Туберозный склероз (ТС), или болезнь Бурневилля, – полисистемное, генетически детерминированное заболевание, при котором доброкачественные опухоли (гамартомы) выявляются в различных органах, включая головной мозг, глаза, кожу, сердце, почки и печень. Данное заболевание впервые описано von Recklinghausen в 1862 г. [1]. Частота ТС в популяции составляет 1:10 000, у новорожденных – 1:6000 [2, 3]. Болезнь наследуется по аутосомно-доминантному типу. Примерно две трети случаев вызваны новыми мутациями в генах TSC1 и TSC2, в остальных случаях болезнь связана с отягощенной наследственностью. Неврологические проявления заболевания включают в себя эпилепсию, аутизм, когнитивные и поведенческие дисфункции.
Так как ТС является врожденным заболеванием, именно антенатальная ультразвуковая диагностика является первичным звеном, определяющим дальнейшую тактику ведения пациентки с подозрением на данное заболевание у плода. В неврологической практике широко используемые первичные (большие: гипопигментированные пятна, ангиофибромы или бляшки на голове, ногтевые фибромы и проч.) и вторичные (малые: пятна типа конфетти на коже, дефекты эмали зубов, фибромы полости рта и проч.) клинические критерии для постановки диагноза ТС (Международная Согласительная (Консенсусная) конференция, 2012) не могут быть в полной мере применимы для исключения данного заболевания антенатально. Ввиду специфичности признаков и поздней их манифестации ТС может быть заподозрен в случае обнаружения у плода опухоли сердца – рабдомиомы, визуализация которой при ультразвуковом исследовании в большинстве случаев возможна после 24 недель беременности [4]. Рабдомиомы, располагаясь в различных полостях сердца, могут быть как единичными (10% случаев), так и множественными (90% случаев) [4]. По данным литературных источников, при наличии единичной рабдомиомы ТС выявляется в 50% случаев, в то время как выявление множественных рабдомиом увеличивает риск заболевания практически до 100% [5–7].
В большинстве случаев изолированная рабдомиома, подвергаясь спонтанному регрессу после рождения, сама по себе имеет благоприятный исход [6, 7]. В связи с этим ключевым прогностическим критерием при обнаружении опухоли сердца может служить выявление признаков вовлечения в патологический процесс других органов плода, а обнаружение специфических очагов в головном мозге может определять тяжесть неврологического статуса после рождения.
Поражение головного мозга при ТС характеризуется аномальной пролиферацией нейронов и глии с последующим формированием в паренхиме туберов, субэпендимальных узлов, гигантоклеточной астроцитомы в сочетании с нарушением процессов миграции и дифференциации. Имеются данные, свидетельствующие о том, что количество кортикальных туберов, их размер и объем связаны с тяжестью церебральной дисфункции [8–11]. Более того, с возрастом у пациентов на фоне регресса рабдомиом может отмечаться прогрессирование количества и размеров туберов. Большинство работ посвящено диагностике поражения головного мозга при ТС с помощью магнитно-резонансной томографии (МРТ) в антенатальном и постнатальном периодах. В то же время возможности нейросонографии (НСГ) плода для идентификации очагов ТС представлены в единичных зарубежных публикациях [12].
Таким образом, в связи с вышесказанным целью нашего исследования явилось совершенствование эффективности антенатальной эхографической и молекулярно-генетической диагностики ТС.
Материалы и методы
Проанализированы 13 случаев рабдомиом сердца в сроки первичного их выявления (от 20 до 36 недель) у беременных, проходивших перинатальный консилиум в ФГБУ «НМИЦ АГиП им. В.И. Кулакова» в период с октября 2017 по март 2020 гг. Гестационный срок устанавливался по данным копчико-теменного размера во время ультразвукового скрининга I триместра беременности. Всем плодам проводились расширенная двухмерная эхокардиография, детальная оценка анатомии центральной нервной системы – НСГ плода (рекомендации ISUOG, 2007) и допплерометрия с интервалом 4 недели. Ультразвуковое исследование (УЗИ) проводилось с помощью двухмерного конвексного датчика 3,5 МГц на аппаратах Voluson E8 и Samsung Medison WS80.
Оценивались: гестационный возраст при первом обнаружении опухоли сердца, их количество, локализация, размер и любые дополнительные пороки развития сердца. При обнаружении патологических очагов в паренхиме мозга оценивались их количество, размеры и расположение. Клинические данные о состоянии рожденных детей были получены в 9 случаях с помощью медицинских карт и/или телефонного опроса родителей и/или врачей.
Результаты
Из 13 исследуемых плодов (12 – от одноплодной, 1 – от многоплодной беременности) у 3 определялись единичные рабдомиомы, у 10 – множественные, в количестве от 2 до 5 очагов (табл. 1). В большинстве случаев (9/69%) первичная эхографическая визуализация опухоли приходилась на период III триместра (у 1 – в 28 недель, у 2 — в 30–32 недели, у 4 – в 33–34 недели, у 2 – в 36 недель). У 4 из 13 (31%) плодов рабдомиомы диагностировались до 23 недель. В нашем исследовании наиболее раннее выявление рабдомиомы было осуществлено в 20 недель беременности у одного из плодов при дихориальной диамниотической двойне. При этом второй плод не имел эхографических признаков анатомических нарушений. Анализ размеров рабдомиом показал, что их диаметр варьировал от 3 мм до 29 мм. Опухоли располагались как в левом, так и в правом желудочках в одинаковом проценте случаев (50% и 50% соответственно). У 4 плодов с ранним выявлением рабдомиом отмечалось увеличение размеров опухолей до срока беременности 32–33 недель. В дальнейшем изменения их размеров не имели статистически значимых различий и оставались практически одинаковыми вплоть до родоразрешения.
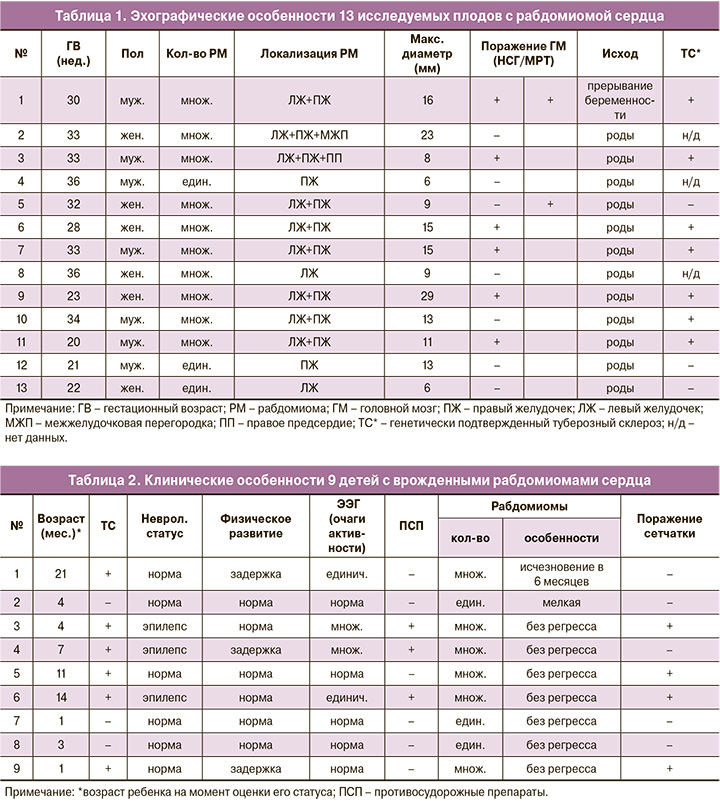
При проведении НСГ у плодов с множественными рабдомиомами в половине случаев (5/10) визуализировались многочисленные туберы (до 20 в одном эхо-срезе) в субкортикальных отделах паренхимы, которые на эхограммах были представлены очагами несколько повышенной эхогенности различной формы (округлой, неправильной, повторяющей контур борозды), расположенными в обоих полушариях мозга преимущественно в лобных и теменных долях с участками слияния в конгломераты. В переделах доступной визуализации максимальный их диаметр достигал 10 мм. Туберы впервые диагностировались у 4 плодов в сроки 30–32 недели и у 1 плода – в 35 недель (рисунок). Двум плодам была антенатально проведена МРТ, при которой, помимо подкорковых туберов, были выявлены субэпендимальные очаги поражения. У плодов с единичными рабдомиомами при НСГ патологических образований в структурах головного мозга обнаружено не было. В рамках перинатального консилиума Центра всем беременным с выявленными у плодов множественными рабдомиомами и признаками поражения головного мозга проводились консультация генетика и в последующем – молекулярно-генетическое исследование на выявление мутаций в генах TSC1 и TSC2, ассоциированных с ТС.

В одном случае с множественными рабдомиомами сердца и туберами в головном мозге было проведено прерывание беременности в сроке 30 недель с последующим гистологическим и молекулярно-генетическим подтверждением ТС (гетерозиготная мутация de novo в 34 экзоне гена TSC2 (chr16:2134638G>GC). У остальных пациенток роды произошли в доношенном сроке через естественные родовые пути: у 9 – в ФГБУ «НМИЦ АГиП им. В.И. Кулакова», у 3 – по месту жительства. Катамнестические данные были собраны в 9 из 12 случаев (табл. 2). Всем детям в первые сутки жизни были проведены эхокардиография (Эхо-КГ) и НСГ. При Эхо-КГ у всех 9 новорожденных подтвердился диагноз «рабдомиома сердца» без гемодинамических нарушений: у 3 – с единичной, у 6 детей – с множественными опухолями. При НСГ у всех новорожденных (6 (100%)) с множественными рабдомиомами сердца были выявлены субкортикальные туберы и у 5/6 (83,3%) – субэпендимальные узлы. МРТ, проведенная 4 новорожденным (66,6%) с множественными рабдомиомами сердца, подтвердила результаты антенатальной и постнатальной НСГ.
У всех детей с единичной рабдомиомой при динамической НСГ и МРТ отсутствовали признаки поражения головного мозга, а показатели электроэнцефалографии (ЭЭГ), молекулярно-генетического исследования, неврологического и физического развития были в пределах нормативных значений. В то же время у детей, имеющих множественные рабдомиомы и туберы в головном мозге, генетический анализ методом таргетного высокопроизводительного параллельного секвенирования (ВПС) подтвердил наличие ТС в 100% случаев. Генетическое обследование родителей проводилось лишь у 4 (50%) детей с ТС; при этом мутации в исследуемых генах выявлены не были, что позволило отнести данные случаи к возникшим de novo.
При исследовании неврологического статуса детей с ТС выявлены характерные особенности, включающие в 60,6% случаев (4 ребенка) очаги повышенной эпилептической активности на ЭЭГ. При этом у троих из их числа отмечались приступы эпилепсии. После назначения последним противосудорожной терапии у двоих отмечена резистентность к проводимому лечению, а у одного – положительный эффект с уменьшением количества приступов.
У 3 детей с множественными кардиальными опухолями были выявлены туберы и кровоизлияния сетчатки обоих глаз, которые сочетались у одного из них с характерными кожными высыпаниями. Также в одном случае определялись кисты почки. У одного ребенка с множественными рабдомиомами сердца при рождении отмечалось полное их исчезновение к 6 месяцам жизни, однако в 1 год на МРТ головного мозга была выявлена астроцитома малых размеров; ЭЭГ зарегистрировала единичный очаг эпилептической активности без клинических проявлений.
Обсуждение
Наиболее часто антенатально выявляемым пораженным органом при ТС (более 50%) является сердце. Именно обнаружение при ультразвуковом сканировании рабдомиомы у плода заставляет специалиста начать поиск других эхографических маркеров данного заболевания. Результаты многочисленных исследований последних десятилетий привели специалистов к мнению, что любой случай антенатального диагностирования рабдомиом должен рассматриваться в контексте подозрения на ТС и может потребовать проведения генетического анализа как плода, так и родителей для выбора дальнейшей тактики ведения беременности и консультирования [13–15].
Рабдомиома преимущественно исходит из желудочков, чаще левого, и межжелудочковой перегородки. Эхографически опухоль проявляется, как образование однородной структуры и повышенной эхогенности; при малых размерах может выглядеть, как локальное утолщение стенки. Более мелкие по размерам опухоли, как правило, множественные и, по данным различных авторов, имеют значимую положительную корреляцию с наличием у плода ТС [4]. Осложнениями рабдомиомы являются аритмии, обструкция выходных отделов, гидроперикард, гидроторакс, неиммунная водянка. Дифференциальный диагноз рабдомиомы следует проводить с гиперэхогенным фокусом, миксомой, тератомой, фибромой, гемангиомой. В мировой литературе встречается описание самой ранней диагностики рабдомиомы в 15 недель беременности, однако в большинстве случаев данные опухоли визуализируются после 24 недель, что согласуется с данными нашего исследования [12]. Кроме того, мы выявили статистически значимую положительную корреляцию (p<0,05) между множественными рабдомиомами и генетически подтвержденным ТС. Полученные нами показатели подтверждают мнение других авторов о высоком риске ТС у плодов с множественными рабдомиомами сердца по сравнению с единичными [3–6, 12–16].
С развитием фетальной нейровизуализации количество пренатально диагностированных случаев ТС неуклонно растет [16–19]. Выявляемые субкортикальные туберы, субэпендимальные узлы бывают единичными и множественными, иногда имеющими сливной характер. Размеры их варьируют от нескольких миллиметров до нескольких сантиметров. При этом необходимо отметить, что ряд авторов считают невозможным определить признаки поражения головного мозга с помощью УЗИ у плода с ТС [20]. Однако в ходе нашего исследования были выявлены множественные субкортикальные туберы у 50% плодов с множественными рабдомиомами. Антенатально не были выявлены субэпендимальные очаги ТС; при этом после родов при НСГ и МРТ практически у всех новорожденных данной группы (83,3%) визуализировались субэпендимальные поражения, сопровождающиеся неровностью контура боковых желудочков. По нашему мнению, это связано с техническими сложностями визуализации паренхимы мозга плода после 30 недель из-за выраженной ее сулькации и оссификации черепа. Возникновение эффекта размытости контура борозд и извилин, ограниченная визуализация контуров боковых желудочков затрудняет возможность четко дифференцировать границы туберов от линии борозды. В связи с вышесказанным, основываясь на опыте зарубежных авторов (Pugash et al., 2012), можно полагать, что выявление нарушения ламинации паренхимы головного мозга еще до начала процесса выраженной сулькации позволит заподозрить нарушение миграции нейронов, характерное для ТС [21].
Наличие даже одного из специфических признаков ТС у плода, выявленного любым методом визуальной диагностики, требует генетического консультирования семьи для решения вопроса о проведении инвазивной процедуры на определение мутаций в генах TSC1 и TSC2. Данные гены участвуют в размерах тела клетки, дендритном распределении, разрастании аксонов, миграции нейронов и слоистости коры головного мозга. Известно, что кодируемые в генах TSC1 и TSC2 белки гамартин и туберин модулируют клеточную функцию посредством ингибирования сигнального каскада mTOR [1, 2, 13, 22, 23]. Непосредственно сам белок mTOR является консервативной протеинкиназой серин-треониновой специфичности, которая контролирует рост клетки, метаболизм, клеточную выживаемость. Внедрение новых технологий, таких как таргетное ВПС, мультиплексная амплификация лигированных зондов (MLPA), а также секвенирование ДНК по Сенгеру позволили диагностировать болезнь на антенатальном уровне в 75–90% случаев. По данным нашего исследования, использование именно ВПС у всех обследуемых нами детей с множественными рабдомиомами сердца и туберами в головном мозге позволило с достоверно высокой точностью подтвердить у них ТС (p<0,05).
В ходе нашего исследования у рожденных детей с генетически подтвержденным ТС были выявлены дополнительные клинические признаки ТС: туберы и кровоизлияния сетчатки у 3/6 детей (50%), кожная сыпь у 1/6 (16,6%), кисты почек у 1/6 (16,6%). Однако данные признаки относятся к постнатальной диагностике, что подтвердилось и в проводимом нами исследовании [7, 24].
У половины находившихся под нашим наблюдением детей с ТС (3/6) диагностирована эпилепсия, в связи с чем назначена противосудорожная терапия. Учитывая проведенный нами краткосрочный катамнестический анализ (возраст детей от 1 до 21 месяца), нельзя исключить усугубление эпилепсии и дальнейшее развитие других признаков ТС, в частности, ментальных и когнитивных нарушений, для которых характерна более поздняя манифестация.
Заключение
Выявленная в нашем исследовании взаимосвязь наличия туберов в головном мозге по данным УЗИ у плодов с множественными рабдомиомами сердца показала статистически значимую ассоциацию с постнатальным генетическим подтверждением ТС в 100% случаев. Безусловно, для получения достоверно значимых результатов необходимо исследование с участием большего количества пациентов. Однако полученные нами результаты и приведенные литературные данные за последние 10 лет позволили сформулировать тактику ведения беременности при ТС и определить направление поиска ранних пренатальных маркеров ТС.
По нашему мнению, всем плодам с рабдомиомой сердца показаны НСГ и с 22 недель беременности – МРТ для выявления церебральных поражений с последующей консультацией генетика. Инвазивная пренатальная диагностика необходима как в случае обнаружения специфических маркеров ТС у плода, так и в случае подтвержденного диагноза ТС у будущих родителей или старших детей в семье. При пролонгировании беременности дальнейшее УЗИ целесообразно проводить с интервалом 4 недели для динамического наблюдения за ростом рабдомиом и обнаружения гемодинамических нарушений. Родоразрешение следует проводить в учреждениях с наличием отделения реанимации новорожденных.



