Informativeness of estimating CD34 expression in the development of pelvic varicose veins in women
Objective. To determine expression levels of the endothelial marker for angiogenesis CD34 in the pelvic veins in women depending on the severity and recurrence of pelvic varicose veins (PVV).Kolesnikova L.I., Gus A.I., Taranenko A.V., Semendyaev A.A., Stupin D.A., Shcherbatykh A.V., Kalyagin A.N., Kolesnikov S.I.
Materials and methods. The expression level of CD34 in the pelvic wall veins was examined in 79 women, of whom 58 had PVV of various severity, 11 experienced recurrences of PVV, and 10 had no venous diseases.
Results. As the course of PVV deteriorated, the number of CD34+ cells in the pelvic wall veins progressively increased and the greatest CD34+ cell counts were found in the newly forming vessels.
Conclusion. The revealed association between the severity of PVV, the recurrence of the disease and the increase in local angiogenic activity is a compensatory mechanism in the setting of hypoxia and trophic changes in the pelvic organs.
Keywords
The current literature is lacking sufficient coverage of the evidence regarding the angiogenic mechanisms of the development of pelvic varicose veins (PVV) in women. Specific features of the structure and functional state of the female pelvic vein network predispose to the onset and progression of varicose veins. Even under physiological conditions, regional phlebohemodynamics is prone to physiological stasis and transient regurgitation. It has been observed that disorders of the venous blood flow do not always stop even after the elimination of the refluxogenic zones - the morphological substrate of the disease [1]. Incomplete recovery after previous treatment is associated with the formation of new vessels contributing to pelvic vein reflux [2, 3].
Some progress in clarifying the angiogenic activity of the pelvic veins in women with PVV has been made with the development of specific endothelial cell markers.
This study aimed to determine expression levels of the endothelial marker for angiogenesis CD34 in the pelvic veins in women depending on the severity and recurrence of pelvic varicose veins (PVV).
Material and methods
The study comprised 79 women aged 20–50 years who gave informed consent to participate in the study. Among women included in the study group (n = 69), 58 had PVV of different severity and 11 experienced PVV recurrences after endovascular therapy. Ten women without venous diseases made up a control group. The age of the participants ranged from 20 to 50 years and was comparable between the groups; the mean age was 34.3 ± 3.7 and 36.8 ± 4.5 years in the control and study group, respectively.
Duplex sonographic findings showed that 25, 19, and 14 patients had grade I, II, and III PVV, respectively, and the recurrence of the disease was verified in 11 women.
Immunohistochemical (IHC) studies were used to examine the expression of an endothelial marker of angiogenesis CD34 in varicose vein specimens of the ovarian pool. In the control group, the vein specimens were taken from healthy areas of isthmic part of the Fallopian tube during laparoscopic sterilization. Refluxogenic areas of the veins were detected using our proprietary “Functional hemodynamic stress test” (RF Patent No. 2646563) [4].
Phlebohemodynamics of the small pelvis was assessed by vascular duplex sonography using the Voluson E10 ultrasound system (USA). Biopsy and injection sclerotherapy was performed under a three-dimensional visual control using Laser optic system (USA-Germany) and the Cooper surgical (USA) and Karl Storz (Germany) laparoscopic equipment.
Morphological and IHC material was prepared in automated preparation devices “Sakura” (Japan). For histological examination, tissue sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin, for IHC - monoclonal antibodies to CD34 (R & D systems, USA). Local angiogenesis was assessed by the change in the content of CD34+ expressing cells in the vein walls, taking into account the severity of PVV and during the recurrence of the disease, in comparison with that in the control group.
The level of CD34 expression in vein tissue specimens was assessed using a Quantimet-550 IW computerized image analyzer (Leica, UK) on a 6-point scale: score 2 - 20% of CD34+ expressing cells, score 4 - 20-40% of CD34+ expressing cells, score 6 - more than 40% of CD34+ expressing cells.
Statistical analysis was performed with Statistica 6.1 (Stat-Soft Inc., USA, the license holder - Scientific Center for Family Health and Human Reproduction Problems). To compare variables of samples with a normal distribution, Student’s t-test was used. If the distribution of the data was not normal, the Pearson χ2 test was used. The relation between variables was also assessed with a nonparametric Spearman correlation coefficient. Statistical significance was assumed for p < 0.05.
Results and discussion
 The expression level of CD34 in the pelvic wall varicose veins in patients with varying degrees of severity and recurrence of PVV is presented in the table and Figure 1.
The expression level of CD34 in the pelvic wall varicose veins in patients with varying degrees of severity and recurrence of PVV is presented in the table and Figure 1.
The study findings indicate that the expression level of CD34 significantly increased (p < 0.05) with worsening of the course of the disease: with grade I PVV, the mean content of CD34 + cells corresponded to 3.25 ± 0.14 points, which was 24.0% higher than the expression level in women of the control group; with grade II PVV it was 4.41 ± 0.23 points and 44.0% higher than the standard values, with grade III PVV - 5.66 ± 0.48 points, i.e., 56.4% higher than the threshold value. The highest level of CD34 + cells was found in patients with PVV recurrence and was 73.6% higher than in the control group.
There was a positive correlation (p <0.05) between the levels of CD34 + cells in the wall of normal veins and in PVV of varying degrees of severity: grade I - r = 0.218; grade II - r = 0,452; grade III - r = 0.536, and in women with disease recurrence - r = 0.729, which may indicate the diagnostic significance of the studied marker in assessing the PVV severity.
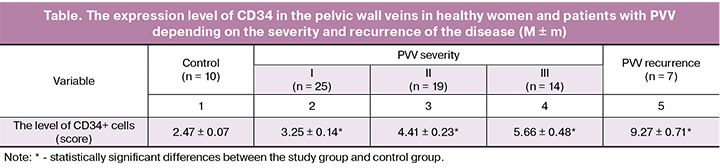
A comparative analysis of the CD34 + cell levels in the samples of normal (Fig. 2) and varicose veins (Fig. 3) showed that CD34 + cells in normal vessels were arranged in a uniform layer around the circumference of the vein, whereas in varicose vein specimens the picture was significantly different: the endothelial layer was characterized by an uneven distribution of cells, the predominance of CD34 expression in some areas and a large number of expressed endothelial cells.
Discussion
Angiogenesis serves as a protective mechanism aimed at delivering oxygen and nutrition to damaged tissues [5, 6]. Complications associated with PVV — a chronic course, frequent recurrence, and a short period of remission — are a serious clinical problem [7, 8]. Functional hemodynamic stress test under laparoscopic control revealed some pattern in women with PVV: an increased volume of the veins with numerous small blood vessels appearing around them. This phenomenon has stimulated interest in the investigation of the nature of the angiogenic activity of the cellular elements of the pelvic veins in women with PVV, taking into account the severity of the pathological process and the recurrence of the disease.
 The use of modern IHC technologies has allowed an assumption that angiogenesis affects the formation and dynamics of the course of this pathology in women.
The use of modern IHC technologies has allowed an assumption that angiogenesis affects the formation and dynamics of the course of this pathology in women.
Antibodies to CD34 are considered one of the most sensitive endothelial markers of angiogenesis. They recognize a large number of micro-vessels and stain both the resting and the activated proliferating endothelium [5, 9].
This study revealed a correlation between the content of CD34-expressing endothelial cells and the progression of PVV severity, with a more pronounced expression of CD34 observed in the small veins, which indicates a high angiogenic activity of endothelial cells and their participation in the formation of new vessels. It is known that normally the processes of angiogenesis occur in the body with moderate intensity [10], and their activation is associated with an increase in hyperoxic reactions [11–15].
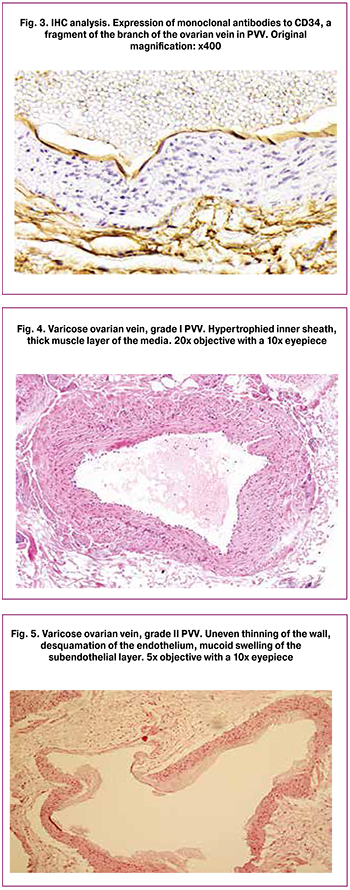
Morphological analysis of the veins showed that with the progression of PVV indurative changes in the vein walls (Fig. 4) transform into degenerative-dystrophic pathology (Fig. 5) with a decrease in muscle layer thickness and an increase in the proportion of connective tissue.
The identified morphological and IHC changes have provided confirmation of the assumption [16] that one of the leading factors in the formation of PVV is the degradation of the vein wall interstitial matrix and proliferation of endothelial cells, leading to tubulogenesis and the formation of micro-vessels, which may be considered as a compensatory mechanism providing nutrients and oxygen of damaged tissues.
Conclusion
Changes in the angiogenesis may be considered as one of the pathophysiological causes of the progression and recurrence of PVV in women. This effect is realized through the increased production of the CD34 antigen, which is mainly expressed on the endothelial cells of the newly forming vessels. Determining the level of CD34 expression in the pelvic vein walls is an informative criterion to optimize the diagnosis of the formation and progression of PVV in women.
References
- Гус А.И., Хамошина М.Б., Черепанова М.А., Бачурина С.М., Семендяев А.А., Ступин Д.А. Диагностика и лечение варикозной болезни вен малого таза у женщин. Новосибирск: Наука; 2014. [Gus A.I., Khamoshina M.B., Cherepanova M.A., Bachurina S.M., Semendyayev A.A., Stupin D.A. Diagnosis and treatment of varicose veins of the pelvis in women. Novosibirsk: Science; 2014. (in Russian)]
- Гус А.И., Семендяев А.А., Ступин Д.А.,Черепанова М.А., Бачурина С.М., Селецкий А.Н., Колесникова Л.И. Профилактика рецидива варикозной болезни вен малого таза у женщин. Акушерство и гинекология. 2016; 10: 103-8. [Gus A.I., Semendyayev A.A., Stupin D.A., Cherepanova M.A., Bachurina S.M., Seletsky A.N., Kolesnikova L.I. Prevention of recurrence of varicose veins of the pelvis in women. Obstetrics and gynecology. 2016; 10: 103-8. (in Russian)]
- Исупова Т.А., Семендяев А.А., Ступин Д.А., Бачурина С.М., Черепанова М.А. Ультразвуковой контроль в периоперационном периоде при варикозной болезни вен малого таза у женщин. Ультразвуковая и функциональная диагностика. 2015; 4(Приложение): 73a. [Isupova T.A., Semendyayev A.A., Stupin D.A., Bachurina S.M., Cherepanova M.A. Ultrasonic control in the perioperative period in case of varicose veins of the pelvis in women. Ultrasound and functional diagnostics. 2015; 4 (Appendix): 73a. (in Russian)]
- Патент на изобретение № 2646563, Российская Федерация. Cпособ определения функционального состояния венозной системы малого таза у женщин. А.А. Семендяев, Д.А. Ступин, М.А. Черепанова, В.М. Бачурина, А.Н. Селецкий, Л.И. Колесникова. Заявлено 20.06.2016; опубл. 5.03.2018. Бюл. № 7. [Patent for invention No. 2646563, Russian Federation. Method of determining the functional state of the pelvic venous system in women. A.A. Semendyayev, D.A. Stupin, M.A. Cherepanova, V.M. Bachurina, A.N. Seletsky, L.I. Kolesnikov. Stated 20/06/2016; publ. 03/05/2018. Bul. No. 7. (in Russian)]
- Ferrara N., Kerbel R.S. Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target. Nature. 2005; 438(7070): 967-74.
- Liman T.G., Endres M. New vessels after stroke: postischemic neovascularization and regeneration. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2012; 33(5): 492-9.
- Бачурина С.М., Гус А.И., Хамошина М.Б., Семендяева М.А., Семендяев А.А., Самчук П.М. Тазовая боль, ассоциированная с бесплодием у женщин: Пути решения проблемы. Сибирский медицинский журнал (Иркутск). 2011; 105(6): 252-5. [Bachurina S.M., Gus A.I., Khamoshina M.B., Semendyayeva M.A., Semendyayev A.A., Samchuk P.M. Pelvic pain associated with infertility in women: Ways to solve the problem. Siberian Medical Journal (Irkutsk). 2011; 105 (6): 252-5. (in Russian)]
- Гус А.И., Бачурина С.М., Хамошина М.Б., Семендяева М.А., Самчук П.М., Семендяев А.А. Алгоритм обследования женщин с синдромом тазовых болей при подозрении на варикозную болезнь вен малого таза. Сибирский медицинский журнал (Иркутск). 2011; 105(6): 83-5. [Gus A.I., Bachurina S.M., Khamoshina M.B., Semendyayeva M.A., Samchuk P.M., Semendyayev A.A. Algorithm for examining women with pelvic pain syndrome when a pelvic varicose vein is suspected. Siberian Medical Journal (Irkutsk). 2011; 105 (6): 83-5. (in Russian)]
- Kolesnikova L.I., Darenskaya М.А., Grebenkina L.A., Labygina A.V., Suturina L.V., Dolgikh M.I., Shiphineeva T.I., Darzhaev Z.Yu., Tsyrenov T.B., Rinchindorzhieva M.P. Activity of lipid peroxidation in infertile women from different populations. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2012; 154(2): 203-5.
- Bennett M.R., Sinha S., Owens G.K. Vascular smooth muscul cells in atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2016; 118(4): 692-702. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306361.
- Колесникова Л.И., Колесников С.И., Даренская М.А., Гребенкина Л.А., Никитина О.А., Лазарева Л.М., Сутурина Л.В.. Данусевич И.Н., Дружинина Е.Б., Семендяев А.А. Активность процессов ПОЛ у женщин с синдромом поликистозных яичников и бесплодием. Бюллетень экспериментальной биологии и медицины. 2016; 162(9): 300-3. [Kolesnikova L.I., Kolesnikov S.I., Darenskaya M.A., Grebenkina L.A., Nikitina O.A., Lazareva L.M., Suturina L.V., Danusevich I.N., Druzhinina EB, Semendyayev A.A. Activity of POL processes in women with polycystic ovary syndrome and infertility. Bulletin of experimental biology and medicine. 2016; 162 (9): 300-3. (in Russian)]
- Колесникова Л.И., Долгих В.В., Поляков В.М., Рычкова Л.В., Мадаева И.М., Погодина А.В., Протопопова О.Н. Психофизиологические взаимоотношения при артериальной гипертензии в онтогенезе. Бюллетень Сибирского отделения Российской академии медицинских наук. 2009; 29(5): 79-85. [Kolesnikova L.I., Dolgikh V.V., Polyakov V.M., Rychkova L.V., Madaeva I.M., Pogodina A.V., Protopopova O.N. Psychophysiological relationships in arterial hypertension during ontogenesis. Bulletin of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences. 2009; 29 (5): 79-85. (in Russian)]
- Колесникова Л.И., Даренская М.А., Гребенкина Л.А., Сутурина Л.В., Лабыгина А.В., Семенова Н.В., Цыренов Т.Б., Даржаев З.Ю., Курашова Н.А., Толпыгина О.А. Особенности состояния антиоксидантной системы у здоровых лиц основных этнических групп Прибайкалья. Вопросы питания. 2012; 81(3): 46-51. [Kolesnikova L.I., Darenskaya M.A., Grebenkina L.A., Suturina L.V., Labygina A.V., Semenova N.V., Tsyrenov TB, Darzhayev Z.Yu., Kurashova N.A., Tolpygina O.A. Features of the state of the antioxidant system in healthy individuals of the main ethnic groups of the Baikal region. Nutrition issues. 2012; 81 (3): 46-51. (in Russian)]
- Kolesnicova L.I., Kolesnicov S.I., Darenscaya M.A., Grebencina L.A., Nikitina O.A., Lazareva L.M., Suturina L.V., Danusevich I.N., Druzhinina E.B., Semendyaev A.A. Activity of LPO processes in women with polycystic ovarian syndrome and infertility. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017; 162(3): 320-2.
- Гус А.И., Семендяев А.А., Ступин Д.А., Бачурина С.М., Черепанова М.А. Значение перекисного окисления липидов в развитии варикозной болезни вен малого таза у женщин. Сибирский медицинский журнал (Иркутск). 2015; 133(2): 122-5. [Gus A.I., Semendyayev A.A., Stupin D.A., Bachurina S.M., Cherepanova M.A. The value of lipid peroxidation in the development of pelvic varicose veins in women. Siberian Medical Journal (Irkutsk). 2015; 133 (2): 122-5. (in Russian)]
- Савельев В.С., Кириенко А.И., ред. Сосудистая хирургия. Национальное руководство. М.: ГЭОТАР-Медиа; 2014: 405-28. [Saveliev V.S., Kirienko A.I., ed. Vascular surgery. National leadership. M.: GEOTAR-Media; 2014: 405-28. (in Russian)]
Received 28.05.2018
Accepted 22.06.2018
About the Authors
Kolesnikova, Lubov I., MD, academician of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Professor, Scientific Director Federal State Budget Scientific Institution «Scientific Centerfor Problems of Family Health and Human Reproduction».
664003, Russia, Irkutsk, Timiryazev str. 16. Tel: +73952207367. E-mail: iphr@sbamsr.irk.ru. eLibrary SPIN code: 1584-0281 ORCID ID - 0000-0003-3354-2992
Gus, Alexander I., MD, head of Ultrasound Department, National Medical Research Center for Obstetrics, Gynecology and Perinatology named after Academician
V.I. Kulakov, Ministry of Health of Russia. 117997, Russia, Moscow, Ac. Oparina str. 4. Tel.: +74954381177. E-mail: a_gus@oparina4.ru eLibrary SPIN code: 1464-2786
Taranenko, Andrei V., pathologist of the highest qualification category of the pathoanatomical department of the Regional Oncology Center of the Ministry of Health care
of Russia. 664035, Russia, Irkutsk, Frunze str. 32. Tel.: +73952261485. Е-mail: stupindima@rambler.ru
Semendyayev, Andrei A., MD, professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology with a course of gynecology of children and adolescents, Irkutsk State Medical University, Federal State Educational Institution of Higher Education. 664003, Russia, Irkutsk, Krasnogo Vosstaniya str. 3. Tel.: +73952207367. Mobile: + 79148950592. E-mail: stupindima@rambler.ru. eLibrary SPIN code: 3598-8817 ORCID ID - 0000-0002-4107-6285
Stupin, Dmitriy A., graduate student, Federal State Budgetary Institution Scientific Center for Family Health and Human Reproduction, Assistant of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology with a gynecology course for children and adolescents, Irkutsk State Medical University, Federal State Educational Institution of Higher Education. 664003, Russia, Irkutsk, Timiryazev str. 16. Tel.: +73952243825. Mobile: +79021782430.
E-mail: stupindima@rambler.ru. eLibrary SPIN-code: 6459-1703 ORCID ID - 0000-0002-0687-4804
Shcherbatykh, Andrey V., MD, professor, head of the Department of Faculty Surgery, Irkutsk State Medical University, Federal State Educational Institution of Higher Education. 664003, Russia, Irkutsk, Krasnogo Vosstaniya str. 1. Tel.: +73952207367.
Е-mail: stupindima@rambler.ru eLibrary SPIN-code: 5056-2573 ORCID ID - 0000-0003-1990-1207
Kalyagin, Aleksey N., MD, professor, head of the Department of Propaedeutics of Internal Diseases, Irkutsk State Medical University, Federal State Educational Institution
of Higher Education. 664003, Russia, Irkutsk, Krasnogo Vosstaniya str. 1. Tel.: +73952207367.
Е-mail: akalagin@yandex.ru eLibrary SPIN-code: 6737-0285 ORCID ID – 0000-0002-2708-3972
Kolesnikov, Sergey I., MD, academician of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Deputy Chief Scientific Secretary of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Employee
of the Federal State Budgetary Institution «Scientific Center for Problems of Family Health and Human Reproduction»,
Professor of Moscow State University M.V. Lomonosov.
664003, Russia, Irkutsk, Timiryazev str. 16. Tel.: +73952207367. E-mail: iphr@sbamsr.irk.ru. eLibrary SPIN code: 1752-6695 ORCID ID - 0000-0003-2124-6328
For citations: Kolesnikova L.I., Gus A.I., Taranenko A.V., Semendyaev A.A., Stupin D.A., Shcherbatykh A.V., Kalyagin A.N., Kolesnikov S.I. Informativity of CD34 expression in development varicose veins of small pelvis in women.
Akusherstvo i Ginekologiya/Obstetrics and Gynecology. 2019; (2): 120-5. (in Russian)
http://dx.doi.org/10.18565/aig.2019.2.120-125



