндометриоза, для того чтобы исключить влияние радикальности хирургического лечения на динамику болевого синдрома, а также фактора повреждения яичниковой ткани на динамику гормонов.
В группе исследования I (n=10) после лапароскопии была проведена адъювантная терапия агонистом ГнРГ Бусерелин-депо 3,75 мг 1 раз в 6 недель. Контрольная группа II (n=10) сформирована нами из пациенток с такими же критериями включения; им назначен Бусерелин-депо 3,75 мг каждые 4 недели.
У пациенток обеих групп введение Бусерелина-депо проводили в раннюю фолликулярную фазу (со 2-го по 6-й день менструального цикла). С целью представления результатов о степени снижения уровня гормонов в сыворотке проводился анализ крови на ФСГ, ЛГ и Е2 перед каждой инъекцией и в конце периода лечения (24-я неделя исследования), а также каждые 4 недели до возобновления менструации. Для оценки степени снижения уровня гормонов после введения Бусерелина-депо применяли статистический критерий суммы рангов Уилкоксона. Эффективность терапии оценивали по снижению Е2 до терапевтического коридора (30–60 пмоль/л). Уровни ФСГ, ЛГ и Е2 оценивали в сроки 0 (исходный), 4 ,8 ,12 ,18 и 24 недели, антимюллерова гормона – изначально и на 18-й неделе.
В указанные сроки пациентка заполняла шкалу ВАШ и в произвольной форме отмечала нежелательные явления. Болевой синдром был представлен дисменореей, диспареунией и тазовой болью, не связанной с менструацией. Интенсивность боли оценивалась по ВАШ от 0 (отсутствие боли) до 10 (сильная боль, ограничивающая трудоспособность или, являющаяся причиной отсутствия половой жизни). Общий балл боли был получен путем суммирования трех вариантов болевого синдрома (максимальный балл=30). Степень выраженности проявлений индуцированного климактерического синдрома оценивалась на основании менопаузального индекса Куппермана (0–11 баллов – отсутствие проявлений менопаузального синдрома, 12–34 – легкой степени, 35–58 – средней тяжести, более 59 баллов – тяжелый менопаузальный синдром). Ультразвуковое исследование органов малого таза выполняли на 0, 4, 12 и 18-й неделях (4-кратно).
Результаты
В группах I и II средний возраст пациенток составил 32,8±6,7 лет, а индекс массы тела – 19,3±2,8 кг/м2. У женщин, участвующих в исследовании, был эндометриоз I и II стадии ASRM (34 и 66%, соответственно). Большинство (19/20 (95%)) пациенток до начала лечения жаловались на дисменорею, у 6/20 (30%) были тазовые боли, не связанные с менструацией, и у 3/20 (15%) имелась диспареуния. Группы были идентичны по степени тяжести эндометриоза и характеристике предъявляемых жалоб.
Концентрация ФСГ в сыворотке крови в группах I и II в самом начале терапии составила 6,21±0,72 МЕ/л и 7,01±0,59 МЕ/л, соответственно, и на 6-й неделе лечения была минимальной (3,19±0,31 МЕ/л и 2,26±0,22 МЕ/л, соответственно). Далее мы наблюдали постепенное повышение концентрации ФСГ и выравнивание его значений к 28-й неделе (рис. 1).

Значения сывороточного ЛГ в группах I и II до начала терапии составили 3,41±0,52 МЕ/л и 2,92±0,61 МЕ/л. На 6-й и 4-й неделе лечения отметили его снижение до 1,33 и 1,18 МЕ/л, соответственно. Следует подчеркнуть, что на 28-й неделе (через 10 недель после последней инъекции) концентрация ЛГ оставалась ниже исходной (2,68±0,67 МЕ/л) (рис. 2).
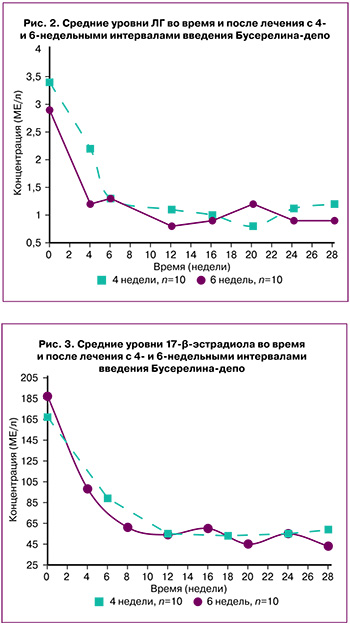
Концентрация E2 в сыворотке крови в группах I и II до адъювантной терапии составила 187,87±34,78 пмоль/л и 172,32±28,73 пмоль/л, соответственно. На 6-й неделе лечения отмечено снижение Е2 до 98,11±12,16 пмоль/л и 89,32±19,44 пмоль/л, соответственно. В течение дальнейшего наблюдения (28 недель) значение Е2 было ниже 70 пмоль/л в обеих группах (рис. 3).
В среднем, менструации возобновлялись в группе I через 78 (56–82) суток после четвертой инъекции, а в группе II – через 82 (71–88) суток после шестой инъекции.
Средний балл тазовой боли по ВАШ до начала терапии составил 9,9.
В период лечения отмечено его снижение: 3,3 балла – в группе I и 2,4 балла – в группе II. После возобновления менструации средний балл боли по шкале ВАШ составил 3,1 и 2,5, соответственно.
Во время лечения отмечены такие нежелательные явления, как головная боль, потливость и приливы, которые по менопаузальной шкале Куппермана имели легкую степень и значительно не ухудшали качество жизни пациенток. Это отмечали все пациентки к 4-му месяцу терапии при 4-недельном режиме (группа II) и 6/10 группы I (6-недельный режим). В группе I пациентки отмечали незначительные ациклические кровянистые выделения. Они появлялись 2–3 раза за 6-месячный период наблюдения и продолжались 2–3 суток у 4/10 женщин. Несмотря на это, ультразвуковой мониторинг показал, что ни в одном случае в I и II группах не было отмечено ни роста эндометрия (все мониторинговые показатели М-эхо были в пределах 1–2 мм), ни признаков фолликулогенеза. Этот факт, главным образом, наряду с гипоэстрогенией, может являться основанием для проведения дальнейшего исследования, подтверждающего одинаковую эффективность 4- и 6-недельного интервала назначения агонистов ГнРГ при лечении болевых проявлений эндометриоза.
Обсуждение
При применении агонистов ГнРГ происходит подавление уровня половых гормонов, что вызывает атрофию, как самого эндометрия, так и эктопических эндометриоидных гетеротопий. Это явление называется индуцированной медикаментозной гипоэстрогенией, которая является обратимой. После прекращения действия агонистов ГнРГ у пациенток репродуктивного возраста полностью восстанавливается гипоталамо-гипофизарная связь.
В данном исследовании мы вводили по одной стандартной дозе Бусерелина-депо 3,75 мг с интервалом в 6 недель (всего 4 дозы за 18 недель терапии); тем не менее, общий период наблюдения составил 48 недель, поскольку проводился контроль за состоянием в течение 6 месяцев после последней инъекции (в том числе, и контроль овуляторной функции, состояния эндометрия, оценка болевого синдрома). Общий период лечения при стандартном режиме введения был таким же, как и при увеличенном интервале (24 недели), однако было введено по одной дозе каждые 4 недели (всего 6 доз за 20 недель терапии) с дополнительным наблюдением в течение 4 недель.
С начала лечения и до 10 недель после последней инъекции концентрации гормонов ФСГ, ЛГ и Е2 в крови достоверно снизились. Темп снижения и достигнутые уровни достоверно не отличались при обоих режимах назначения. Нормальный менструальный цикл в репродуктивном возрасте восстанавливается через 2–3 месяца после отмены препарата. Возобновление менструации в нашем исследовании происходило в среднем через 78 дней после пролонгированного режима дозирования и через 82 дня при стандартном режиме введения. Болевой синдром, вызванный эндометриозом, значимо снижался на фоне применения Бусерелина-депо в обеих группах и не зависел от режима назначения препарата, одинаково положительно влияя на качество жизни пациенток.
Broekmans F.J. et al. [6] оценивали функцию гипофиза и яичников после однократного внутримышечного введения депо-трипторелина в дозе 3,75 мг. Секреция Е2 постепенно восстанавливалась в течение 7–8-й недели после инъекции, а менструации возобновились между 11-й и 13-й неделями. Cheung T.K. et al. [13] провели рандомизированное двойное слепое перекрестное исследование, в котором участницам с эндометриозом назначались 3 дозы трипторелина внутримышечно по 3,75 мг с интервалом в 4 недели, за которыми следовали 3 дозы лейпрорелина внутримышечно по 3,75 мг с 6-недельным интервалом (n=27) или в обратной последовательности теми же двумя препаратами депо ГнРГ (n=21). Эффективность обоих режимов в подавлении концентраций Е2, ФСГ и ЛГ в сыворотке крови была сходной, а относительная частота и тяжесть нежелательных эффектов были сопоставимы. Однако продолжительность супрессии гипофиза, индуцированной трипторелином, была значительно больше, чем у лейпрорелина. Время до повторного появления спонтанной менструации также было значительно больше после последней дозы трипторелина (последовательность лейпрорелин-трипторелин; 129±7 дней), чем после последней дозы лейпрорелина (последовательность трипторелин-лейпрорелин; 104±5 дней).
С целью оценки продолжительности десенсибилизации гипофиза после однократной внутримышечной инъекции 3,75 мг трипторелина или лейпрорелина Matteo М. et al. [19] набрали в исследование 60 женщин с эндометриозом I–II стадий и вводили депо-препарат агониста ГнРГ на 21-й день цикла однократно. Основываясь на последовательных еженедельных определениях уровней ФСГ, ЛГ и Е2 в сыворотке крови, оба препарата аналогичным образом подавляли ось гипофиз–яичники до 4-й недели после инъекции. С 5-й по 8-ю неделю концентрации ФСГ и ЛГ в сыворотке крови были выше в группе лейпрорелина, чем в группе трипторелина. Полное угнетение функции яичников сохранялось до 6-й недели после однократной инъекции лейпрорелина и до 7-й недели после однократной инъекции трипторелина.
Yang Y. et al. [11] провели рандомизированное контролируемое исследование по изучению эффекта послеоперационного перорального приема даназола в дозе 600 мг/сутки (n=20) в сравнении с трипторелином в дозе 3,75 мг каждые 6 недель (n=20) в течение 6 месяцев после операции по поводу эндометриоза III или IV стадии. Различий в снижении выраженности боли между группами не наблюдалось, но трипторелин переносился лучше и был связан с более высокой частотой аменореи, чем даназол. Уровни ФСГ, ЛГ и Е2 в сыворотке крови снижались достоверно трипторелином, несмотря на увеличенный до 6 недель интервал между четырьмя введенными дозами.
Kang J.L. et al. [18] сформировали выборку из 70 пациенток с симптоматическим аденомиозом или эндометриозом для 6-месячного курса трипторелина в дозе 3,75 мг внутримышечно каждые 6 недель (n=35), или каждые 4 недели (n=35). Авторы не наблюдали существенных различий между группами в степени подавления функции гипофиза и яичников, частоте индуцированной аменореи, снижении оценки боли или частоте побочных эффектов.
Liu D.Y. et al. [10] провели небольшое параллельное когортное исследование с участием 36 женщин, которые применяли послеоперационный трипторелин в дозе 3,75 мг в течение 24 недель. Авторы не наблюдали различий в уровнях E2, ФСГ и ЛГ в сыворотке крови у 8 женщин, получавших стандартную 4-недельную схему, по сравнению с 10 женщинами, получавшими стандартную дозу плюс пероральный прием тиболона в дозе 1,25 мг/сутки, и 16 женщинами, получавшими пролонгированную интервальную 6-недельную схему. Время до возобновления менструаций было одинаковым в трех исследуемых группах и составило 81±18 дней в группе с обычным режимом дозирования и 76±22 дня в группе с увеличенным интервалом. Никаких различий в облегчении болевых симптомов авторами обнаружено не было.
Приведенные выше данные подтверждают, что режим дозирования агонистов ГнРГ с увеличенным до 6 недель интервалом не снижает клинического эффекта в сравнении со стандартным применением.
Заключение
Наше исследование показало, что у пациенток эффективность применения Бусерелина-депо с увеличенным до 6 недель интервалом между инъекциями эквивалентна эффективности введения в стандартном режиме (каждые 4 недели).
Такой режим на всем протяжении исследования (28 недель) приводил к значимому уменьшением болевого синдрома. Однако побочные эффекты на протяжении всего исследования были менее выражены. Ультразвуковой мониторинг не выявил признаков фолликулогенеза или роста эндометрия при стабильно низком уровне E2 и ФСГ.
Также к преимуществам пролонгированного режима введения относится снижение стоимости лечения за счет меньшего количества доз при достаточной гормональной супрессии.
Следует отметить, что необходимо проведение дальнейших исследований для уточнения эффективности пролонгированного межинъекционного интервала.



